
Project Gutenberg's Life and Adventure in the South Pacific, by John D. Jones This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook. Title: Life and Adventure in the South Pacific Author: John D. Jones Release Date: June 6, 2019 [EBook #59684] Language: English Character set encoding: UTF-8 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK LIFE, ADVENTURE IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC *** Produced by Chris Whitehead, Robert Tonsing and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images generously made available by The Internet Archive)


The present volume lays no claim to literary merit. Two young men, led to engage in the whale-fisheries, and spending five years in the employment, have compiled from their log-books and their recollection a plain, unvarnished narrative of this period. The work is placed before the public as an account of localities few have visited, and the detail of an employment of which little is generally known. The chief effort in the way of style has been to give vivid descriptions, and make the reader the companion of the traveler. Aside from the information of the volume, it is enlivened by “life on shipboard.”
In these days of many books, in which “voyages” have no small representation, it may seem almost presumptuous to put forth another tale of travel. Yet every traveler has his own experiences; and the sailors who offer here their narrative for the landsman’s inspection believe that their yarn is not an old one, and they have some confidence that the reader will not say it is a dull one.
| New Bedford.—Fitting out a Whaler.—Shipping A Crew.—Green Hands.—Shippers.—Outfitters.—A Sailor’s Wardrobe.—All Hands on board.—Good-by to Yankee Land.—The Pilot taking leave.—The last Farewell.—Captain’s Speech.—Choosing Watches.—The Modus Operandi of Ships’ Watches.—Sea-sickness. | Page 13 |
| Sick of the Sea.—Description of the Boats and Whaling Apparatus.—Boat-headers.—Boat-steerers.—Mastheads.—The first Whale.—“There she blows!”—All hands excited.—Lowering the Boats.—“Pull, every man of you.”—A Fisherman’s Luck.—Whales again.—Cape Verd Islands.—St. Antonio.—St. Jago.—Fogo, the Island of Fire.—Going ashore.—A noisy Crowd.—Tom and the Portugee Donkey.—Manuel.—Now for Cape Horn. | 25 |
| Our Captain.—Officers.—Boat-steerers.—Foremast Hands.—Jo Bob.—Sailor’s Fare.—The Cask of Pies.—Mackey.—Lawrence asleep. | 35 |
| Crossing the Equator.—Barney looking for the “Line.”—Spoke Ship “Java.”—Spoke Ship “Ontario,” homeward bound.—Writing Letters Home “under Difficulties.”—Sperm Whales again.—A Fast Boat.—The Red Flag.—The Flurry.—The Fluke-chain passed. | 41 |
| Description of the Sperm Whale.—Described externally.—Difference between the Sperm and Right Whale. | 49 |
| “Cutting in”. | 59 |
| “Trying out.”—“Stowing down.”—“Cleaning up.”—Gale off the River De la Plata.—Thunder and Lightning.—Narrow Escape of the Ship. | 62 |
| vi | |
| Preparing for Cape Horn.—Head Winds.—Staten Land.—Cape Horn.—Heavy Gale.—Porpoises and Albatross.—Mackey and the Third Mate.—Captured a Sperm Whale.—Preparing for Port.—The Anchor down. | 67 |
| Talcahuana.—Its Streets.—Public Buildings.—Market.—Calaboose.—The Harbor.—Churches.—Paulparees.—Inhabitants.—Manners and Customs.—Getting off Water.—Mackey again in Trouble.—In the Calaboose.—Californians.—Climate and Products of Chili.—Horseback Riding.—Spanish Wake.—Desertion.—American Consul.—Mackey’s Oration.—Swimming ashore.—Departure. | 71 |
| Cruising.—Boat’s-crew Watches.—Deserters by wholesale.—A large Reward.—Public Auction.—Juan Fernandez.—Peaches.—Robinson Crusoe’s Cave.—Fishing.—Ship “Java.”—Masa Fuero.—St. Felix.—St. Ambrose.—San Lorenzo.—Callao.—A Railroad. | 78 |
| Payta.—Its Appearance.—Inhabitants.—Shipped three Spaniards.—Gamming.—Exchanged Boat-steerers.—Gloomy Forebodings.—Whales again.—Stove Boat.—Manuel overboard.—No Sunday off Soundings.—Mackey and the Mate.—Star-gazing.—Reflections.—A County Fair.—Lawrence in Trouble. | 86 |
| Marquesas Islands.—Dominica.—Its Appearance.—Visitors.—Tattooing.—The Chief.—His costly Dress.—Delivers his Papers.—A “Recommend.”—Society Islands.—Roratongo.—Its Appearance.—New York.—New Bedford.—Too many Friends.—The universal Remedy.—Fruit.—A thieving Set.—Missionaries.—Petty Tyrannies practiced.—Rev. John Williams.—His Death.—The staple Commodity.—The Desire for Sea.—Queen and Government.—Desertion.—General Losses.—Jo Bob’s Choice.—A merry Time. | 92 |
| Making Passage to King Mill Group.—Fourth of July.—Byron’s Island.—Perote Island.—Drummond’s Island.—Sydenham’s Island.—Visit from the Natives.—Their Canoes.—Themselves.—Trade.—“Dittoes.”—Taking of the “Triton.”—A treacherous Portuguese.—A bloody Massacre.—A just Retribution.—The Kanaka’s Stratagem.—The Natives frightened.—Prisoners ashore.—A young Hero.—Hostages.vii—The Prisoners released.—Proceed to the Sandwich Islands.—Henderville’s Island.—Woodle’s Island.—Natives again.—“Teka moi moi.”—Young Cocoanuts.—Decidedly Jewish.—Easily satisfied.—Description of Natives.—The Females.—A large Fleet.—Comparisons.—Simpson’s Island.—Ship “Narragansett.”—Stove Boat.—Fisherman’s Luck.—Experiments in Mesmerism.—Somebody “sold.” | 99 |
| Pitt’s Island.—Knox and Charlotte’s Islands.—Base Conduct.—Thieving.—Jack and Manuel.—Almost a “dead Nigger.”—Bark “Belle.”—Ship “Boy.”—Wreck of the “Flying Fox.”—Plundered by the Natives.—Hall’s Island.—Desertion.—My Man Friday.—A wet Berth again.—Ship “Hector.”—Anxiety for Letters.—A Canoe in distress.—A heart-rending Sight.—Gratitude of the Natives.—Pleasant Island.—Its Natives.—Murder of white Men.—Brig “Inga.”—Thieves again.—Search-warrant issued.—Property found, Culprit tried and punished.—A heavy Squall.—Strong’s Island. | 110 |
| Strong’s Island.—King.—Canker.—Dress.—Chiefs.—Description of the Island.—Large Island.—Small Island.—Productions.—Wild Game.—Canals.—Stone Walls.—Who built them?—Ruins.—Suppositions.—A Rebellion.—Customs.—Queen.—Princes and Princesses.—Sekane.—Cæsar.—Natives.—Females.—“Strong’s Island Trowsers.”—Employments.—Houses.—Marriages.—Sports.—Canoes.—Carva.—Banyan-tree.—Religion.—“Blueskin.”—Traditions.—Priests.—Rites and Ceremonies.—Funeral Ceremonies.—Rotumah Tom.—Food of the Natives.—Blueskin and his Procession.—Friday’s Opinion.—The Feast.—“Very good,” but think we won’t indulge.—Choose our “Hotel.”—An unpleasant Surprise.—“Planter.”—Mutiny and its Consequences.—Desertion.—One kind of Navigation.—A Stroll to Large Island.—Friday and the Taboo.—Incidents in Port.—Weighed Anchor.—“Mary Frazier.”—Death and Burial of Mr. S.—A few random Thoughts. | 120 |
| “A happy New-year to all.”—Rather poor Luck.—Pitt’s Island again.—Description.—Natives.—King.—Religious Belief.—Funeral Ceremonies.—“Jentsh.”—Houses.—Costume.—Food.—Language.—Weapons of War.—Mode of Warfare.—Return to Strong’s Island.—Improvements.—Singing-school.—The Royal Family to Dinner.—Canker’s Guilt.—Poisoned Carva.—Return to our “Hotel.”—Our Suspicions strengthened.—“Stop Thief!”—Gas.—New Zealand Dance.—Grand Feast.—Tall Dancing.—“Cheers” by the Audience.viii—“Go it, Cæsar!”—Grand Boat-race.—The Boasters beaten.—Another great Feast.—Ball-Alley.—Narrow Escape of the Ship.—Departure for Guam. | 144 |
| Guam.—Invasion of the Ladrone Islands by the Spaniards in 1554.—Getting off Recruits.—Fruit.—Climate.—Captain Anderson.—Massacre of Captain Luce and Boat’s Crew.—Proceed to Japan Cruising-ground.—Ship “Boy.”—Boat’s Crew taken down by a Whale.—Albicore and Skipjack.—“Our Luck” again.—The Spell broken.—Bark “Medina.”—Manuel and the Hog.—A slight Tap. | 154 |
| Food of the Sperm Whale.—Manner of Feeding.—Swimming.—Breathing.—Herding. | 161 |
| Nature of Sperm Whales’ Food.—“Sepia Octopus.”—Nautilus. | 178 |
| Close of the first “Season” on Japan.—Making Passage to the Group.—“Land ho!”—“Breathing-places for Sailors.”—Henderville’s Island.—Unpleasant Prospect.—Narrow Escape from the Breakers.—A large Whale.—An ugly Customer.—Ocean Island Dick.—Ocean Island.—“Some Pumpkins.”—Bound for Strong’s Island.—Calms.—“Blow, ye gentle Breezes.”—At our “Hotel” once more.—Hospitality of the Natives.—A diabolical Scheme.—Anger of the King.—Narrow Escape of all Hands from Poisoning.—Wilds and the Queen.—A sudden Awakening.—Wild Boar.—Join in the Chase.—Brave Men.—The Boar presented in great State to the King.—Bravery of the “White Man.”—“Hog not Dog.”—At sea again. | 187 |
| Blackfish.—Ship “Phocion.”—Ship “Ganges.”—Bark “Belle.”—“Chips” in Prison.—Friday’s Departure.—Sorrowful Leave-taking.—Ship “Bengal.”—Ship “Lion.”—Henderville’s Island once more.—Dick Simpson.—Ship “John and Elizabeth.”—Another New Year.—“Music by the Band.”—Variations.—An “Amateur” Concert.—Bark “Alfred Tyler.”—Wreck of the “Ontario.”—Ocean Island again.—Freshwater Cavern.—Superstitions.—Beachcombers.—Rascally Operations.—Convicts.—Taboo.—Natives.—Climate.—Houses.—Religious Belief.—Sharp Practice.—Characteristics.—Whaling.—Pleasant Island.—Disturbance with the Natives.—Ship “Mohawk.”—Pitcairn’s Island.—Mutiny of the “Bounty’s” Crew.—Death of Mrs. P.—“To my Husband.”—Massacre at Covill’s Island.—Whaling again.—A few stray Thoughts upon that subject.—Heavyix Gale.—A “Gemman ob Color.”—His splendid Dress.—Passage to Guam. | 198 |
| Island of Rota.—Appearance.—Streets and Houses.—Inhabitants.—Governor.—Guam.—Umata Bay.—Procuring Water.—Marisa.—Its Appearance.—Port of Apia.—Fort.—Liberty.—A splendid Ride.—Boarding-houses.—Police.—Reflections.—Inhabitants.—Choppers.—A cowardly Murder.—Bombardment of the Palace.—Attend Mass.—Toddy.—Streets.—Houses.—Palace.—Calaboose.—Cock-fighting.—Seminary.—Insurrection of Prisoners.—Females.—Take a Stroll.—Ruins.—Reservoir.—Tobacco.—Betel Nut.—Captain Anderson.—Rebellion.—Jollification.—A novel Mode of choosing a Governor.—Congratulations.—Parade.—Aguadente.—Caroline Islanders.—Last Day on Shore.—Arguing the Point.—Disarming the Guard.—“Where is my Musket?”—Visit to the Fort.—Strange Doings.—Ready for Sea. | 222 |
| Bailey’s Island.—Turtle.—Whaling.—Ship “James Allen.”—Water-spouts.—A heavy Gale.—Monotony.—A Swimming Adventure.—Ship “Atkins Adams.”—Spanish Jack again.—Tow-line Tea.—Captain’s stump Speech.—A large Whale.—Bark “Antelope.”—Strange Incident.—Passage to the Group.—Pitt’s Island.—Bark “Smyrna.”—A rummy Set.—Ship “Susan.”—Fearful Tragedy.—Passage to Strong’s Island.—Ship “Atlantic.”—Ship “Charles W. Morgan.”—“At home” once more.—Rev. Mr. Snow.—Characteristic Meanness.—Rotumah Dance.—Feast and Dance.—Sickness of Mr. L.—Divine Service on Board.—New Zealand Native.—Farewell to Strong’s Island. | 240 |
| Success of the “Mohawk.”—Ship “Napoleon.”—Whaling.—Bound to the southward.—Sickness and Death of Mr. L.—Ship “Roscoe.”—Pleasant Island.—Massacre of the “Inga’s” Crew.—Narrow Escape.—Ship “Hannibal.”—Christmas and New-Year.—Ship “William Tell.”—Ship “John Wells.”—Violent Death of Captain Hussey.—Bound for Hong Kong.—H. B. M.’s Brig “Serpent.”—Island of Rota.—Wild Boar.—A general Stampede.—“All Hands and the Cook.”—Man the Victor.—Heavy Gales.—Gad’s Rock.—Formosa.—Bashee Islands. | 255 |
| Chinese Fishermen.—Pedro Blanca.—Preparing for Port.—Chinese Pilots.—Beating up the Passage.—Hong Kong.—“Hail Columbia.”—The “Susquehanna.”—Stars and Stripes.—Chinese Merchants.—Washerwomen.—Bumboats.—Dick Simpson and John Chinaman.x—Chinese mode of Trading.—Sanpan.—A floating Community.—Boston Jack.—Victoria, its Situation, Streets, etc.—Chinese Barbers.—Fortune-tellers.—Policemen.—Chinese New-year.—A busy Time.—Firing a Salute.—Arrival of Governor Bonham.—English Barracks.—Churches.—Hotels.—Dog or Horse?—Visit from Men-of-war’s-men.—Tom and the Lieutenant.—Commodore Perry.—Midshipmen.—Visit to the Barracks.—Theatre.—Fort.—Make some Purchases.—Counterfeit Money.—Tricks of the Chinese Merchants.—Females.—Gambling.—Cut-throats.—Short-tailed Gentlemen.—Chinese Funeral.—Marriages.—Education.—Ouang Ouci Yuen.—Infanticide.—Twenty-second of February.—Chinese Artists.—Their Powers of Imitation.—Sam Shu.—Domestic Life of the Chinese.—Food.—Temple, or Joss House.—Worship of Idols.—Joss Sticks.—Tom as a Yankee Naval Officer.—Chinese Men-of-war.—Pirates.—Chinese Theatre.—Masonic Temple.—The Bethel.—Chinaman and his Shoes.—The Arrest, Trial, and Acquittal.—Departure for Sea. | 265 |
| Fishing Junks.—New Companions.—Stove Boat, yet good Luck.—Heavy Gales.—Bashee Islands.—Loo Choos.—The “Reaper” again.—Whaling Ship “Jireh Perry.”—Ship “Alabama.”—“Gamming.”—Ship “Roscoe.”—A Cure for “Bruisers.”—Ship “E. L. B. Jenney.”—Bark “Empress.”—Ormsby’s Peak.—Bonin Islands.—Turtles.—Peel’s Island.—A narrow Escape.—Bonin Island Inhabitants.—Japan Expedition.—An old Shipmate.—Another Runaway.—Fourth of July Celebration.—Ship “Rambler.”—Ship “Hope.”—Parting with an old Friend.—Fishing.—The last Lowering.—Bound for the Sandwich Islands.—Maui and Molokai.—Lahaina.—Anchor down.—Description of Lahaina.—King’s Palace.—Lahainaluna.—Rules and Regulations.—Sports and Pastimes.—Letters from Home.—Productions of Maui.—Captain M‘Culloch.—Sad News.—Death of Stoddard.—Voracity of the Shark.—Kanaka Church.—Small-pox. | 301 |
| Legend of Kinau and Tuanoa: a Tale of the Sandwich Islands. | 332 |
| “Homeward bound” at last.—The prevailing Feeling.—Wauhoo and Atoowi.—“Stowaways.”—Farewell to the Sandwich Islands.—Ship “Uncas.”—On the Equator.—Whytootucke.—Roratongo.—Meeting of old Friends.—Interesting Missionary Incidents.—A good Reason.—Good-by to Roratongo.—Preparing for Cape Horn.—Christmas.—A heavy Gale.—Off Cape Horn.—New Experiences.—In the Atlantic again.—Ship “Betsey Williams.”—Brazilian Coast.—North of the Line.—Hurra for Yankee Land.—Brig “Alpha.”—Try-works overboard.—Scudding off Bermuda.—Gulf Stream.—Soundings.—Old “Hard-a-lee.”—The old Adage.—“Home at last!”—Conclusion. | 344 |
| NEW BEDFORD | Frontispiece. |
| NEW BEDFORD FROM A WHALEMAN’S POINT OF VIEW | Page 15 |
| THE PILOT | 19 |
| THE MATE | 22 |
| DRUG | 26 |
| WHALING IMPLEMENTS | 27 |
| THE MASTHEADMAN | 30 |
| “GIVE IT TO HIM!” | 45 |
| TOWING A DEAD WHALE | 47 |
| SPERM WHALE | 49, 51 |
| RIGHT WHALE | 53 |
| RIGHT WHALE BONE | 55 |
| CUTTING IN | 58 |
| TRYING OUT | 63 |
| JUAN FERNANDEZ, FROM THE SEA | 80 |
| PEAK OF YONKA | 82 |
| CRUSOE’S CAVE | 83 |
| SYDENHAM ISLAND CANOE | 100 |
| STRONG’S ISLAND | 121 |
| STRONG’S ISLAND HOUSES | 128 |
| STRONG’S ISLAND CANOE | 129 |
| STOVE | 159 |
| SPOUTS OF THE SPERM AND RIGHT WHALE | 165 |
| HEAD OUT | 169 |
| BREACHING | 173 |
| A SCHOOL | 175 |
| USING HIS JAW | 208 |
| GOING DOWN ON A SCHOOL | 210 |
| TRADING AT PLEASANT ISLAND | 211 |
| A RACE FOR A WHALE | 217 |
| THE “OLD MAN” TALKS | 246 |
| ORMSBY’S PEAK | 309 |
| “THERE SHE BLOWS!” | 315 |
| CHART OF SANDWICH ISLANDS | 317 |
| LAHAINA | 320 |
| HOMEWARD BOUND | 346 |
| A LANDSHARK | 356 |
| JUST LANDED | 359 |
The city of New Bedford, Mass., has for many years been the principal whaling-port of the United States. From there hundreds of young men have annually gone to different parts of the world to battle with the monsters of the deep, and, after a long and weary absence from home and friends, returned with ships “laden with the spoils.” It is not our purpose to give a description of this far-famed (among whalemen) place, but we trust it will prove interesting to the reader if we briefly sketch the modus operandi of fitting out a whaler, and “shipping a crew,” that if any one shall be tempted to see the world in a whaler, he may be put upon his guard against some of the impositions practiced upon “green hands” by the “shippers,” as they style themselves, of whaling-ports.
In fitting out a whaler for a voyage, every thing is usually done as cheaply as possible, and often on the “penny-wise and pound-foolish” plan. With some owners, however, we are happy to say, it is different. They have a regard for the health and comfort of the 14 ship’s company, and their ships are generally well fitted, with good provisions, good whaling material, and every thing necessary to make the voyage one of pleasure and comfort to the crew as well as profit to themselves. In nine cases out of ten such ships get good crews, and make profitable voyages. But there are others who are actuated by a niggardly disposition in fitting and provisioning their ships, and the result of the voyage, as far as profit is concerned, is a corresponding one.
After a ship has her provisions, water, and every thing necessary for the voyage on board except her crew, she is “hauled into the stream,” ready for sea as soon as the ship’s company can be got on board, which generally occupies a day or two, as many of them are having their last “spree,” spending their “advance,” and often coming on board half intoxicated. Some of them, when they ship, are in that condition, and hardly know, until they are at sea, their true situation and how they came there. The majority of a whaler’s crew (foremast hands) are “greenies,” hardly any of them ever having smelt salt water, and knowing nothing of a seaman’s life, its hardships, its exposures, its joys, or its sorrows. But the poor fellows soon learn, and many of them, before they have been clear of the land a week, vainly wish themselves at home. Many of them are picked up by “shipping agents” throughout the country, who send them on to their respective shipping-houses in New Bedford. They are then furnished by the shippers with second or third rate boarding-houses, the board to be paid out of their advance. It is a common practice for the shippers to make contracts with owners to furnish them with so many “green hands” at so much per head; the shipper receiving his price from the owner, and then, in addition, charging poor “greeny” ten dollars for “getting him a ship.”

He is then, after being shipped in a vessel of whose captain, officers, destination, etc., he is entirely ignorant, consigned to the tender mercies of the “outfitter,” who is to furnish his wardrobe for a five years’ voyage. The poor fellow is here sadly taken in. The outfitter will spin him a nice yarn, and promise him a splendid outfit, “enough to last him the whole voyage,” which he manages to postpone giving him until the ship is just ready to sail, when he will “fit him out” with a wooden box, made of pine boards, which he calls a chest, size about seven by nine, with perhaps a broken lock, and “stowed” with his five years’ clothing. As a general thing, this clothing is made in such a manner and of such material that it gives out before the ship gets into the Pacific, and the “slop-chest” is resorted to for a new supply. It is a common remark among whalemen who have been “bit,” that the cloth is “made of bull’s wool and dog’s hair, woven together by thunder and lightning.” The “five years’ supply” generally consists of two red or blue woolen shirts, two under-shirts, two pairs of drawers, one pair of woolen pants, one round-jacket, one monkey-jacket, two pairs of thin pants, two “hickory” shirts, a sou’wester or tarpaulin, two pairs of stockings, one pair of shoes, a jack-knife, comb, looking-glass, paper of needles, one quarter-pound of thread, five pounds of tobacco, a keg of oil soap, a tin cup, pan, and spoon, mattress, pillow, and blankets. For this lot of stuff the outfitter charges the moderate sum of seventy-five dollars, draws an order for that amount upon the owners, and, just as the ship is to sail, tells the “greeny” he must sign it, or he can’t go in the ship. Many times he is urged to, and often does, sign an order, the amount of which is left blank; and, after the ship sails, the outfitter fills the blank to suit himself. The poor victim is thus completely in their power, and they know it, and act accordingly. There are exceptions, of course; some men are engaged in the business who would scorn to do 18 a mean action, but, generally, the outfitters of New Bedford are, politely speaking, gentlemen robbers.
Our ship was to sail on the 23d of October, 18—. Accordingly, on the morning of that day, every thing on board was in a glorious state of confusion. Chests, bundles, bedding, etc., were strewn about the decks until the lawful owners should take charge of them.
As soon as the crew were all on board, orders were given to “man the windlass,” and in a few moments the anchor was on the bow, and our last hold on American soil broken. Many an hour must pass, and many a mile of the blue wave be plowed, ere we could again drop our anchor in this port. The captain now came on board, accompanied by his wife and son, the huge sails were loosed, and we left the city of New Bedford with fine breezes and pleasant weather; many of us with gloomy forebodings, vainly endeavoring to penetrate the dim veil of the future and conjecture as to whether we should be spared again to tread our native shores; again to clasp in our embrace those dear friends we were leaving behind us sorrowing. But the future was all shrouded in mystery, and we could but sigh farewell, and place our trust in Him who “doeth all things well.”
As we are now at sea, the pilot takes his leave, with those who have come off to bid adieu to their brothers, sons, friends, etc.; and now the weather-beaten tar as well as the green hand brushes away a tear, as they bid a long farewell to happy homes; and as their native shores gradually sink behind the wave, all appear to be suddenly impressed with the loneliness of their situation, and the dangers they have to encounter and overcome ere they again behold the dear ones at home.


23
At about 6 P.M. the captain came on deck, called all hands aft, and made a short speech, the substance of which was that, “as long as they behaved themselves, they should receive good treatment, should have plenty to eat and drink, and a regular watch below; that they were to go when told, come when called, and that without grumbling; and if any of them should act contrary to this, they would find they had come to the wrong place; that there were some thirty of the crew, and he but one, and it was utterly impossible for him to do every thing to please so many different minds, yet it was perfectly easy for them to so conduct themselves as to suit him; and,” he adds, “let every person sweep his own door clean and mind his own affairs, and there will be no difficulty; but if not, look out for ‘breakers:’ in fine, he hopes there will no trouble, and in forty months to be sailing up Buzzard’s Bay with a full ship.”
The captain and chief mate then proceeded to choose watches. Of the modus operandi of ships’ “watches” we presume a great many are conversant; but, for the benefit of those who are not, we will here relate it. The ship’s company is first divided into two equal portions, called the larboard, or mate’s watch, and the starboard, or captain’s watch, which is commanded, or, technically speaking, “headed” by the second mate. At 8 P.M. the “watch is set,” one watch remaining on deck, and the other going below until twelve. They then change, those on deck going below, and remaining until 4 A.M., when they again change for four hours more, until eight. At that time they are again changed, the watch that had “eight hours out” having the “forenoon watch below,” from 8 till 12 M.; and in the afternoon the watch that had but “four hours out” the night before have the afternoon watch below, from 12 to 4 P.M. The time from 4 to 8 P.M. is divided into two short watches, called “dog-watches,” for the purpose of regulating or keeping them in proper succession. For instance: the larboard watch is on deck from 8 P.M. to 12; the starboard from 12 to 4 A.M.; the larboard from 4 to 8 24 A.M.; the starboard from 8 A.M. to 12 M.; the larboard from 12 to 4 P.M.; the starboard from 4 to 6 P.M., and the larboard from 6 to 8 P.M., when the watch is set. They are thus changed every night, one having eight hours on deck and four below one night, and the next vice versa, continuing thus for the voyage.
It being 8 o’clock, eight bells were struck, and one watch was sent below. About this time the majority of us landlubbers were paying tribute to old Father Neptune—casting up our accounts—and it mattered very little to some of us whether the ship went up or down.
Of all the miserable beings in the world, the sea-sick “greeny” is the most miserable. Those who have been sea-sick can appreciate his situation when we tell them that, in addition to the feeling produced by the sickness, he is made the butt and laughing-stock of those around him who escape the infliction. Those who have never experienced this sickness can not appreciate the blessing of having escaped it, and we will not attempt, therefore, to describe it. However, to use a homely expression, when one is really sea-sick, good and strong, he “doesn’t care whether school keeps or not!”
It blew very fresh through the night, and could the old ship have come to an anchor about this time, we hardly think many of the “green hands” would have remained on board. But it was of no avail now to complain; all were in for it, and must take the evil with the good from this time until the end of the voyage.
Nothing worthy of note transpired, with the exception of occasionally seeing a sail, until Wednesday, November 31st, being about five weeks out, when we saw our first sperm whale. But before we lower the boats and capture this fellow, let us make the reader acquainted as much as possible with our boats and whaling apparatus.
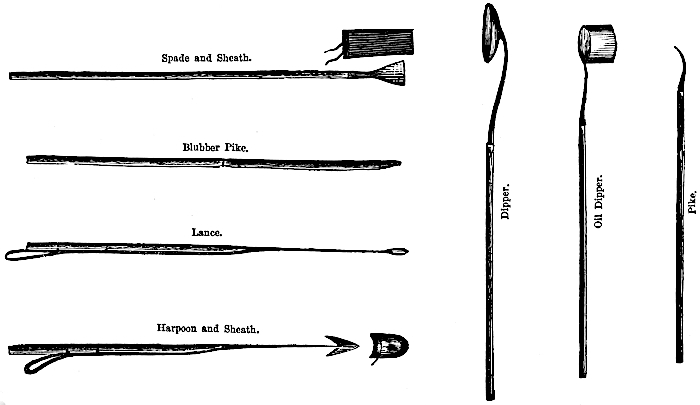
Our ship carried four boats on the cranes, besides four more spare ones in case of accident, such as a boat being stove, etc. They are built in a manner to enable them to stand a very heavy sea, and at the same time very light and buoyant; about twenty-five feet in length and four in breadth, and sharp at both ends, for motion in either direction without turning. Near the stern of the boat is placed a strong, upright, round piece of wood, a little one side from the centre, which is termed the “loggerhead.” The whale-line passes two or three times around this when running out of the boat. At the head 26 or bow is a groove, exactly in the centre, through which the line passes when taken out by the whale. In each boat are two tubs, containing each about one hundred and fifty fathoms, or eighteen hundred feet altogether in length, of the best Manilla tow-line, very carefully coiled, that it may run out perfectly clear and free; for such is the velocity of its egress sometimes that, should any thing obstruct its free passage, the boat, with all its contents, would be immediately drawn under the surface. There are also five or six harpoons, three lances, a keg, called the lantern-keg, containing a lantern with candles, matches, tinder, bread, pipes, and tobacco, that the boat’s crew may have something with which to sustain nature in case of being off in the night-time, or losing the ship in the day-time; a waif, which is a small flag fastened to a pole, to be inserted in the dead whale, as a signal to the ship that it is a “dead fish;” one or two drugs, which are pieces of plank about a foot or eighteen inches in diameter, with a centre-post, and short line attached, by which they are fastened to the whale-line, serving to check the speed of the whale in sounding or running.
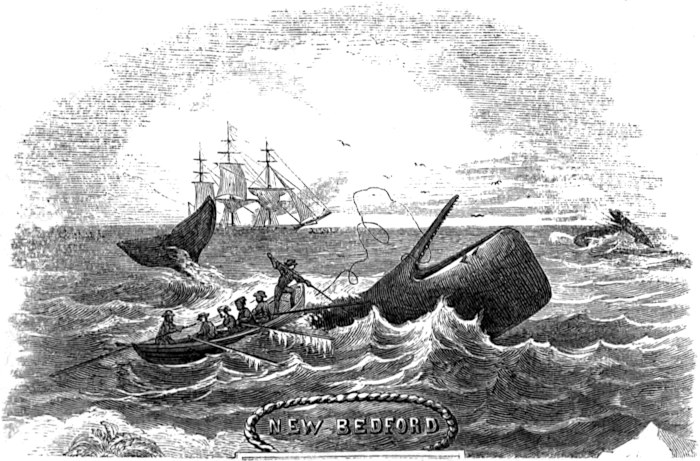
Each boat is commanded by one of the officers of the ship, who is styled “boat-header;” the captain commanding the starboard boat, the first mate the larboard boat, the second mate the waist-boat, and the third mate the bow boat; and they are manned each by a crew of five, one of whom is the harpooner, or “boat-steerer.” All four boats are used in the chase, the race often becoming exciting as to which shall be the “first boat fast.”

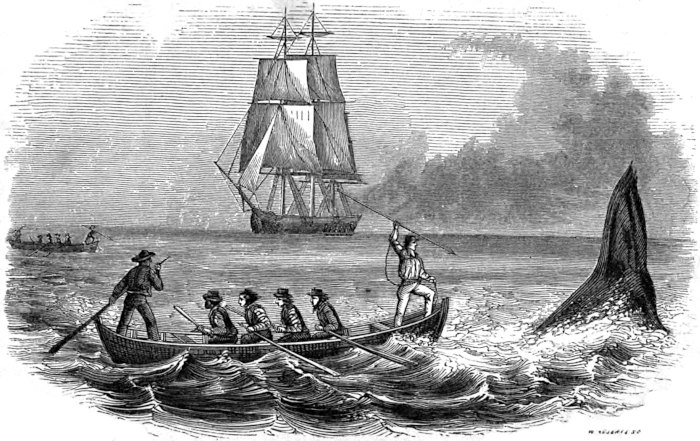
From the commencement of the voyage to its close men are stationed at each masthead, on the look-out for whales, and are relieved every two hours. When a whale is seen by any one of the men aloft, he immediately sings out in a peculiar voice, “There she blows!” and repeats it as often as the whale spouts. The officer of the deck immediately cries out, “Where away?” and the look-out replies, giving the direction of the whale from the ship. The officer again asks, “How far off?” The distance is given, and, in a shorter space of time than is occupied in relating it, the captain is at masthead with his spy-glass. As soon as he ascertains the fact that they are sperm whales, he sings out, “Call all hands; get the boats ready, and stand by to lower;” at the same time giving directions to the man at the wheel to keep the ship in the proper direction.
It is impossible to describe the excitement that now prevails. All are anxious to obtain a glimpse, many for the first time, of the monster. The lethargy produced by the hitherto monotonous voyage is now shaken off, and one and all partake of the excitement. All is bustle and animation; some are at masthead, some are in the rigging, and others flying around, getting the boats in perfect order, and ready to be lowered at a moment’s notice. If the whale is to the leeward of the ship, she is kept in that direction; if to windward, the boats are sent in chase, which often proves to be an arduous task. In this instance the whale was to the leeward. When we were within proper distance, the captain coming down, called out, “Haul aback the mainyards;32 lower away the boats,” and the respective crews follow them down. In a moment more they are pulling for the whale. From hour to hour, and often from sunrise to sunset, do these hardy men toil at the oar, enduring suffering and fatigue, almost unnoticed under the eager excitement of the chase, to be the head boat, or the “first boat fast;” and this under a scorching tropical sun. The waist boat draws near the whale, and all is excitement; the officer crying out, “Pull, men, do pull; now, my hearties, give way; oh! men, do pull; I’ll give you any thing I’ve got, only put me alongside that whale; there he blows; only three seas off,” etc. The boat is close to him; it draws nearer and nearer; the officer orders the boat-steerer to “stand up;” he rises in his place and lifts the fatal weapon; and, when the boat is close enough, the order is given, “Give it to him; give it to him, I tell you!” The boat-steerer darts and misses him, and the whale is “gallied,” or frightened, and takes French leave. Thus ended our first chase after a whale, as did many more during the voyage, and, after having pulled nearly all day, they returned to the ship, all hands disappointed, but the captain cheering us with “better luck next time.” Having thus disposed of our “first whale,” we kept on our course, steering southeast, for the Cape Verd Islands.
On Tuesday, November 27th, we again saw sperm whales, lowered all the boats in chase, but they were going too fast for us, and, pulling a long time with no success, gave up and came on board.
The next day we saw the island of St. Antonio, and ran in toward the land. The inhabitants of this island, like all others of the Cape Verd group, are Portuguese. They subsist principally on the yam, sweet potato, cocoanut, banana, orange, etc., and fish; live in nearly a nude state; are, as a general thing, treacherous, thieving, 33 ignorant, and superstitious. The Roman Catholic religion is the only one tolerated.
On Thursday, the 29th, we passed the island of St. Jago, another of the same group. We were now steering for Fogo, which, on the following morning at daybreak, we saw distant about nine miles. On this island is a volcano, whose summit is one and a quarter miles above the level of the sea. From this volcano the island derives its name, “Fogo, the Island of Fire.” Some years since an eruption took place, which destroyed most of the vegetation, and many of the inhabitants lost their lives. Those that escaped took boats and proceeded to the island of Bravo, a few miles distant. Our captain sent two of our boats in to the shore, for the purpose of trading with the natives, exchanging calico, beads, looking-glasses, trinkets, etc., for various fruits. The opportunity now being given us of visiting dry land once more, we accepted it joyfully. As we drew in near to the shore, the island presented a beautiful appearance; the mountains and hills were covered with green verdure; the natives were seen flocking down their sides, some loaded with baskets of fruit of various kinds, some driving a miserable-looking donkey before them, with a basket of fruit on one side and a pig on the other; here, too, might be seen a great strapping Portuguese woman, with a pig over her shoulder, shouting as loud as her burden squealed, and all hallooing to the boats; the waves breaking over the reef in thunder tones, and all together creating one of the wildest scenes of confusion we have ever witnessed. We finally found, after pulling along the shore for some distance, an opening in the reef, where we might land without danger of getting our boats stove to pieces, and pulled in. As soon as we landed we were surrounded by nearly two hundred Portuguese, and a scene now ensued that beggars description. Imagine a flock of two hundred birds,34 all chattering, about fifty hogs squealing, goats bleating, donkeys braying, and sailors shouting and laughing, and you have some faint idea of the real scene. Some of our men, too, went in for a little fun. One of them, Tom W., a regular wag, managed to steal a Portuguese’s donkey for a short ride up the mountain and back. When he returned, the donkey’s master wanted the moderate sum of seven dollars for the use of the animal. Tom told him he would give him his note for ten years; but the Gee would not be satisfied, until, a crowd gathering around, the matter was finally compromised by Tom’s buying his basket of oranges, containing, perhaps, a hundred, for which he gave him about one eighth of a pound of tobacco.
In the afternoon we returned to the ship, our boats loaded with fruit. We also brought off with us a wild Portugee, who was determined, in spite of the remonstrances of our officers, to “see the elephant.” He could not speak a word of English, and seemed to look on all the proceedings on board ship with a great deal of comical dignity and interest. He made the captain understand by signs that he wished to go the voyage. Accordingly they soon struck a bargain, and Manuel became a member of the ship’s company. He was furnished with a couple of suits of clothes, Tom W. gravely remarking that “it was the first suit of clothes that was ever in the family,” and sent forward. He was of noble build, being six feet three inches high, and well proportioned. He soon, however, was obliged to “cast up his accounts,” and we never saw a more pitiable-looking object than sea-sick Portugee Manuel; and, while many of the crew were passing jokes upon him, he looked as if he fully believed he had fallen into the hands of barbarians.
From this island we shaped our course for Cape Horn.
The ship being by this time “shipshape and Bristol fashion,” and the crew pretty well acquainted with each other, we will give a brief description of the officers and crew. Our captain is a man of about fifty, and has “beat the wash” for the past twenty-six years. He is a thorough sailor, a skillful navigator, and an impartial and decisive judge, and one who commands the respect of both officers and crew. His lady is an agreeable, intelligent woman, well fitted to be the wife of such a man; his son, a lad of about ten years, a smart, active boy, and cut out for a sailor.
Our chief mate, Mr. C., is a seaman of the first water, one thoroughly versed in the mysteries of sailorship, prompt and efficient, kind and obliging, and, above all, a most skillful whaleman.
Our second officer, Mr. L., is also an excellent seaman, an experienced whaleman, and one whom the whole ship’s company love, for he is a good man, and to them all a kind friend.
Quite the contrary is our third officer, Mr. K. He is a pompous, windy sort of a being, who knows more than the captain and all hands, and one whom the men detest.
Our fourth officer, Mr. F., is a fine jovial fellow, as smart as a steel trap, and perfectly at home on board ship. He is also an excellent whaleman.
The boat-steerers are good-natured boys, always ready in the discharge of their duties; and the cooper, a quiet,36 peaceable man, who attends to his own business, which he thoroughly understands, and does not trouble himself with other people’s.
The crew represent most of the states of the Union, England, and France. We have with us, also, a Kanaka, a native of the island of Roratongo, one of the Society Islands; a good-natured, lazy fellow, with but one eye, who goes by the very expressive name of Jo Bob. He speaks but little English, and that so broken as to make it difficult to understand him; nevertheless, in the first watch at night, he takes our wild Portuguese on the heel of the bowsprit, and endeavors to teach him English, and rather comical work they make of it. Most of the mechanical trades we find represented among our crew, as well as the professions, and the “art preservative of all arts.” One or two, from their appearance and conversation, would lead a person to suppose they had never before been beyond the boundaries of a cow pasture. Some have been driven to the sea to escape the consequence of rascalities at home; others from family difficulties; some have come to sea to repair their broken health; a few have run away from home to escape the fancied tyrannies of parents, and still others from an inclination to follow the sea and a love of adventure; and all have come to a good school, in one sense of the word. Shut out from all society; prescribed to a certain portion of the ship; to go when told, come when called, and that without grumbling; put upon sailor’s fare, which generally consists of coffee and tea, without milk or sugar, and sea-bread, with cold salt pork, for breakfast, beef and pork for dinner, with “duff” for dessert—and we will give a brief description of this beautiful dish: Take flour, which has previously been dug out of a cask with mallet and chisel, and then pounded fine, mix it with water to the consistency of a paste, and then “dump” it into a canvas bag, and boil37 for three hours, with about the third quality of West India molasses, well diluted with water, for sauce, and you have the sailor’s delicacy—“duff!” This food, with the manner of living, generally brings them to their senses; they begin to realize the comforts and blessings of a good home, and make the important discovery that their wisdom is not quite so extensive as Solomon’s, and that they were sadly mistaken in supposing they knew more than their parents. If any young men who may chance to read this book should have a longing for the sea and all its pleasures, we will inform them how they may obtain a slight foretaste of those joys. Let them choose a dark, cold, rainy night, such as we often have in the month of November, and be roused suddenly out of a snug, cozy sleep, mount into the top of the tallest tree they can find, and there stand and endure the pitiless beatings of the storm for four long hours, and we think they will get a slight foretaste of the joys of a sailor’s life. But still, whenever we have been asked the question by such, we say, “Go, by all means, and then you will be satisfied.” The old adage proves true here as well as elsewhere, “Experience is a dear school.”
We will here give one or two anecdotes in relation to life on shipboard, which will serve to illustrate the tricks and games often practiced. We had with us, by some means unaccountable, a young fellow from Taunton, Mass., a lazy, half-foolish, soft piece of humanity, to whom we soon gave the dignified appellation of “Barney.” When only a few days out, and Barney was partially recovering from his sea-sickness, the poor fellow, missing the accustomed good things at home, and not relishing the hard fare of ship-life, complained sadly of his want of appetite; that he could not relish the fat salt pork and hard bread which he was obliged to eat. One of the old seamen, who are always up to such jokes,38 said to him, “Why, Barney, you fool, why don’t you go and ask the captain or mate to break out that cask of pies that they have got in the main hold, and give you one? They were put on board expressly for the green hands when recovering from their sea-sickness.”
“Cask of pies!” replied Barney, opening his eyes and mouth wide with astonishment. “Is there a cask of pies aboard?”
“Certainly,” replied his tormentor, “and it was put aboard on purpose for the green hands, and you’re a fool if you don’t go and tell the old man[1] you want some.”
So off Barney posts aft to the captain and mate, who were walking the quarter-deck together. It was not long before he returned to the forecastle, his countenance considerably elongated, and feeling very much crestfallen.
“What’s the matter, Barney? Didn’t you get any pies?”
“No, I didn’t get any pies, and there ain’t any aboard the ship either, and you knew there was not.”
“Why, what did the old man say?”
“He said that some one was making a fool of me, and if I came to him after any more pies he would stop my watch below for the whole cruise.”
Poor Barney was obliged to submit, not only to sailor’s food, but to be one of the butts of the ship’s company for the voyage.
We had on board a fellow from Nova Scotia by the name of Mackey. It was the delight of some of the watch to “stuff” Mackey with all sorts of imaginable stories on divers subjects, and to get the poor fellow, who was very credulous withal, into some scrape. One night, when it was blowing very hard, and the ship lying-to under easy sail, rolling heavily, some one of the39 watch told Mackey to place a handspike in one of the lee scupper-holes to prevent the ship rolling so badly. Off posts Mackey for a handspike, but, finding none, he contented himself with using a scrub-broom handle, which he placed in the scupper-hole, and commenced jumping upon it, until he finally broke it. The officer of the watch espied him, and sang out,
“What are you about there, you Mackey?”
“Stopping the old ship from rolling, sir.”
“Well, I guess you have worked at that about long enough; now point yourself aloft, and try your hand at slushing down the masts; away you go!”
Poor Mackey starts off, grumbling that they should give him a work-up job for trying to stop the ship from pitching about so. He gets up aloft, and finds rather a difficult job before him.
“How shall I hang on, sir?”
“By your eyelids.”
“But I can’t do it, sir.”
“Then let go; probably the deck will bring you up.”
As this is all the consolation Mackey gets, he goes to work, muttering all sorts of invectives against whale-ships and mean men, and wishing them all in Tophet, and that he was at home, down in Nova Scotia, and guesses he would not trouble salt water again.
Our pompous third officer was very much opposed to allowing the men to sit down in the night watches, for fear they should take a short nap now and then. We had one fellow on board who was one of the laziest fellows in existence, so very lazy that before we were two weeks out he had received the appropriate sobriquet of “Lazy Lawrence.” He possessed, in addition to the excellent trait of character above mentioned, that of being the most inveterate liar ever known, and at the same time the greatest sleepyhead on board. As soon as he would come on deck in the middle, or morning40 watch, he would invariably bring himself to an anchor somewhere, and then—he was fast asleep. One night one of the crew, stationed on the look-out, espied him, and, thinking to have a little sport, goes aft to the binnacle lamp (which is the lamp that gives the light to the helmsman at night), covered his hands with oily smut, and, coming forward to the place where Lawrence was so quietly reposing, probably dreaming of his home, “’way down East, in the State of Maine,” and the farm, drew both hands very quietly across the poor fellow’s face several times, giving him very much the appearance of a molasses-colored darkey. Next morning all hands were called to go through the usual process of washing decks, etc. Lawrence, making his appearance with the rest, presented a comical spectacle. All hands roared with laughter; he, not imagining what was the cause of their merriment, joined in. At last the chief mate, who had an inkling of the matter, sang out,
“What is the matter with you this morning, Lawrence; are you sick?”
“No, thir,” lisped Lawrence.
“I guess you got asleep during your watch last night, did you not?”
“No, thir; I never closed my eyes the whole watch!”
“Don’t lie to me; what were you doing on the windlass, just after four bells?”
“Only thinking, thir.”
“There, that will do; go wash, and point yourself aloft, and stay there till I call you down; and learn, when I ask you a question, to tell the truth; away you go!”
So away goes Lawrence, imagining himself the most abused man in existence, and says a state prison would be preferable to an old blubber-hunter. After he had been kept aloft two or three hours, he was called down, told to tell the truth after this, and sent about his business.
On the 13th of December, 18—, we crossed the equator in longitude 24° 30´ west. The weather was delightful; pleasant breezes and sunshine; the heat not uncomfortable, but just enough to make thin clothing desirable. Old Neptune did not favor us with a visit, although rather fearfully expected by some. This practice, we believe, has become obsolete, and we rejoice heartily at it, for a more barbarous one never was invented.
Barney was very anxiously and busily engaged during the middle and morning watches, and most of the day, in looking for the “line” as we crossed it. He had talked of nothing else for several days, and was keeping a bright look-out for it, losing his watch below for the purpose. But he was doomed to disappointment. No “line” was visible when we crossed the equator, and poor Barney went below, when the announcement was made that we were south of it, muttering to himself, “It is certainly strange; I have often seen it on the maps, and I can’t imagine how we crossed it without seeing it.” Barney found out his error before the voyage was up.
The same day we saw the first whale-ship at sea, the ship “Java,” of Fairhaven, Captain Thompson. She, like ourselves, was bound for the Pacific. Had taken no whales as yet.
On the twentieth of the same month, while in company 42 with the Java, we spoke the “Ontario,” of Sag Harbor, bound home, with a full cargo of whale oil. Paper, pens, and ink were now in great demand, all eager to send letters home. And now a great many of those who attempted writing for the first time found out the difficulty, we might almost say folly, of attempting to write legibly at sea. We had by this time, from having practiced it daily in keeping a journal, acquired the knack, though at first our efforts in that line were really astounding, to us at all events. Even now it is hard deciphering the marks we first “entered in our log,” they having a closer resemblance to the tracks of an old turkey who had stepped in a pool of ink and walked over paper than any thing else we can liken them to.
But we must hasten, as the good ship “Ontario” is waiting anxiously for her master to return on board, that she may be on her way “homeward bound.” Her crew were pitying us poor fellows—outward-bounders on a long voyage—while we were vainly endeavoring to conjecture how soon the time would arrive when we should be homeward bound with a full ship, and could look with an eye of pity upon poor outward-bound whalemen.
The morning of the twenty-second commences with light breezes from the northeast; pleasant weather. Suddenly, about 9 A.M., the monotony is broken by the welcome cry from masthead,
“T-h-e-r-e she b-l-o-w-s! T-h-e-r-e she b-l-o-w-s!”
“Where away?”
“Four points off the lee bow, sir.”
“How far off?”
“About two miles, sir.”
“What does it look like?”
“Sperm whales, sir.”
“Ay, ay; sing out every time you holler.”
43
By this time the captain was aloft, and, on taking a view with his spy-glass at the “spouts,” sings out, “Sperm whales! Call all hands; bear a hand there, and get your boats ready.”
“Ay, ay, sir,” is the reply. All hands are called, and the different crews stand by their respective boats, “all eager for the fray,” and expressing their determination to capture a whale before returning to the ship, taking for their motto, “A dead whale or a stove boat.”
“Lower away the boats!” shouts the captain, as he descends to the deck. They are instantly lowered, followed by the crews, and now comes the tug of war. Each boat sets her sail, and the men pull in good earnest. While they are skimming the waves the whale is still spouting, and all are anxious to reach him before his “spoutings are out.” It frequently happens, when in pursuit, that, just at the moment the boat-steerer “stands up” to strike the whale, he suddenly descends; but experienced whalemen can generally tell the direction they take while down by the position of the “flukes” when going down. The boats are then pulled in the direction the whale is supposed to have taken. They also judge of the distance the whale will go under water by the velocity of the animal when last seen. After the boats have pulled what is judged to be the proper distance, they “heave up,” or cease pulling. A large whale, when not “gallied,” or frightened, generally spouts from sixty to seventy times before going down, and remains down from fifty to seventy minutes.
The boats have now got close on. Those left on board the ship are watching with breathless anxiety, occasionally exclaiming, “Oh pull, boys! do pull!” Meantime the men in the boats are bending back to it, but the bow boat has the advantage; she is the head boat. Mr. K. is jumping up and down in the stern, crying, “Once more, my hearties; give it to her! a few44 more strokes, and we have him; pull, my children! why don’t you break your backbones, you rascals? so there you are now; that’s the stroke for a thousand pounds; start her, but keep cool; cucumbers is the word; easy, easy; only start her! why don’t you snap your oars, you rascals? bite something, you dogs! easy now, but pull; oh, you’re all asleep! stop snoring, and pull; pull, will ye? pull, can’t ye? pull, won’t ye? pull, and start your eyes out! that’s it; now you start her.” Thus, one moment coaxing and the next scolding; but no one heeds him, as all are bent on taking the whale. “Stand up!” shouted he; and the boat-steerer rose to his feet, grasped his iron, and, as the boat neared the monster, “Give it to him!” is the next cry, and “chock to the socket” went the first iron, followed as quick as thought by the second. One deafening cheer, and the cry resounded over the waters, “We are fast! we are fast!” The sea, which but a moment before lay still and quiet, with scarcely a ripple to break its even surface, is now lashed into foam by the writhings of the whale. “Stern all!” shouts the officer. The boat is immediately backed, and removed from present danger; the officer takes the head of the boat, and the boat-steerer takes the steering oar to manage the boat; the whale is sounding, and the line is running through the “chocks,” or groove in the head of the boat, with the rapidity of lightning, and as it passes round the loggerhead it ignites from the heat produced by friction, but the tub-oarsman is continually dashing water upon it in the line-tub. The whale sounds deep, and the line is almost out; a signal is made to the other boats, which are coming down. They come near enough, and bend on their lines; but presently it ceases running out and slackens; the whale is coming to the surface again. All hands now commence to “haul in line” as fast as he rises, and the boat-steerer coils it away, as fast as hauled in, in the stern sheets. He soon breaks water, and the boat is gradually hauled up to him. Another boat now fastens, and he again attempts to sound; but, being weakened by loss of blood, he is soon at the surface again. The boats now draw alongside, and the officer of the first boat fast prepares his lance. He darts it for his vitals (just behind the fin), and the first one proves fatal, for in a moment more he shows the “red flag;” the blood flows freely from the spout-hole in a thick, dark stream; the sea is stained for some distance, and the men in the boats are covered with the bloody spray, but glory in it.

The monster now attempts to sound, but is obliged to keep to the surface, and he soon goes in what is technically termed by whalemen his “flurry,” but what landsmen would call his dying agonies—and terrible48 they are. The sea is beaten into a perfect foam by his writhings and contortions; and, after a short time, as if with accelerated strength, he starts off with lightning speed, describing in his course circles, each growing smaller than the preceding one, and his speed slackening, until he finally gives one monster throe and dies, rolling fin out, with his head to the sun.[2]
The battle is now ended, and the “huge leviathan lies a victim to the superior power and mind of man.”
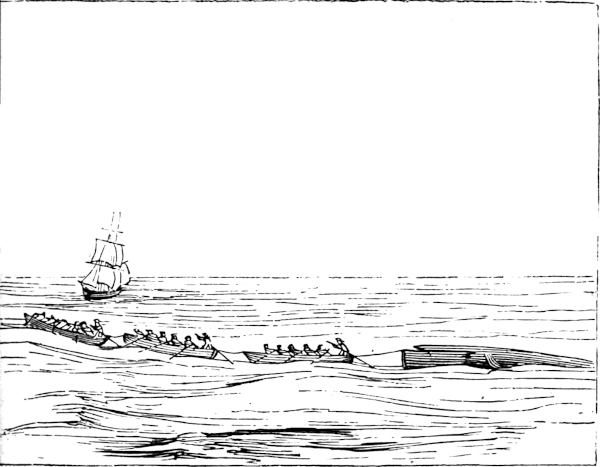
Now that life is extinct, a hole is cut in his head, the line made fast, and all the boats “hook on” and tow him to the ship, where he is made fast by means of a fluke-chain being passed around his tail, which chain is brought to the forward part of the ship, and passed through a “hawse-hole,” and made fast to the “bowsprit bits,” bringing the whale with his head pointing aft, and in a proper position to commence the operation of “cutting in.”
Before proceeding farther, perhaps it will be interesting to the reader if we give a brief description of the external form of the sperm whale. The following draft represents the shape of the animal, and the various dotted lines show the manner of dividing it, in order to “heave it in on deck.”
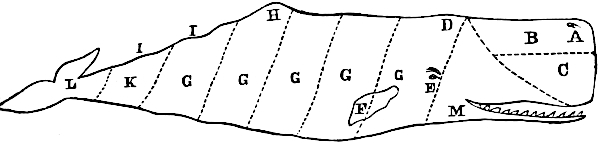
The head of the whale presents in front a thick, blunt appearance, and constitutes about one third the length of the animal. At its junction with the body is a protuberance on its back, called the “bunch of the neck;” immediately back of this is the thickest part of the body. It then gradually tapers for about another third of the whole length, when the “small,” as it is called, commences; and at this point on the back is another and larger prominence of a pyramidal form, called the “hump,” from which a series of smaller prominences runs half way down the small, forming the “ridge.” The body then contracts so much as to become not larger than the body of a man, and terminates by being expanded on the sides into the “flukes,” or tail. The flukes 50 resemble somewhat in shape the tail of a fish, only being placed horizontal instead of perpendicular. In the larger whales these flukes are from eight to ten feet in length, and from fourteen to sixteen feet in breadth. The depth of the head and body is greater than the width.
At the angle formed by the superior and anterior surfaces of the head, a little on the left side, is the nostril, or “spout-hole,” which, in the dead animal, presents the appearance of a slit, or fissure, in form resembling an S, extending longitudinally, and about twelve inches in length. The “case,” situated in the upper part of the head, is a large, almost triangular-shaped cavity, lined by a beautiful glistening membrane, and covered by a thick layer of muscular fibres and tendons running in various directions, and finally united by common integuments. This cavity is for the purpose of containing and secreting an oily fluid, which after death concretes into a granulated substance of a yellowish-white color—the spermaceti. The quantity of fluid contained in the case depends on the size of the whale; from that of a large whale fifteen barrels of liquid spermaceti are often taken.
Immediately beneath the case, and projecting beyond the lower jaw, is situated the junk, which is composed of dense cellular tissue, strengthened by numerous strong tendons and fibres, and infiltrated with spermaceti.
The mouth is at the base of the head, and continues nearly its whole length. The lower jaw is pointed in front, and gradually widens till it is received in the socket of the upper jaw. It contains forty-two teeth, conical in shape, and, in the large whale, formidable in appearance. There are none, however, in the upper jaw, but indentations which receive the points of those in the lower jaw. Sometimes a few rudimentary teeth are found in the upper jaw, never, however, projecting beyond51 the gums, upon which those in the lower jaw strike when the mouth is closed.
The tongue is of a white color, exceedingly small, and does not appear to possess the power of very extended motion.
The mouth is lined throughout with a white membrane, which becomes continuous at the lips, and borders with the common integument, where it becomes of a dark brown or black color.
The eyes are small, and are furnished with eyelids. They are situated above and behind the angle of the mouth, at the widest part of the head. At a short distance behind the eyes are the external openings of the ears, of sufficient size to admit a small quill, and unprovided with any external auricular appendage.
The fins are not far from the posterior angle of the mouth, and are analogous in their formation to the anterior extremities of other animals. They are not much used as instruments of progression, but probably in giving a direction to motions in balancing the body, in sinking suddenly, and occasionally in protecting and supporting their young.
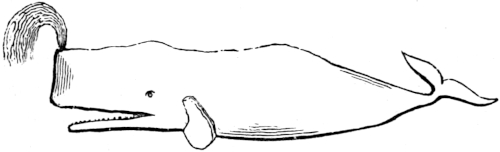
In a full-grown male sperm whale of the largest size the dimensions may be given as follows: Length, from eighty to ninety feet; depth of head, from ten to twelve feet; breadth, from seven to ten feet; depth of body, from sixteen to eighteen feet; swimming paws, or fins, about eight feet long and three broad; the tail, or flukes, have been previously mentioned.
52
In reviewing the description of the external form and some of the organs of the sperm whale, it will, perhaps, not be uninteresting if some comparison is instituted between them and the corresponding points of the right whale. One of the greatest peculiarities of the sperm whale, which strikes, at first sight, every beholder, is the apparently disproportionate and unwieldy bulk of the head; but this, instead of being, as might be supposed, an impediment to the freedom of the animal’s motion in his native element, is, on the contrary, in some respects very conducive to his lightness and agility. A great part of the bulk of the head is composed of a large, thin, membraneous case, containing, during life, a thin oil of much less specific gravity than water, below which again is the junk, which, although heavier than the spermaceti, is still lighter than the element in which the whale moves; consequently, the head is lighter than any other part of the body, and will always have a tendency to rise, at least so far above the surface as to elevate the nostril, or “spout-hole,” sufficiently for all purposes of respiration. In case the animal should wish to increase his speed to the utmost, the narrow anterior and inferior surface, which bears a resemblance to the cut-water of a ship, and which would, in fact, answer the same purpose to the whale, would be the only part exposed to the pressure of the water in front, enabling him thus to pass, with the greatest ease and celerity, through the boundless track of his wide domain.
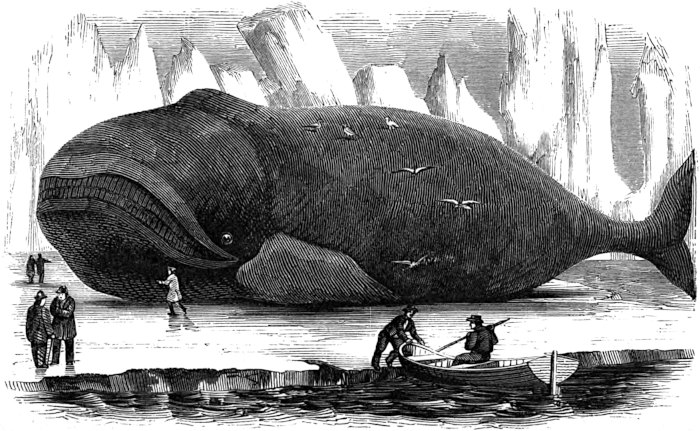

It is in the shape of the head that the sperm whale differs, in the most remarkable degree, from the right whale—the shape of whose head more resembles that of a porpoise—and in it the spout-hole is situated much farther back, rendering it seldom or never necessary for the nose to be elevated above the surface of the water. The eyes, in both the sperm and right whale, are exceedingly small in comparison with their bulk; still, 55 they are tolerably quick-sighted. We are not aware that the sperm whale possesses, in any respect, any superiority. We again observe, in the formation of the mouth, a very remarkable difference in the two animals; for, in place of the enormous plates of whalebone which are found attached to the upper jaw of the right whale, we only find depressions for the reception of the teeth of the lower jaw, which plainly point out that the food of the two animals must be very different.
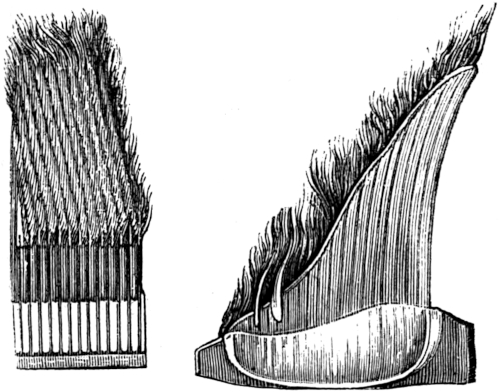
There are several prominences or humps on the back of the sperm whale, which constitutes another difference in their external aspect. These prominences are not altogether peculiar to the sperm whale, as there is a species of fish, called by whalemen “humpbacks,” which possesses a prominence on the back very similar to that of the sperm whale.
The skin of the sperm whale is smooth, but occasionally, in old whales, wrinkled. The color of the skin, over the greatest part of the body, is very dark. In different whales there is considerable variety of shade; some are even piebald. “Old bulls,” as full-grown males are called by whalemen, have generally a portion56 of gray on the nose above the fore-part of the upper jaw, and they are then said to be “gray headed.” In young whales the “black skin,” as it is called, is about three eighths of an inch thick, but in old ones it is not more than one eighth.
Immediately beneath the black skin is the blubber, or fat, which is contained in a cellular membrane, and which is much strengthened by numerous fibres. The average thickness of the fat on the breast of a large whale, when in good condition, is about eighteen inches. The “hump” is generally the thickest part of the blubber, being sometimes from twenty-two to twenty-six inches in thickness; and, in most other parts of the body, it measures from nine to fourteen inches. The head is not, however, supplied with this covering, or blubber, having only the black skin, which lies close to a layer of very dense cellular tissue, under which is seen a considerable thickness of numerous small tendons, intermixed with muscular fibres.
This thick covering of blubber, or fat, is called the “blanket;” it is of a yellowish color, and, when melted down, furnishes the sperm oil. It also serves two excellent purposes to the whale: rendering it buoyant, and furnishing it with a warm protection from the coldness of the surrounding element—in this last respect, answering well to the name bestowed upon it by whalemen.
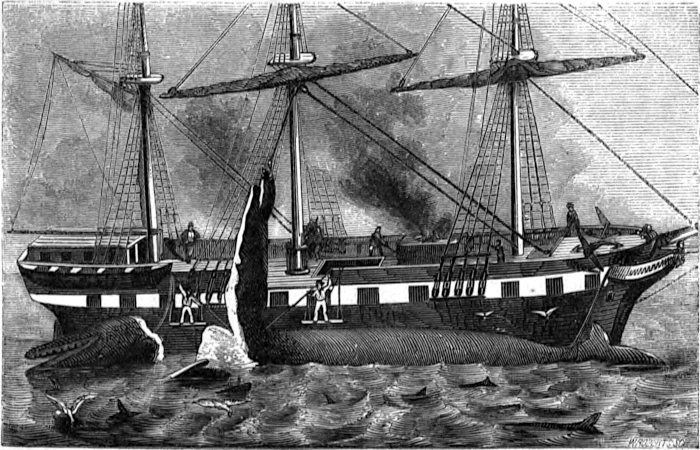
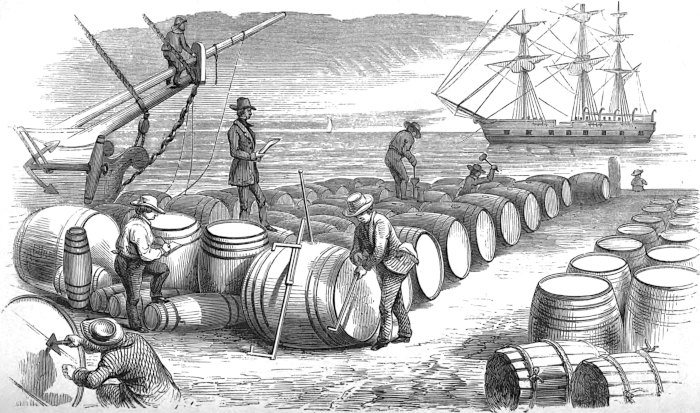
As we are now ready to “cut in” the whale, we will briefly explain the modus operandi. In the first place the decks are cleared, in order to have room to work. The ponderous cutting tackles are swayed up to the lower-mast head (the main), the strongest point any where above a ship’s deck. Large hawsers are then rove through these blocks, then through similar ones on deck, to the windlass, in the forward part of the ship. To the lower blocks are attached ponderous iron hooks, weighing over one hundred pounds each. These hooks are for the purpose of “hooking on” to the blubber, and can be put on and taken off the blocks at pleasure. And now, suspended in stages over the side, the first and second mates, armed with their long spades, begin cutting a hole in the body for the insertion of the hook just above one of the fins. This done, a broad semicircular line is cut round the hole, the hook is inserted, and the main body of the crew, striking up a wild chorus, now commence heaving at the windlass. The entire ship careens over on her side; every bolt in her starts like the nail-heads of an old house in frosty weather; she trembles, quivers, and nods her frighted mastheads to the sky. More and more she leans over to the whale, while every gasping heave of the windlass is answered by a helping heave of the billows, till at last a swift, startling snap is heard; with a great swash the ship rolls upward and backward from the whale, and the triumphant tackle rises into sight, dragging60 after it the disengaged semicircular end of the first strip of blubber. Now, as the blubber envelops the whale, as we described in the last chapter, precisely as the rind does an orange, so is it stripped off the body precisely as an orange is sometimes stripped by spiralizing it. The strain, constantly kept up by the windlass, continually keeps the whale rolling over and over in the water; and as the blubber in one strip uniformly peels off along the line called the “scarf,” simultaneously cut by the spades of the mates—the chief mate separating the head from the body while the whale is being rolled over the first time—and just as fast as it is thus peeled off, and indeed by that very act itself, it is all the time being hoisted higher and higher aloft till its upper end grazes the main-top; the men at the windlass then cease heaving, and for a moment or two the prodigious, blood-dripping mass sways to and fro as if let down from the sky; and every one present must take good care to dodge it when it swings, else it may box his ears and pitch him overboard.
One of the attending boat-steerers now advances with a long, keen weapon, called a boarding-knife, and, watching his opportunity, he dexterously slices out a considerable hole in the lower part of the swaying mass. Into this hole the end of the second alternating great tackle is hooked, so as to retain a hold upon the blubber, in order to prepare for what follows. Whereupon this accomplished swordsman, warning all hands to stand off, once more makes a scientific dash at the mass, and with a few sidelong, desperate, lunging slicings, severs it completely in two; so that, while the short lower part is still fast, the long upper strip, the “blanket piece,” swings clear, and is all ready for lowering. The heavers forward now resume their song and their work, and, while the one tackle is peeling and hoisting a second strip from the whale, the other is slowly slackened away, and down61 goes the first strip through the main hatchway right beneath, into an unfurnished parlor called the “blubber-room.” Into this twilight apartment sundry nimble hands keep coiling away the long blanket-pieces, as if they were a great live mass of plaited serpents. And thus the work proceeds; the two tackles hoisting and lowering simultaneously, both whale and windlass heaving, the crew singing, the blubber-room gentlemen coiling, the mates cutting, the ship straining, and all hands swearing occasionally, by way of assuaging the general friction.
And now the “body” of the whale is all in; the carcass has floated off, food for the sharks; the head, which has been made fast alongside the ship, is brought to the gangway, and the junk is separated from the case, and “hove in” on deck. Now comes the bailing of the case. It is hoisted up alongside the gangway, nearly level with the ship’s deck; a “whip” is rigged, being simply a rope, one end on deck, the other passing through a single block made fast to the main-yard, to which is attached a bucket of the capacity of about a gallon. One of the boat-steerers stands on the end of the case, with a short spade cuts a hole in the case, and the bucket is then sunk into it by means of a long pole, until it is filled, when it is hoisted out and emptied, and so on until the liquid oil is all bailed out. From the case of a hundred-barrel sperm whale from fifteen to seventeen barrels of liquid oil is generally obtained, though a great deal is unavoidably wasted. After the case is bailed it is cut loose, and immediately sinks with great rapidity.
The whale is now cut in; then comes the process of “trying out.” In the centre of the deck, somewhat forward, are the try-works for the purpose of trying out the oil. It is a square place, built up with bricks and iron, about four feet high and ten square. It has two large iron pots in the centre, each one containing between three and four barrels, with furnaces underneath. The liquid spermaceti from the case is first put into the pots, the fires are lighted, and the process of “trying out” commences. Here we would state that, in a whaling voyage, the first fire in a try-works has to be fed for a time with wood. After that no wood is used, except as the means of quick ignition to the staple fuel. In a word, after being tried out, the crisp, shriveled blubber, now called scraps, still contains considerable of its unctuous properties. These scraps feed the flames. Like a plethoric burning martyr, or a self-consuming misanthrope, once ignited, the whale supplies his own fuel and burns by his own body. Would that he consumed his own smoke! for his smoke is horrible to inhale, and inhale it you must; and not only that, but you must live in it for the time. It has an indescribable odor about it, such as one might imagine would arise from a Hindoo funeral pile.
The blanket-pieces are cut into small pieces, varying from twelve to twenty inches in length, and about as wide as the thickness of the blubber, called “horse63 pieces.” They are then pitched on deck, and forward to the mincing machine, where they are cut into very thin slices, and are then ready for the pots.
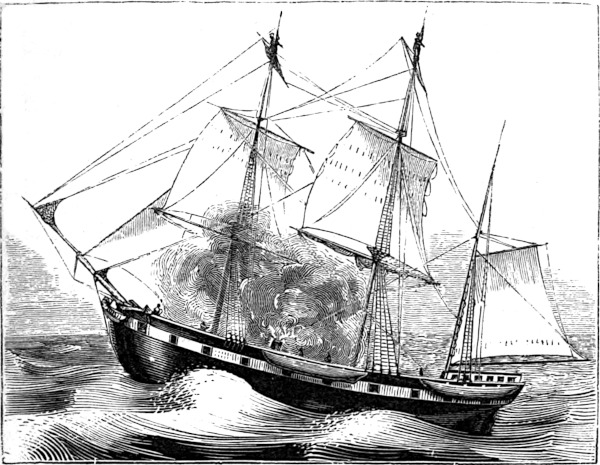
As soon as the oil is extracted from the blubber, the scraps are skimmed off, and the oil bailed out of the pots into a large copper cooler, which stands by the side of the try-works. When it is sufficiently cool that it will not burn the casks, it is poured into them, and allowed to remain on deck for two or three days. It is then “coopered,” that is, the hoops on the casks are all driven tight, to prevent them from leaking, it having been rendered necessary by the hot oil shrinking the casks. At length, when the last pint is casked and coopered, and all is sufficiently cool, then the great hatchways are unsealed, the bowels of the ship are thrown open, and down go the casks to their rest in the hold. This done, 64 the hatches are replaced and hermetically sealed, like a closet walled up.
And now comes the process of cleaning up. From the ashes of the scraps is made a powerful lye, which is used in removing the grease from the bulwarks and decks of the ship. Hands go diligently along, and with buckets of lye and water, and rags, restore all to its full tidiness. The soot is brushed from the lower rigging; all the numerous implements which have been in use are likewise faithfully cleansed and put away. The great hatch is scrubbed and placed upon the try-works; every cask is out of sight; all tackles are coiled in unseen nooks; and when, by the combined and almost simultaneous industry of the ship’s company, the whole of this duty is concluded, then the crew themselves proceed to their own ablutions, shift themselves from top to toe, and issue forth to the cleaned and white decks, fresh and all aglow, as bridegrooms new leaped from out the daintiest Holland.
We now continued our way for Cape Horn, having beautiful clear weather with fine southeast trade-winds.
On Tuesday, January 8th, 1850, we were off the River De la Plata. This region is notorious for its heavy gales and “pamperos,” a species of hurricane. We had, for three days, been having a severe gale. On this evening (the third day) the wind died away; the heavens were shrouded with heavy black clouds; every thing so quiet, and yet so gloomy, seemed but the forerunner of a storm of the wildest description. Sail was taken in, and all put in readiness, awaiting its approach. Presently the heavens were illuminated with the glare of lightning, followed by the hoarse and deep thunder that appeared to come from the very bottom of the great deep. It increased until the whole heavens were one broad sheet of flame, and the reflection upon the surface of the water gave it the resemblance of a sea of fire; 65 and the constant thunder, seeming to shake the earth to the very centre, added to the sublime grandeur of the awe-inspiring scene. On every hand, and in whatever direction the eye turned, the same continual blaze of lightning, accompanied by the heavy and continuous thunder, presented itself to the beholder. It was certainly the most awful and yet sublime scene we had ever witnessed.
All hands were gazing upon the grand spectacle, when, suddenly, a clap immediately over our heads—a sudden flash—a jar, followed by impenetrable darkness. All hands were dumb; no one dared to speak. The ship had been struck, but none could ask where, fearful of being told we were lost. The mate, however, soon came along, and gave proper directions to examine the ship. He then went to the main-top, and found the powder, which had been placed there for safety, all right. Another descended to the hold, but discovered no fire. It appears the lightning struck our main-royal truck, and descended to the deck, which being wet, it passed off with but little damage. The next morning, on unfurling the main-royal sail, we found thirteen holes burned in it, about the size of a musket ball. The lightning went through the “bunt,” as it was rolled on the yard, thus accounting for the large number of holes.
As soon as it was generally known we had escaped with so little injury, all experienced a feeling of gratitude for our truly remarkable escape. As we before remarked, the powder, which was contained in two “breakers,” or long, narrow barrels, each containing four kegs, was placed in the main and mizzen tops, one 66 breaker on each side of the mast. The lightning had descended immediately between the two breakers in the main-top. Had it ignited the powder contained in one of the kegs, in all probability our voyage at sea, and perhaps for life, would have been soon ended. We felt truly thankful that we had so miraculously escaped. Some two or three of the men were knocked down, and others stunned, but nothing serious. The night slowly wore away; the constant glare of the fierce lightning, and the never-ceasing roar of the thunder, continuing until day dawned.
We all felt relieved when daybreak once more came over the sea. The gale, which had increased during the night, now abated; the clouds broke away, even the one with the “silver lining,” and “old Sol” once more showed his cheering face, and sent his gladsome rays rejoicing over the face of the great deep.
We now commenced making preparations for that much-dreaded place, Cape Horn. Took the anchors in on deck, and lashed them solid; also the boats from off the cranes, and secured every thing generally. We were now sailing along with fine breezes from the northward, but the coolness of the air reminded us that we were approaching the southernmost point of land. On the 13th of January the wind veered round to the south, and increased to a heavy gale. We reduced the sail to a close-reefed main-topsail, sent down top gallant yards, and prepared for a regular “Cape Horner.” At midnight, however, the wind abated, and sea went down; next morning it was pleasant, with fine northerly breezes; but at night the wind again hauled to the southward, blowing heavy, with rain, which obliged us to heave to. Thus the wind often changes in the Atlantic in this latitude; sometimes ships are kept here for weeks by head winds.
On the 25th we were off Staten Land. This island presents a bleak, rocky appearance. Saw a ship trying out, which assures us that sperm whales have been taken here lately.
On Saturday, the 26th, we were off the island of Cape Horn. This island is said to have received its name from its conical shape. We here saw quite a fleet of merchantmen and whalemen bound round the Horn,68 no less than twenty-two ships being in sight from masthead. About nine o’clock this morning, while sailing along with a fair, pleasant wind, carrying studding-sails, all hands were suddenly called to take in sail, and, before the ship was under snug canvas, the gale broke upon us in all its fury, coming, as seamen say, “butt-end first.” However, we soon had every thing snug, and then “let the winds pipe.” With a good ship and plenty of sea-room, we felt no danger. The next day great numbers of porpoises were seen, going through the water like race-horses. Plenty of albatross and Cape pigeons were in sight also. We caught an albatross, a beautiful large bird, perfectly white, measuring sixteen feet from tip to tip of its wings. They are called by seamen “Goneys,” for what reason we know not. We also saw large numbers of “Mother Carey’s Chickens,” that beautiful little bird so well known to all. They were flying in the wake of the ship, skimming along its surface, apparently happy and contented. As we sat watching them and the noble albatross, as he went wheeling and circling in the air, we could not but think of that great Creator who endowed them with the instinct which they possess—an instinct that guides them over the trackless waste of waters hundreds and thousands of miles from land, and then to land again, day after day, and week after week. No place in the world presents so many evidences of a great and a good God as the vast and mighty ocean.
Spoke the ship “Henry,” of Portsmouth, New Hampshire, bound for California. The heavy gales of wind still continued, with rain, hail, snow, and sleet at intervals, until Friday, the 8th of February, when we found we had passed the Horn, and were fairly in the Pacific.
About this time an occurrence transpired which shows a seaman’s love of a good joke, even at the expense of an officer. It appears our third mate, Mr. K.,69 whom we have before spoken of as a very pompous, great-I-and-little-you sort of a man, was much opposed to the men enjoying themselves in any manner if he could prevent it, and, for this reason, they were continually devising some plan to torment him. He had given express orders that no one of the watch should go below during their watch on deck. Mackey, who much preferred the warm forecastle to the cold deck, would skulk below every opportunity he could get. Mr. K. went forward on this occasion, and, as usual, Mackey was enjoying a fine nap on a chest. Mr. K. ordered him on deck, telling him “if he caught him in the forecastle again that night he would break his head,” and then strutted aft. It was not long after this before one of the watch sang out, in a voice just loud enough to be heard aft, “Mackey, you had better come up on deck; if Mr. K. catches you down in the forecastle, he will surely kill you.”
Then another sings out, “Mackey, come up out of that; the third mate is coming.”
Mr. K., who had been listening, rushes forward with a determined air; “he would show that Mackey that he had got to walk chalk, or he would break his head.” Arriving at the forecastle scuttle, he cried out, in a voice of thunder, “Come up here, you blackguard, and bear a hand, too.” No answer.
“Do you hear me? If I come down there, I’ll kill you deader than the d—l.” No answer yet. Mr. K., now fairly boiling with rage, cries out, “I’ll fetch you out of that; I’ll show you a trick or two;” and, on turning to go down, espied some one dodging around the foremast that bore a striking resemblance to the missing Mackey. Quickly coming up again, he saw that it was really Mackey, who had not left the deck. He then turned to the men, quite chopfallen, telling them he “never wanted to hear any more such stuff,”70 and, cursing them until he was satisfied, he turned and went aft, leaving the watch convulsed with laughter.
As we were now fairly in the Pacific, with pleasant weather and fine breezes, steering to the northward, we put the boats upon the cranes, the anchors on the bows, and cleared up generally, all hands rejoicing that the stormy Cape had been at length passed.
On the 13th of February we saw our first sperm whale in the Pacific. It was not long after our boats were down and pursuing him before the starboard boat fastened, and the old man brought the “claret” the first lance. Soon we had him alongside, his coat on deck, tried out, and down in the hold. We were now about four months out, with one hundred and eighty barrels of oil, which was a good foundation for a first-rate voyage.
On the 1st day of March, 18—, the welcome news came from aft, “All hands to bend cables,” and soon the massive chains were dragged from their resting-places below, and fastened to the huge anchors, which were got ready for “letting go” in the harbor of Talcahuana, Chili. But there is “many a slip,” etc., and we experienced it here, as we were beating about for nine days, unable to enter port on account of boisterous head winds. At length, however, on the 9th, we got a fair wind, and entered the harbor with every thing set, and “let go” our anchor—the old ship at rest for the first time in four and a half months.
Talcahuana is the sea-port of the city of Conception, and is situated at the head of a beautiful bay, protected from all winds by the high lands inclosing it. At the entrance of the harbor is the island of Karakina, on the north side of which is the passage, and on the south side the false passage, as it is called, not being navigable for ships. Abreast of the anchorage, which is immediately in front of the town, is a small fort, with but few guns, and in a very good position to do execution, with proper management. The houses are mostly one story, and of stone. They are obliged to build them thus on account of frequent earthquakes. They present a very neat appearance, being nearly all painted white, or whitewashed. The streets are rather narrow, but kept very clean. Talcahuana can not boast much of her public buildings, they being “few and far between.” The market, if it may be so called, is very large in proportion to the size of the town, being a wide space of ground, inclosed by high brick walls, with no roof. The church, of which the inhabitants appear very proud, presents much the appearance of an old stone barn. The calaboose, or jail, is an old stone building in rather a dilapidated condition; but the “city fathers,” with a just appreciation of the wants of their “constituents,”72 are engaged in the erection of a new one on a much larger scale.
Immediately in the rear of the town is a fine eminence. On arriving at its summit we found ourselves well repaid for our trouble by the beautiful prospect before us. The busy multitude in the streets below—the neat, bright appearance of the houses—the shipping lying at anchor, with their various national colors flying—the smooth, unruffled surface of the waters of the bay, inclosed by beautiful green hills and mountains—in the distance the blue waters of the Pacific—all united to bring before us one of the most beautiful scenes our eyes ever beheld.
A number of years since the old city of Talcahuana was destroyed by an earthquake, a large portion of which sunk. Where the most thriving part once stood, nothing is now to be seen but a low, marshy waste. Some remains of the old city are yet visible in the town.
The inhabitants speak the Spanish language—are hospitable, good-natured, and, as a general thing, very indolent. They are very loose in their morals, but warm supporters of their religion, which is the Roman Catholic, it being the only creed tolerated. The females are rather dark, very graceful and sprightly, beautiful singers, and some of them are very handsome. The town is filled with “Paulparee,” or rum-shops, which are frequented principally by Spaniards and seamen.
On Monday, March 11th, we commenced getting off water and fresh provisions, such as potatoes, onions, turnips, etc. In getting off water, two boat’s crews are generally dispatched to the watering-place with a “raft of casks,” which are filled and towed to the ship, and then hoisted on board. In this manner four or five hundred barrels of water are obtained in about two days—a sufficient quantity for a six months’ cruise. By some fortune or misfortune, Mackey was one of the crew dispatched73 to the watering-place, and, while there, he thought he would take an observation of the country round about. Accordingly, he wandered some distance to the top of a high hill, and, while much engaged in viewing the beauties of nature, two or three “vigilantes,” or policemen, appeared, and demanded of him “what he was doing there.” Mackey replied, “Nothing, but looking at the country.” They then asked him if he had a pass (which is a necessary article to every person while on shore), and Mackey was obliged to confess he had not, when they very politely offered to show him “the elephant.” Mackey begged to be excused, declining their services; but the vigilantes were not to be put off. There was no help for him; go he must; he was in a fix; so off he marched, muttering about liberty, etc., until they arrived at the calaboose, where he was snugly quartered.
The next day, being on shore, we thought we would give Mackey a call, and see how the poor fellow fared. We found him in excellent spirits. He said he “had just as lief stop there as not; for, if he was on board the ship, he would have to work, and there he got plenty to eat and had nothing to do.”
To-day the town was filled with Californians and sailors—some trying their hands at riding on horseback, and rather comical work they make of it. Others are exploring the town, chatting with pretty girls, bantering with the Spaniards, or enjoying themselves in dancing. Some of them require considerable sea-room, whether it is from the effects of coming ashore after a long passage, or the spiritual influence of the aguadente, we can not say. However, they appear to be perfectly at home and contented.
Chili has a very mild and wholesome climate, and is very fertile. Large quantities of fine wheat are raised, and agriculture generally receives much attention. Apples,74 peaches, and pears are raised in abundance, while grapes are cultivated to a very great extent, principally for the purpose of making wine, which is said to be of a very superior flavor. The face of the country presents a rolling appearance, with occasional high hills, and in the distance are seen, towering above the clouds, the snow-covered peaks of the Andes.
Chili is also renowned for its extensive mines of silver, gold, and copper, which, however, are not worked so much at present as formerly. The government is republican, and quite liberal in its views.
The next day, Friday, the 15th of March, we devoted to riding through the country. The horses here are well trained, but, to one unaccustomed to the Chilian mode of guiding them, ludicrous incidents will sometimes occur. If you wish to turn to the left, you must pull the right rein, and vice versa. They are very tender-bitted, and a slight jerk of the reins will bring the horse to an immediate stand. It is very common to see a rider urging his horse to a full run, and, not understanding them, pull the reins in order to sit secure, when, lo and behold, the horse suddenly stops, and the rider keeps on going, measuring his length in the road some distance ahead.
While strolling about town in the evening, we heard low musical sounds proceeding from a house near by. On presenting ourselves at the door we were cordially invited to enter, and were immediately ushered into a large, square room, filled with Spaniards of both sexes. On a table at the farther end of the room was the corpse of a beautiful child of about two years of age, in a sitting posture. Its little arms were crossed on its breast; the sweet, heavenly smile that still lingered on the features of clay, and the fresh, rosy cheeks, gave it a most beautiful and angelic appearance. Our first conjecture on entering the room was that it was wax-work. It 75 was dressed in white, and decorated with flowers. On the table were a large number of wax tapers burning, while the wall around and above was covered with paintings of the Crucifixion, Virgin Mary, etc. In one corner of the room some seven or eight persons were chanting the solemn death-chants of the Catholic Church, accompanied by several guitars. The parents of the child were seated on a low bed, mourning and sobbing in a most piteous manner, while several relatives, as we supposed them to be, were gathered around, endeavoring to comfort them in their affliction.
We advanced by invitation and saluted the corpse, and, as our eyes were fixed on the lovely image, we thought we could almost perceive it answer our gaze by a sweet smile, so fresh and life-like did it look. It was truly a solemn, mournful, and yet beautiful sight. Still, the appearance of the bottle disgraced the scene, as it was passed from one to the other, although it is customary at all Spanish wakes.
On the morning of Saturday, the 16th of March, we found that five men had deserted from the ship. The liberty of the remainder of the crew was therefore stopped, which appeared to cause considerable dissatisfaction. However, this was the only course left for the captain, as most of the men on board had made up their minds to desert in order to get to California. Stopping all communication of the crew with the shore must put an end to the desertions.
This state of affairs continued until the following Monday, when the crew, being so very much dissatisfied, sent a petition to the American consul requesting to be discharged from the ship. He came on board, and all those wishing to be discharged were ordered to take the starboard side of the quarter-deck. The captain, by request of the consul, inquired of each separately his reasons for wishing to be discharged. Some gave as a reason76 that they did not like the business; others, that they had been ill treated; and one, that he was under age when he shipped, and he wanted to go home. The consul could scarcely refrain from laughing outright at such reasons, and finally told them he could not help them. As they had signed the ship’s articles, he could not interfere in the matter; the captain was the man to settle that.
Mackey, who had been intently watching every word that fell from the lips of the consul, thought it about time for him to put in his oar, and, speaking out, said he “had been abused at various times, and once had been kicked while at the helm.” The officer who had taken this liberty said that “Mackey was asleep at the helm one night, and he gave him a slight kick, just sufficient to waken him.” The consul replied that he could do nothing about that. Mackey now broke forth with great earnestness: “I thought American consuls were sent to these places to protect and defend American citizens, whether sailors or captains; but you say you can do nothing about it. What are you good for, then? What business have you here? You might much better be at home about your business. Any way, you are good for nothing here but to pamper to every captain’s wishes that will give you a cake of hard bread and a pint of beans.”
This speech Mackey delivered with great gusto, making flourishes that would have shamed an orator. The speech, of course, “brought down the house,” and caused a broad grin upon the countenance of all. The consul took it very coolly; the men were sent forward, and he, in company with the captain, left for shore.
And here we would remark that in many cases Mackey’s words were true. It is a shameful and lamentable fact, that in many instances American consuls regard seamen as “having no rights that they are bound to respect;”77 and it is often the case that masters of vessels who have been ill treating their men will, on entering port, present the consul with a small quantity of provisions, or something of that kind, and the result is, that no “foremast hand” from that ship can obtain justice from the consul. We make no comments on this; we simply state the facts, and let our readers make their own.
Our crew were now heartily sick and tired of port, and longed to be on the “open sea” again. On Wednesday, March 20th, while all hands were at breakfast, Mackey determined to make one more effort for his liberty. Accordingly, he made his clothes up in a nice little bundle, fastened them on his back, slipped cautiously down the cable, and struck boldly out for the shore. On his crossing the stern of a ship, the captain of which had just come on deck, and espying a man swimming, hailed him:
“Where are you going, my man?”
“Going ashore; where do you suppose?” shouted Mackey.
One of our officers, happening to come up on deck at this moment, thought he saw something black bobbing up and down in the water quite a distance off. On looking with the glass, it was found to be Mackey, with his bunch of clothes on his back, and almost ashore. A boat was immediately lowered and went in chase. Mackey espied it coming, and struck out manfully; as for dear life he swam, but it was of no avail. When nearly to the shore, he was taken and thrust into the bottom of the boat, brought on board, and put in irons. A ship’s company near us mounted their rigging and gave “three cheers for the man who attempted to swim ashore!”
At 10 A.M. of that day we weighed anchor, and, with beautiful weather and a fine breeze, left the port of Talcahuana.
We were now fairly at sea again, cruising for whales. We were now, as is customary for whalemen alone while on cruising ground, standing “boats’-crew watches.” It will be recollected that in a former chapter we explained the “regular watches” of a ship’s company; but this is something entirely different. The ship’s company are now divided into three equal portions, and each watch has only “four hours out” each night and “eight hours in,” instead of four and eight hours alternately, as in the regular watches. They are regulated so as to alternate them every night, and are generally “headed” or in charge of the boat-steerers.
It was during one of these watches, on the morning of the 25th of March, that a boat-steerer and five foremast hands took the bow boat from off the cranes and deserted the ship. The boat-steerer who left was the one who headed the watch. It was blowing quite fresh from the southeast at the time, the ship standing to the westward under double-reefed topsails. The plot had probably been concocting for some days, as they took with them, in addition to most of their clothing, all the boat sails and a quantity of provisions and water, disabling the other boats by taking the “thole-pins” and hiding them. It was very rugged weather, and the experiment was dangerous, as the ship was going through the water about six knots. They succeeded, however, in getting clear.
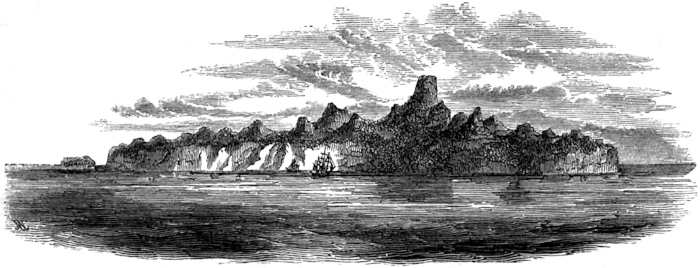
81
As soon as their absence was discovered, all hands were called, sail made, and we tacked ship and stood in for the land, which was about one hundred and eighty miles distant. At daybreak the captain offered a reward of one hundred dollars to the person who should first raise the boat from the masthead, but the reward was never claimed.
The man who was at the wheel at the time the boat was taken said he knew nothing about the boat going, although the boat-steerer came to the binnacle and took one of the ship’s compasses before his face. He said he thought the man wished to fix the compass. The captain was very much enraged, and could hardly keep his hands off the man.
After cruising a few days for the missing boat, and seeing nothing, we squared away for Juan Fernandez. The remark that “we see something new every day” is as applicable to whalers, and perhaps more so, as to any thing else. We now had something new, a public auction; the public, the ship’s company; the auctioneer, the captain; the “stock,” not Central Railroad, nor yet La Crosse and Milwaukie bonds, but the clothing and other valuables (!) left on board by deserters. This is the usual practice on board of whalemen, and we had several “public auctions” during the voyage.
On Tuesday, April 2d, 1850, we first sighted the island of Juan Fernandez, and the next day sent a boat on shore for peaches. Another boat and crew were dispatched fishing. This island looks beautiful from the sea, being very high land, and completely covered with verdure. Peaches and quinces grow here in great abundance. Wild goats are also found here in large numbers. There was but one family living on the island at this time, the head of which, we believe, was governor! We need hardly repeat here that this island is famous for having been the residence of Alexander Selkirk, a Scotch sailor, who was put ashore some years since, and remained a long time on the island, his adventures giving rise to the well-known story of Robinson Crusoe. The cave spoken of in that work as “Robinson Crusoe’s Cave” is still pointed out, whether the true one or not we are unable to say.

We now returned to the ship with our fish, etc., after having spent most of the day with poor success, and lost our boat-anchor. We found the other boat had arrived with peaches and quinces. We altered our course and steered north.
The next day we saw the island of Masa Fuero, very similar in its appearance to Juan; and on the 10th sighted the islands of St. Felix and St. Ambrose. They present a rocky, barren appearance, and are uninhabited except by sea-birds, who flock there in great numbers.
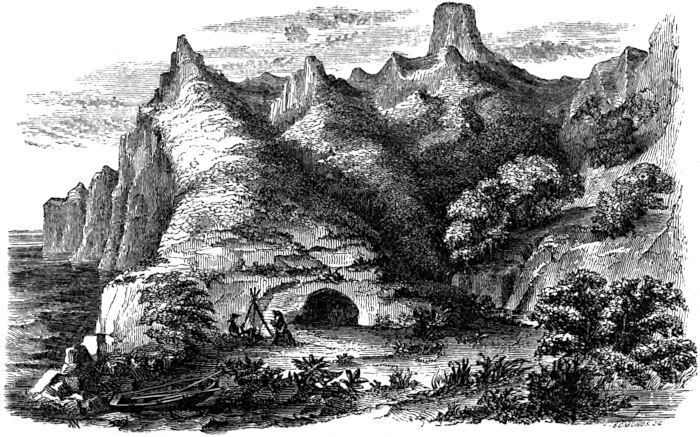

On the 17th we saw the island of San Lorenzo, off the town of Callao; and the next day we were “standing off and on” in the Bay of Callao, Peru. Our captain here went ashore to obtain medical advice and assistance for Mr. Lowe, our second officer, who has been for some time off duty, sick, his right side being affected with palsy.
85
This town is well laid out, the houses mostly one story. The streets are of good width and clean. This city was also destroyed in 1746 by an earthquake, and remains are yet to be seen as gloomy monuments placed over the ill-fated persons who were thus suddenly cut off. There is a railroad building from Callao to Lima, which is but seven miles distant. About 4 P.M. the captain and Mr. Lowe returned, and we filled away for Payta.
On Thursday, 25th of April, we were off the anchorage of Payta. The land here presents a bleak, barren appearance; not a tree or shrub in sight; nothing but sand and rocks as far as the eye can reach. Water is furnished the inhabitants by persons who make it a business, and bring it a long distance in skins on mules. The streets of this town are narrow and dirty; the houses are miserable; women and men dissipated and ugly-looking; fleas abundant, and loafers plenty.
While on shore here the captain shipped three green Peruvians, who answered to the cognomens of Manuel Maria, Tom, and Jack; the last two soon getting additions to their titles, making them “Spanish Tom” and “Nigger Jack.” We now squared our yards, made sail, and bid farewell to this outlandish hole, and also to the South American coast. We here spoke and gammed with the “President,” of Nantucket, and the “Marcus,” of Fairhaven, bound home. This gave us another opportunity of sending a line to the “loved ones at home,” which we were glad to improve. One of our boat-steerers, having been on the sick-list nearly all the voyage, expressed a wish to return home in the “Marcus.” Accordingly, an arrangement was soon made between the two captains, and we took a Mr. Smith in exchange. All bid Gifford an affectionate farewell, hoping he might87 be spared to reach his native land, and be restored to the bosom of his family. Farewell, Gifford—a long farewell. You are going to your own dear home; you will soon be clasped in the embrace of a dear mother and affectionate sisters. God grant that your life may be spared, that you may enjoy these blessings.
We are bound for the cruising grounds to the westward, with some three or four years yet before us ere we can behold those that are near and dear to us; and how many of our small company may be spared to again tread their native shores, God alone knows. Let us yield a cheerful compliance to the will of the Almighty, knowing that we are safe in His hands, and in faith say, “Thy will, not mine, be done, O Lord.” With heavy hearts we squared our yards and headed for our cruising grounds.
On Monday, May 13th, spoke ship “Rebecca Sims,” of New Bedford, with whose ship’s company we passed a very pleasant day. How cheering to the lone mariner while cruising, with no land in sight, and thousands of miles from our own home, to meet a ship from the same port, and a crew speaking the same language as ourselves! It is like meeting old friends.
On Saturday, the 25th of May, we raised a school of sperm whales. We immediately down boats and after them. After some pretty hard pulling, the chief mate’s boat fastened to a cow whale, and killed it. During the melee the boat was badly stove, and our giant Manuel, the Portugee, knocked overboard. The whale was running with great speed at the time, and, as a matter of course, poor Gee was soon left a long distance astern. However, one of the other boats, seeing what had transpired, came to the rescue, and Manuel was picked up. When they reached him he was striking out manfully for the boat, which was now miles ahead of him, and calling on all the saints in the calendar for help at the88 top of his voice. He was an excellent swimmer, but greatly frightened; so much so that some of the boat’s crew that picked him up declared that he was ten shades lighter. At sundown we had the jacket of the whale on deck.
The next day was Sunday, but not Sabbath. On all whalers, while at sea, mast-heads are manned, whales chased and captured, cut in and tried out on Sunday as much as any other day in the week. Nothing else, however, except what is absolutely necessary for navigating the ship, is done on this day, which is generally spent by the crew in reading and writing. To-day, while all hands were busily employed in cutting up the blubber, trying out, and clearing up the decks generally, the mate missed our friend Mackey from his post, which was to assist in hoisting the blubber from the blubber-room. He accordingly went forward to the forecastle, and, calling out, asked him what he was doing below.
Mackey replied, “Breaking out my chest to get a chaw o’ tobacco.”
“But would not any of the men on deck give you a chew?”
“No, sir, I don’t believe they would,” replied he, coolly.
“Well, just point yourself out of that, aft, to the main hatchway, and get up on the bitts, and stand by to hoist that blubber on deck. Now, mind, don’t let me have to look after you again, if you do there will be trouble; stay there till I call you down!”
Mackey took the place, and appeared perfectly contented with his new position, as he could sit down. Presently the mate sang out, “Come this way, all of you, and shove this case overboard.” It had just been bailed, and was now ready to launch into its native element, from which it had been taken. After tugging and shoving for a long time to no purpose, the mate89 looked around to see if any one was missing, and, not seeing him, called out, “Where is that Mackey?”
“Here I am, sir,” shouted Mackey, sitting at his ease on the bitts, looking on with perfect indifference and composure.
“What in the name of goodness are you doing there?”
“You told me to stay here till you called me, sir,” said Mackey, not loving work well enough to offer his services until he was called on.
“Get down out of that, you blackguard, and come here where the work is.”
Mackey left his stand amid the roars of the crew; the mate himself, who could always appreciate a good joke, could not refrain from joining in the general laugh.
On Tuesday, May 28th, we had most delightful weather, and the evening was one of those beautiful, mild, calm nights so common to the Pacific. With gentle breezes, we were slowly plowing our way to the Marquesas Islands. The stars shone forth in all their resplendent beauty, and not a cloud was to be seen in the whole face of the heavens. It was truly a lovely night, and the all-pervading stillness seemed to remind us of our own loneliness, and our thoughts naturally reverted to other scenes—to the far-distant home; to the dear friends and loved ones to whom we bid a hasty but sad farewell. Do these dear friends ever bestow a thought or breathe a prayer for the welfare of the wanderer? Were they thinking of the one far, far away? and when they assemble around the festive board, or form the family circle about the fireside, do they miss the absent one? Oh, what joy would it have been to have known that there were some in the land of our birth that missed us, and prayed for the return of the wanderer! What joy would it have been to know that our friends were enjoying that blessing, health! What a consolation 90 to have been assured that they were spared the ravages of disease and death! But this pleasure was denied us. Thousands of miles of blue water rolled between us and our homes. What recollections crowd upon the mind at the mention of home! The dear old village, where we have sported with all the joys of youth—the old school-house, where we for hours and hours have sat trying the patience of the teacher, conning our lesson, perhaps, or engaged in some mischief—the stream, along whose banks we have so often strolled, listening to the merry carol of the birds, and annoying the finny tribe—the hills, over which we have rambled with boyish glee—the woods, in whose pleasant retreats we have passed so many happy hours—schoolmates, the beautiful fair ones—and lastly, though not least, dear parents, brothers and sisters—all rushed through the brain in a tumultuous whirl, and we found ourselves unconsciously sighing for the pleasures of home. But, alas! we awoke to the sad reality of our situation. Thousands and tens of thousands of miles of blue water, must be beat ere we could again clasp in our arms those we held so dear; and we could only look up to Him who “ruleth the waves,” and trust in His protection. What consolation to our fainting heart these words: “Be still, and know that I am God.”
The men forward had aroused from their lethargy, and some were whiling away the time singing, others telling yarns; Spanish Jack and Portuguese Manuel were seated by themselves, thumping on an old fiddle; Jo Bob was amusing some of the boys by giving them a specimen of his island dancing and singing. The watch below were in about the same condition, “lying around loose,” listening to a long yarn spun by Lawrence about a county fair that took place down in Maine. As usual, his stories would not “match.” He gave a full description of the whole affair. “The table,”91 he said, “was about three or four hundred feet long, and about six thousand people sat down to dinner at one time!” Some of the boys inquired “what they had to drink.” “Strong beer,” replied Lawrence; whereupon one of the watch said “he had lied to him, as he had often stated that the people down in Maine never indulged in strong drink.” But Lawrence was not to be caught in this manner, and he readily replied, “Well, it was not so very strong; it was made of spruce!” All the watch now joined in a hearty laugh at Lawrence’s expense.
Meanwhile the order of arrangements on deck were somewhat different. It happened that Lawrence’s berth, which was an upper one, was chock forward in the “eyes” of the ship, and one of the dead lights—used for the purpose of letting air and light into the forecastle, which opened exactly abreast his face—was left open. One of the watch on deck, having listened to Lawrence’s yarn, and wishing to have a little sport at his expense, stationed himself over the bows, on the martingale guys, and, as Lawrence rolled over, gave him a bucket of water, dash in the face, almost drowning the poor fellow. As soon as he could speak, for he was terribly frightened, and his bed was fairly afloat, Lawrence commenced jawing about the man at the helm “getting the ship off her course.” It was as smooth as a mill-pond, but he had the idea that the sea had washed in. His sleep was spoiled for that watch below, as the whole watch were shouting and laughing, and he growling and putting on dry clothing.
On Thursday, June 6th, we raised the island of Dominica, one of the Marquesas group. This island presents a beautiful appearance from the sea. The thick groves of the cocoanut, orange, lime, and bread-fruit-trees, with the native huts occasionally peeping out from under the foliage; the mountains in the background, thickly studded with magnolia groves; a beautiful stream of water tickling down the sides of large mountains, here and there inclosed by the trees, are all plainly visible from the ship, and make us long to ramble among them.
A canoe was seen approaching us, and the main yard was hauled aback, when it was soon alongside. The natives were certainly the most singular-looking beings we had ever beheld. They are about medium size, copper-colored, and wear no clothing except a small piece of tappa—a native cloth pounded out from bark—around their loins. Their faces and bodies were tattooed in such a manner that they look truly frightful. Some have a broad stripe running diagonally across the face; others had half the face tattooed; others one eye, with a black mark abreast of it; some the lower half 93 of the face. Their bodies presented all the variations of the kaleidoscope.
The chief, who is quite a dignitary, was “dressed up” for the great occasion. His dress consisted of an old overcoat that reached nearly to his knees, with a large white button tied by a string about a foot in length to the back part, and an old bell-crown “beaver,” about four sizes too large, completely covering his head and ears. This completed his wardrobe, and a truly comical appearance he presented as he approached the captain, pulled off his beaver, pulled out his papers, and presented them with the air of a man of business. The papers were recommends from captains who had traded with him, but he knew nothing contained in them. One of them, of which we obtained a sight, read in this wise: “Beware of this fellow; he is dishonest and a villain; do not allow him to persuade you to go ashore with him.” A nice “recommend,” truly. And here we will remark that the tribe at this bay are cannibals of the fiercest kind, and it would not be very safe for a boat’s crew to go among them.
As we were in haste to reach the Society Islands, we politely took leave of our visitors and the comical-looking old chief, and braced forward, soon leaving the beautiful island of Dominica far astern.
We, in the course of two or three days, passed several of the Societies, and on Saturday the 22d of June, sighted the island of Roratonga, the one to which we were bound. The island, like all those in the tropics, especially those composing the Marquesan and Society group, presents the most rich and beautiful appearance. The land, as it recedes back from the sea, rises to a considerable height, and is dressed in the brightest green foliage; the sandy beach, washed by the never-ceasing rollers, with the neat white houses quietly reposing beneath the thick shade of the myriads of cocoanut, orange, and94 banana trees, renders it the most beautiful island we have ever beheld. As we stood viewing it from the ship, while drawing nearer and nearer, we could but imagine it to be some Eden of happiness, where yet the passion of man had not stepped in to mar and spoil its beauty. But even here we found that the “serpent” had entered and filled it with sin.
There are three villages on this island, named New York, New Bedford, and the one at which we stopped, Roratongo. We believe there are about eight hundred inhabitants in this village. From appearances, they are not very cleanly in their persons, and are rather forbidding. Most of them, however, wear European clothing, which they obtain from ships. They endeavor to make themselves very friendly, and, as soon as you land, they throng about you as numerous as runners in Albany on landing from a North River steam-boat, exclaiming, in very good broken English, “How de do, my fliend? You be my fliend? Go my house; me got plenty fruit my house.” Each one does his best to make you understand he is your very particular friend; very disinterestedly, of course, as we found to our cost. We accepted the invitation of one of these, who would have it that he was our very particular friend—in fact, he almost claimed relationship—and accompanied him to his house. On arriving at his “house,” we found it to be a long stone building, whitewashed, consisting of but one apartment, with a curtain or screen in the centre, which probably served as a partition, making two rooms. The inmates consisted of two or three young, dirty, ugly-looking females, one of them cross-eyed, and another that had lost an eye, and an old lady, who kept up a constant cry, begging for tobacco. “Too much sore, my toose; small piece bacca.” We soon found this “sore toose” very prevalent, and “bacca” the universal remedy—the great cure-all. After supplying their “immediate necessities,”95 we sat down to eat some oranges and bananas offered to us. This island abounds with all kinds of tropical fruit, and we soon struck a bargain for all we wanted; and, on arising to go, found they had stolen all our tobacco and pocket-knives. They are expert thieves and arrant rogues; no dependence can be placed on them.
The English have a missionary station here, established several years since. Some of the natives like the present missionary, and some do not. The chiefs or rulers uphold him, but the “people” say he is “no good;” he makes them “work too much.” One of them informed us—and we afterward found it to be true—that if a Kanaka failed to attend church on Sabbath, he had to pay the missionary one dollar, either in money or fruit; if he smoked on the Sabbath, the same penalty; and several other petty tyrannies are practiced, which has the effect of causing the natives to hate the missionary and the Gospel he teaches, and shows that unprincipled as well as good men are sent out, though not known to be such by those who send them, to spread the Gospel among the heathen. If a native wishes a Bible, he must pay the sum of one dollar for it, and the same if a sailor wants one. Such things as these tend more to cause a feeling of hatred against the missionary and his work than of love.
On this island is the grave of the Rev. John Williams, the pioneer missionary, who was universally beloved and respected by the natives. He was a noble as well as a good man, and was actuated by none but the purest motives. He faithfully labored to enlighten the heathen, and to diffuse the glorious blessings of the Gospel of Jesus Christ among them, and his labors were greatly blessed. After establishing several missionary stations, he went to the island of Tanna, one of the Hebrides, where the natives were cannibals, and groveling96 in the darkest superstition. On attempting to land, with a desire to create a friendly feeling with the natives, they rushed for him, and, as he attempted to reach the boat, he was struck by a spear and killed. They hauled the body clear of the beach, and refused to give it up. However, we learn they have since delivered up the remains, which were taken to Roratonga and buried. Thus perished this great and good man, at the hand of those to whom he would have done naught but good.
The staple commodity here is tobacco, which is very scarce, and readily commands a high price. For instance, half a pound of ordinary “plug” will purchase two hundred oranges, and other fruit in the same proportion. The natives, both male and female, are very much addicted to its use—never chewing, but forever smoking.
Quite a number of the natives came on board, wishing to go to sea with us, as they say “too much work ashore.” It appears they are building a church, and they do not wish to work, as they receive no pay. We are glad to be able to say that this missionary station is an exception; that at no other one that we visited during our wanderings were the natives tyrannized over as they were here. We are glad, too, for the honor of our country, that this missionary was not an American.
The government is administered by the queen and missionary, or, we should rather say, the missionary and the queen, as she is merely a nominal sovereign. She is a very dignified lady, weighing about three hundred pounds. Next in rank come the “chiefs,” who are members of the royal family, and, with the sovereigns above mentioned, form the council, or law-making power. Next come the “kikos,” or constables, who see that all laws are properly enforced, and arrest those who are guilty of violating them. As there was a law in force preventing any of the inhabitants leaving the island97 without the consent of the missionary, those who had come on board, wishing to go to sea with us, were compelled to return to land, which they did with sorrowful hearts. Our captain, however, obtained the necessary consent, and shipped three, whom he chose while ashore.
Wood and water all aboard, ship loaded down with luscious tropical fruit, such as oranges, bananas, pine-apples, cocoanuts, limes, lemons, plantains, etc., on Tuesday, June 25th, we were ready to take our departure from this lovely isle. In the last boat that went ashore this morning, one of the crew, by the name of Bob White, a miserable specimen of a most miserable Frenchman, who had imposed upon the captain, palming himself off as a “first-rate steward,” and who had been shipped in that capacity in America, but kicked forward the second day out from home, managed to steal into the boat unobserved, and, while ashore, deserted. All hands, from captain down, were glad to be well rid of him.
When once more at sea, the crew, on looking into chests and examining their possessions, begin to miss different articles of clothing, etc.: one has had his shoes stolen; another a shirt; another his blanket; another his jacket, etc. All appear to have lost something, and they say, if we had remained there much longer, the natives would have stolen us poor.
Perhaps, however, we were well recompensed, as, upon examination when the watch was set, we found that we had three more Kanakas than were shipped by the captain. The old ship had stolen them in return for the natives plundering her crew. The captain was much opposed to this proceeding on the part of the ship, but, as the island was now out of sight, and we were fast leaving it with a fair wind, he consented to their going with us.
98
Our old Kanaka friend, Jo Bob, who had come from America with us for the express purpose of going home and remaining, after being ashore a day or two, came on board, and wished to “go the voyage.” We were very much surprised at this, and at first could not account for it, but presently he “let the cat out of the bag,” saying the “Kanakas had got to work—build meetin’-house,” and, as he was a sailor, he spurned the idea of mixing mortar or carrying the hod. Jo thought the least of the two evils was the old ship; and he might well say that, for he was as lazy as a “Mahone soger,” and had seen easy times on board.
In the evening all hands appeared to be in the best humor possible. The fruit had been freely distributed, and each man had received as much as he wanted for a month. All were busy discussing its qualities, spinning yarns, singing and dancing; while the Kanakas, seven in number, were having their “hula hula,” or dances, accompanied with songs, in high glee. These performances were very interesting to us, as we never before witnessed them. They have what they call their love dance, missionary dance, whaling dance, and war dance. Their gestures, songs, and dances very much resemble those of the North American Indians.
We were now making passage for the “King Mill Group,” which is a group of small islands greatly celebrated for being a good sperm whaling ground. Our captain had filled the same ship in which we now were on this ground but a few years before, and it was to be our principal place of cruising for a year or fourteen months, at least.
And now we come to Thursday, July 4th—the never-to-be-forgotten Fourth of July—our first one at sea. While our friends at home are celebrating the anniversary of American Independence, we are deprived the pleasure of being with them in person, yet we are with them in spirit, and the spark of patriotism glows as brightly in the small company of Americans on board as if we had been within hearing of the booming cannon, the joyful peal rung out by the merry bells, the patriotic oration and sentiment; and, although among the wild Isles of the Pacific, and thousands of leagues from the “home of the free,” yet the return of this day100 sent a thrill of joy through every frame, and we felt thankful to the God who watched over the cradle of the infant nation, who still guides its footsteps as it approaches manhood, and who is ever blessing it with heaven’s choicest blessings. May no American ever fail to render thanks for this anniversary, in whatever clime he may be situated.

On Tuesday, July 23d, we saw the most eastern island of the group, Byron’s Island, and the next day sighted Perote Island. These islands are all coral formations, very low, are inhabited, and thickly covered with cocoanut-trees. On Saturday, the 27th, we passed Drummond’s Island, and sighted Sydenham’s Island. From the latter the natives came off in great numbers to trade. Their canoes are constructed of narrow, thin101 strips of wood, the cocoanut, fastened with small line made from the cocoanut husk; are sharp at both ends, very narrow, and are prevented from capsizing by a long piece of wood placed parallel with the canoe and made fast to it, called the “outrigger.” They have a mast, with a three-cornered mat sail, made from the leaf of the cocoanut-tree, and rigged in such a manner as to admit of sailing in either direction without turning the canoe. They have them of all sizes, from the small one carrying but one person, to the large war-canoes carrying one hundred.
The natives are a wild-looking set of copper-colored beings, in a complete state of nudity, their bodies tattooed, and covered with cocoanut oil, which is their perfumery. They are of medium size, but very powerful. They are all merchants, bringing with them, to trade with ships, shells, fish, mats, cocoanuts, and a species of fruits called “dittoes.” These grow in large bunches, very compact, and similar to figs packed in a box. On the outside of the bunch they are green; on breaking them apart, you find about two thirds of the length, from the inner end, is of a bright golden color, and of an excellent flavor. The currency here, as at most of the Kanaka Islands, is tobacco and pipes, and for this they will follow a ship for miles. As it was near night, we made sail and motioned them ashore.
At this island a few years since, the natives, led on by a Portugee, who was living among them at this time, attempted to take the ship “Triton,” of New Bedford, Captain Spencer. The plot was well laid and matured, and the natives went off to the ship and informed the captain, by signs, they had a fine “fluke-chain” ashore, and wanted to sell it. He asked them where they got it, when they replied, “Kiabuka broke” (ship broke), conveying the idea that a ship had been wrecked here some time previous. As the captain was desirous of obtaining102 a chain of this description, he immediately, without suspecting their dark and bloody designs, ordered his boat to be lowered away and manned. On arriving on shore, and before they suspected any treachery, they were seized and bound. The Portugee then, with a large number of natives, went off to the ship to trade, as they intimated. The crew, when they arrived, were mostly down below, and the third mate was asleep in one of the boats. When the natives had collected on deck in sufficient numbers, they made a rush for the “spades,” which hung overhead on the quarter-deck, and, before any one was aware of what was transpiring, had possession of the deck. They killed the man at the helm, two or three foremast hands, the second mate, steward, and cook, and then proceeded to the cabin, where the mate was lying asleep. He was aroused by the noise, but too late to offer any resistance; they, attacking him, cut and mangled him in a horrible manner, and left him, as they supposed, dead.
The Portugee, who led on the savages, now proceeded to the deck in order to make a finish of the bloody job, massacre the remainder of the crew, who were confined in the forecastle, and then work the ship ashore into the breakers. The third mate, who had become aroused by the noise, but wisely kept quiet until he saw the Portugee passing abreast of him, suddenly darted a lance with such unerring aim that it was driven completely through his body, killing him instantly. The natives were greatly frightened at this, and attacked the third officer, but he managed to elude them, and escaped below. They now fired muskets, which they had taken from the cabin, already loaded, down the skylight, until they saw it was useless, when they directed their whole energies to getting the ship into the breakers. One of the crew happened to be a Kanaka, and they ordered him to the helm, and to keep the ship headed for the103 land, threatening him with instant death if he failed. But he was secretly determined to thwart their horrible purposes, and accordingly kept the ship headed nearly in a contrary direction. As soon as the natives discovered they were leaving the land instead of approaching it, they were about to put their threat into execution; but he made them to understand that he could not steer the ship, knew nothing about it, etc. One of the chiefs then told him to go to masthead and keep a look-out, and he would steer the ship ashore. He immediately mounted the rigging, and with the agility of a monkey was soon aloft at masthead. Not deeming it prudent to make known his purpose too soon, he waited; the ship was gradually approaching the breakers, where she would soon be more than ever in the power of these bloodthirsty cannibals. But the time has come for relief; “Sail ho!” is the cry from aloft; and the rascals are jumping overboard into the water and their canoes, and paddling for dear life to the shore, with fright depicted on every countenance. The brave Kanaka, who had by this stratagem succeeded in saving the ship, now came down on deck and released the men in the forecastle, who, with the third mate, immediately headed the ship off shore, and, supposing the captain and his boat’s crew all murdered, made all sail. The mate, who was left for dead, recovered gradually. After a long passage, they made the port of Honolulu, Sandwich Islands.
The captain, together with his boat’s crew, whom we left on shore bound, were, for some unknown reason, kept still alive as prisoners. The natives finally, at a council held, determined to murder them all. The arrangements were all completed. The captain was first led forth, firmly bound, and, in imitation of our North American Indians, they laid his head upon the fatal block; the executioner, with his massive war-club in readiness, awaits but the word from the chief which is104 to send a soul into eternity. But who is this rushing forward, and, Pocahontas-like, braving the ire of that dread chief, and proudly, firmly demanding the life of Captain Spencer and the white men with him? ’Tis the son of the chief, who, with fire in his eye and determination in every line of his features, tells them “they must not murder the white men; if they do, plenty America Fire Kiabuka come, kill all Kanaka.” The bravery and reasoning of the brave boy-chief prevailed, and their lives were spared, though still kept “in bonds.”
After some weeks had passed a ship came to the island to trade, and, through some one of the natives, the captain ascertained the fact that Captain Spencer and his men were held prisoners. The captain and crew of the ship trading immediately seized and bound a number of the natives on board as hostages, telling the remainder that if Captain S. and his men were not instantly forth-coming, unharmed, those detained on board as hostages should swing at the yard-arm. This threat had the desired effect. Captain Spencer and his men were liberated from their cruel bondage, and kindly received by all on board. The captain proceeded to the Sandwich Islands, where he now resides; and when narrating to us the above particulars, although an old sea-dog, the tear would trickle down the weather-beaten cheek as he recalled to mind the fate of those who were so cruelly murdered, and his own miraculous escape.
On Wednesday, July 31st, we saw Henderville’s and Woodle’s Islands. We headed for the latter, and when two or three miles from land our decks were crowded with natives, all bringing something to trade. A lively scene now presented itself, equaling any of our large trading marts, though not, perhaps, on quite as extensive a scale. Here might be seen a native offering a hat to a sailor, and each one endeavoring to get the best of the bargain; another was offering mats, another shells, and105 so on to the end, all for “’baccy.” At this island we found something in the shape of molasses that we had never yet seen. It is made from the milk of the cocoanut boiled down, and called by them “teka moi moi.” It resembles maple molasses, both in color and flavor, more than any thing else, and was quite a treat to our ship’s company, who purchased large quantities—five cocoanut shells filled with it for one “plug” of tobacco.
Those who have never tasted the young cocoanut may be excusable in eating, and drinking the milk of the miserable things called cocoanuts which are exposed for sale at our fruit-stands. But, to enjoy it in all its delicious fullness, one must eat them when they are green, and when the shell is so soft as to admit of a knife being passed through the husk and shell, as one would “plug” a melon. In this state the nut is full of the rich milk, and, on breaking them open, some are so young that no meat has yet formed; in others it is like jelly; and, as it advances in age, the milk loses its rich flavor, and the meat becomes hard and oily.
The natives of this island are shrewd customers, and drive a bargain with all the tightness of a Jew, bantering until they find they can obtain no more, and then sell. In one respect, however, comparatively speaking, they are easily satisfied. A “head” of tobacco goes a great way with them; and he is considered a rich man among them who becomes possessed of two or three “heads.” They appear, also, to be much better natured and better looking than any we have yet seen; have more of that noble, manly appearance than those of Sydenham’s Island. They are much larger, also, and many of them wear the “tappa” about the loins. The females are very fair-looking, with regular features, small and delicate in size and structure, and appear very graceful and sprightly. They are very cleanly, and when they come off to ships have their heads decorated with wreaths 106 of wild flowers, and generally a bunch in each ear as a substitute for ear-rings. They are merry creatures, always laughing, and showing teeth of pearly whiteness, that any woman might be proud of, which are not manufactured for the occasion by a dentist. Were they white, they would create no small sensation among the belles and beaux of America; and we have seen some who have just color enough in the cheek to make them truly beautiful. In fact, it is rather a dangerous affair to be placed amid such fascinating creatures after a long cruise, and having seen none but our own ship’s company. From the affectionate glances bestowed by some of our sailors upon the dark-eyed beauties, we fear they will leave their hearts behind as well as their tobacco.
The sea between the ship and the shore was completely covered by myriads of canoes, some going ashore, and others paddling for the ship. We were thus trading about four hours, till, having procured all we desired “in their line,” we bid them adieu, and turned our thoughts to whaling.
Thursday, August 8th, we again sighted Sydenham’s Island, the natives coming off as usual to trade. One can not but notice the difference in the appearance of the natives of this and Woodle’s Island; yet they are only sixty miles apart. Those of the latter have a noble, manly look, are smooth-skinned and good-natured, while those of the former are a sullen, inferior-looking set of beings, many of them scaly or rough-skinned. They have a regular hang-dog, villainous expression, that plainly says “plunder and murder.” The females are even worse than the men, being very masculine in appearance, manners, and speech, with high cheek-bones, and mouths that would drive a hungry man crazy. They are very indolent, and seldom bring of any trade, a few fish or shells generally comprising the whole assortment.
107
The next island we saw was Simpson’s, but passed it without stopping. On Friday, August 16th, we spoke the ship “Narragansett,” Captain Rogers, soon bound home. We enjoyed a very pleasant “gam” with them, they all feeling very happy, thinking they would so soon be homeward bound. We could but wish them joy, with a safe and quick passage home.
On the 2lst, Tuesday, we lowered for whales. One of the boats succeeded in fastening to a “cow,” and, after some running, sounding, etc., she began to think it “boys’ play,” and about time to end the sport, and coming up under the boat, gave it a rap that knocked it into “kindling wood,” and hoisted the boys a pretty good distance in the air. Appearing perfectly satisfied with this part of the performance, she departed for “parts unknown” with two irons and about eighteen hundred feet of line attached to her. The crew were picked up after a bath of about an hour. The next day saw whales, and concluded to try our luck again. The waist-boat finally succeeded in fastening to a large fat cow, and all hands were chuckling over the idea of having outwitted this one, when lo, and behold! her majesty turns and bites the line in two as coolly as you please, and makes off. The boys returned on board, acknowledging that “there’s many a slip ’twixt the cup and the lip” in whaling as well as every thing else.
About this time Mackey and Tom W. had quite an extensive argument on mesmerism. Mackey was a great skeptic, but finally agreed to become a sound believer and disciple if Tom would mesmerize him. To all this Tom readily consented, and preparations were accordingly made with the gravity and demeanor of a regular professor of the humbug. Strict silence was imposed upon all hands; not a word was to be uttered, not even in a whisper, or the spell would be broken. Two tin pans were introduced as “mediums,” and Mackey was108 instructed to hold one with the bottom toward the mesmerizer, and look him steadily in the eye, while he took the other in the same manner. Tom now informed Mackey that he must do exactly as he did—go through with the same motions, etc.; to all of which he readily consented, and the manipulations commenced. Unfortunately, it happened that the bottom of Mackey’s pan had been smoked considerably, if not more, and as Tom would draw his fingers around on the bottom of his own pan (which was clean), and then over his face, Mackey would “follow suit,” and by this operation his face soon began to assume the appearance of a striped zebra. The hands were then changed, and the other side mesmerized in the same manner. After Mackey was nicely blacked, so that it was almost impossible to tell whether he most resembled an Indian painted for the war-dance or the aforesaid striped zebra, Tom said he guessed he would have to give it up; there was too much noise on deck, and his “mediums” did not work well; but asked him if he did not feel sleepy. Mackey stoutly denied being sleepy, and said he knew it was all a humbug—couldn’t fool him; saying which he started aft for a drink of water. The watch on deck were employed mending sails, and, as Mackey rolled along, they all broke into one simultaneous roar on beholding his comical physiognomy. The mate asked him if he “was sick.”
“No, sir,” replied Mackey, boldly.
“Well, then, what is the matter with you? You look very pale!”
Mackey knew hardly what to say to this, but finally replied, “One of the watch has been trying to mesmerize me, and it might have affected me some.”
The mate told him he had better go below and turn in instantly, as he was sure something ailed him. This frightened Mackey, and he hastened down, got out his looking-glass, and, at the first sight, dropped it. However,109 he mustered courage, and looked again; then at the watch, who had all assembled about him in perfect silence; then at the pan; and, after a few moments, the light broke in upon him, and he exclaimed, “Sold, by thunder!” and rushed on deck to try the virtues of salt water and oil soap, greeted with a perfect storm of laughter from the watch. It is useless to add that Mackey never after, so long as he remained with us, had any thing to say upon the science of Mesmerism.
We were now getting down to the more westward of the group, and on Sunday, the 25th, saw Pitt’s Island. This is one of the finest-looking islands of the whole group; the land being higher, with more verdure. The next day we saw Knox’s Island. The natives of this and Charlotte’s Island are now at war, instigated, we are sorry to learn, by the base conduct of an American whaling captain, who has taken sides with one party, and who takes great pleasure in slaughtering those of the other side.
Whenever the boats are off after whales, a certain number of the ship’s company remain on board to work the ship, who are called “ship-keepers.” One of these ship-keepers was “Nigger Jack,” whom, the reader will recollect, we shipped at Payta. It appears he was in the habit, at these times, of going down into the forecastle, and pilfering whatever he saw that would strike his fancy. He also was troubled very much with a sweet tooth, and would help himself to the other men’s allowance of molasses, not touching his own. This kind of work went on for some time, and, as the men could prove nothing, they kept quiet and waited, Micawber-like, 111 for something to “turn up.” The opportunity soon came. The boats were all off after whales, and our Spanish darkey was, as usual, spending his time below, when one of the other ship-keepers, going into the forecastle, caught him in the very act of helping himself to molasses from the allowance of Portugee Manuel. He said nothing to him, however, but waited until the men returned for the opportunity of “opening the ball.” It so happened that, on this occasion, the men were down all day, from 7 A.M. to 8 P.M., with little or no food, and came on board, without having fastened, nearly exhausted with pulling, hungry as bears, and in none of the best of humors. Supper was sent down, and Manuel went to his keg to get some molasses for his “duff,” but, to his surprise, found it empty! His Gee blood was up in an instant, and he sang out, “What man been takey my molass?” Some one replied, “Nigger Jack;” and, before the darkey could contradict it, the heavy molasses keg struck him, bim! full in the face. The blood flew on all sides, and he ran for the deck, and, fully believing that he was about to “kick the bucket,” commenced chanting the Paternoster, occasionally interspersing it with exclamations of “Muerto! muerto!” signifying “Killed! killed!” in a most pitiful tone. But he was suddenly interrupted by an order from aft to present himself. He crawled off, and, after a long time, succeeded in making the captain understand what the difficulty was. Manuel was now sent for, who sputtered out his side of the story, in half English and half Portugee, to the no small amusement of the captain and officers, and appeals to the person who saw the theft committed. The old man reprimanded Manuel for throwing molasses kegs, and told the Spaniard that if the men caught him stealing again, they would, in all probability, kill him outright, and sent him off about his business. There is nothing so much despised on board ship as these petty 112 thefts, and he who commits them generally leads a hard life.
We here saw the bark “Belle,” of Fairhaven, Captain Handy. This vessel was engaged in trading at the different islands for cocoanut oil, which was sold in Sydney, New South Wales.
On Thursday, September 26th, we picked up part of a ship’s topmast, and, on sighting Sydenham’s Island, discovered the hull of a vessel fast ashore on the reef, with her lower masts standing. Our captain intended to take a boat and ascertain something in regard to this ill-fated vessel, but the wind died away before we approached within a proper distance, and the current soon drifted us far away.
The next day we spoke the “Boy,” of Warren, Captain Luce. From him we ascertained the vessel ashore at Sydenham’s to be the bark “Flying Fox,” of Hobarton, Van Diemen’s Land, Captain Brown, who, with his lady, and several of the officers and crew, were on board the “Boy.” It appears, by the captain’s statement, that on the morning of the 25th they were sailing along with a fine breeze, all sail set, when they were suddenly startled by the ship striking a reef which projected two or three miles from the island, and was not laid down on the charts. The topmasts were all carried away by the shock; the ship was fast on the reef; and, had there been a heavy swell, she would have gone to pieces immediately. As all hopes of saving the ship were at an end, on seeing their situation they took to their boats as soon as possible. Already were the decks crowded with natives, who had begun the work of plunder, helping themselves to whatever they wished. They obtained possession of the spades, and were ready and willing to fight, if necessary. The captain had to work very cautiously to get his wife into the boat without being seen by the natives; and, closely veiled, she was placed in 113 the boat, choosing the mercy of the winds and waves rather than that of a barbarous set of cannibals, in whose hands she would have suffered worse than death.
The next day, the boat containing the captain and lady, with some of the crew, were picked up by the “Boy.” The remainder of the crew, it was supposed, had gone to Woodle’s or Simpson’s Island. The captain of the “Boy,” on learning the particulars of the sad accident, proceeded immediately to the wreck; but the natives had not been idle; they had carried off every thing of value, and that which they valued not had been destroyed by them. The water and oil casks had been stove for the sake of the iron hoops which bound them.
On Thursday, October 3d, we traded with the natives of Hall’s Island. Cocoanut oil is the principal trade brought off here. The natives on the islands north of the equator look much better than those of the same group situated south of it.
We were now getting short of water, and the captain determined to land a raft of casks at Pitt’s Island, leave them for the natives to fill, and return for them in a few days. Accordingly, on the 16th, we sent a raft ashore, three boats towing it. We had now been out of port nearly seven months, and most of the crew were becoming discontented—thought it was about time they had a run ashore, etc.; and some of them expressed the determination to have it, if the opportunity offered, at Pitt’s Island. The officers having charge of the boats were ordered not to land, but to deliver the raft to the natives and return immediately to the ship. The third mate, however, who was one of the disaffected, instead of doing this, pulled close in shore, and told his men, if they wished, they could go; he should not hinder them. Two of them immediately jumped out of the boat and went ashore; the boats returned to the ship; and the captain and third mate had some rather plain conversation in regard 114 to the affair. It ended, however, in the old man’s leaving a reward for them, and we made sail.
We took from this island a noble-looking, fine-built native, who is a chief of some importance; but he wished to try his hand at whaling, as near as we could understand by his signs, for he could speak but little English. The captain bestowed upon him the name of Friday, which suited him just as well as any other. He soon became a general favorite with all hands, was very good-natured, quick to learn, as spry as a cat, and as strong as a giant.
We visited the island again on Tuesday, the 22d, for our raft of water. We there learned that the two deserters had sailed in the bark “Belle,” for Sydney, the day previous.
An amusing little incident, common to whaling, but still enough of interest to make it worth relating, occurred on Saturday, 16th of November. The waist-boat had fastened to a cow whale, and were going along very smoothly, when she suddenly sounded, and, by some means, drew the bow of the boat down with her sufficient to “end it over,” and spill out the whole crew very unexpectedly. It happened that two of the men were unable to swim, and, strange as it may appear, they were the first to scramble on to the bottom of the boat (which was upset), and that without wetting a hair of their head; and so anxious were they to keep dry, that they kept the boat rolling over and over, they meanwhile scrambling in the most ludicrous manner. After a little time, and partly by the threats of the second mate and their own fears, they became quiet, and remained so until they were picked up. The whale was killed by one of the other boats, and was soon cut in and tried out.
Monday, November 18th, was a very clear and calm day, not a breath of air stirring, and “old Jamaica” coming down with a vengeance. At daylight the look-out115 from masthead raised a sail a long distance off. About 1 P.M., “Boat ho!” was the cry, and it proved to be a boat pulling to us from the ship in the distance. About 3 they came alongside, and reported themselves to be from the ship “Hector,” of New Bedford, Captain Smith. They had pulled about sixteen miles, under the scorching sun of the equator, with not a breath of air stirring, merely to ascertain if we had letters for them. They were about three years out, and had heard that we were on the cruising-ground, and on raising us that morning hoped it might prove to be the “Emily Morgan;” and such was their anxiety for letters from their friends at home that they gladly pulled this long distance. We were glad that their labor met with its reward, for they received a large package, and soon forgot their fatigue amid the excitement incident to receiving news after so long an absence. About 5 P.M. a light breeze sprung up, and they left us in high spirits.
As we were cruising along on Wednesday, November 19th, with no land in sight, we saw a large canoe, which appeared at the mercy of winds and waves. We immediately bore down to it, and found that it contained twenty-two natives in a starving condition. We lowered a boat, towed them to the ship, and found them so much reduced as to be hardly able to speak, and could get them in on deck only by slinging them in a “boatswain’s chair” and hoisting them in. The canoe was cut adrift after taking out and sinking the dead body of a boy, apparently about fourteen, which it contained. Some of them presented a wretched and distressing appearance; they were nothing but skin and bones, and scarcely that. In several cases the skin on the joints was broken, and the bones had worked through. We went to work and cleared out the “blubber-room,” and by spreading mats around made it very comfortable for them. Their constant cry was “Ki ki” (eat). We prepared116 some farina, and fed them cautiously; but they acted more like a pack of ravenous wolves than like human beings. By the aid of Friday, our Pitt’s Island native, we learned the following particulars: They left their island (Charlotte’s) for another on account of the war raging there, but lost their reckoning, and the current, which sets very strongly to the northwest, swept them off. They had been so drifting for six weeks, and during that time had no food except a shark, which they captured. Four of their number had died, two men and two children. Seven of them were females, two of whom had nursing infants. The poor creatures would fall into a short slumber, and awake crying for food. It was truly a heart-rending sight, but we felt assured every thing that could be had been done to render them comfortable. They endeavored, too, to express their heartfelt gratitude to us by signs, and would cry, “Mortarkee kiabuka” (good ship). As we were near Pleasant Island, the captain determined to land them there.
Accordingly, we sighted it on the morning of Friday, the 21st. About 9 A.M. canoes began to flock off to us in great numbers, and the natives whom we had picked up were sent ashore in them. They had so far regained their strength as to be able to move about quite briskly. The chief addressed the captain in his own language, which was translated by Friday as far as lay in his power, to the effect that they were very grateful to the captain and all hands for the kind treatment they had received; and as the poor grateful beings shook hands with us on passing over the gangway, tears of gratitude trickled down their tawny cheeks. They were placed in the canoes, waved their hands feebly, and started for the shore.
Pleasant Island is a very beautiful island, and well does it deserve its name, if we say nothing of its inhabitants. It is moderately high, and more thickly covered117 with verdure than any island of the group. The natives are the most finely-built of any we have yet seen—large, athletic, and ferocious-appearing, presenting quite a contrast to some of the diminutive natives of the Windward Islands. They speak a different language, also, from that of the natives of the other islands, though but a few degrees apart. They appear far superior to them in shrewdness and cunning, it being much harder to drive a trade with them. The females are very small, very good-looking, and some of them quite handsome, several shades lighter than the men, and much lighter than those of the other islands. We bought quite a number of fowl, and some hogs of the regular racer breed, Berkshires not having been introduced here.
A white man came off from this island, and wished the captain to ship him, as he was afraid to remain on shore. He reported that, the day before, five white men had been murdered by the natives. A part of them were from the ill-fated “Flying Fox.” It appears that they had landed at this island perfectly destitute, and some of the white men residing there, fearing the chiefs would take them under their protection and allow them to remain, thereby diminishing their chances of trade with ships, persuaded the leading chiefs that they came there for the purpose of taking the island and poisoning all the Kanakas. They are so superstitions that, no matter how absurd the story, they believe the white man capable of doing any thing. At the instigation of these rascally “beach-combers” residing on the island, the poor fellows were butchered in a manner too horrible to relate. This man informed us that his life had been repeatedly threatened, and, had not he had the influence of one of the highest chiefs on the island, he would have shared the same horrid fate as the others. The captain informed him he could go with us, at which he was greatly rejoiced.
118
We spoke the brig “Inga,” of New Bedford, Captain Barnes, on Sunday, the 24th. We had here an opportunity of sending letters home via Sydney, New South Wales, as she was bound there with a cargo of cocoanut oil. Captain B. reported that, a few days previous, his steward and seven of his crew took a boat in the night-time and deserted. The steward stole about three hundred dollars from the captain’s state-room, a sextant, quadrant, and charts; the crew took provisions and water. He supposed they had gone to some of the Windward Islands.
Our “Spanish Jack” has got himself in trouble again. For several weeks complaints had been made by nearly all of the crew that their tobacco was disappearing very fast and very mysteriously. From the fact that Jack never bought any, had but little when he came on board, and was continually smoking, he was strongly suspected. One fine morning the captain ordered the mate to go forward and search the Spaniard’s chest. Accordingly, the chest was hauled out and opened. It was well filled with clothing, all new, that he had bought and never worn, which he was keeping, he said, to wear ashore. On looking deeper, several knives were found, which were claimed by some of the crew, and various small articles, which he had pilfered at different times from different persons. Finally, the mate found a large quantity of tobacco, and a tin box belonging to the captain’s son, which he had taken from the binnacle while at the helm. The guilty Spaniard was brought aft, seized by his wrists to the mizzen rigging, his back bared, and a slight dose of “hemp tea” administered, said to be a very excellent remedy for the disease which troubled Jack so much, viz., sticky fingers. He called on all the saints in the calendar to come to his assistance, but they very politely refused, as it is believed they did not strongly object to the medicine being administered. It had one good 119 effect, to say the least; it made him promise that he would never steal again while on board the ship, no matter how small the value of the article. And, in justice to him, we will say that he kept his promise, not from want of a desire to steal, but from fear of punishment.
The idea of flogging a human being is certainly shocking, and the poor fellow who receives it generally has the pity and sympathies of his shipmates; but in this case all hands felt that the culprit got no more than his deserts, for the true sailor despises a thief. The sailor is proverbially charitable; he will see a shipmate want for nothing so long as he can supply that want, even to dividing his last crust; and it is not given grudgingly, but with his whole heart.
We were now making the passage to Strong’s Island, and, on the night of Friday, December 6th, were struck with a severe squall, laying the ship almost on her beam ends. All hands were called to take in sail, but, before the men could get on deck, away went mainsail, foretopsail, and jib. Whew! how the wind whistled and howled! It was impossible for the captain to make himself understood amid the deafening roar of the winds; and the waves, madly pitching and tossing the ship to and fro, seemed to wish to ingulf her in their bosom. It was grand, yet terrible. By dint of hard labor we succeeded finally in reducing the sail, so that she rode easy through the night, the gale continuing with almost unabated fury. The next day a tremendous whirlwind passed astern of us about a mile, and it was through the mercy of God alone that we escaped it. The gale continued, with more or less rain, until Wednesday, December 11th, when Strong’s Island hove in sight, distant about eighty miles.
For nine long and weary months had the “Emily” been from port. During this time but few of the ship’s company had put foot upon land, and glad indeed were we when Strong’s Island hove in sight. We were experiencing heavy weather, but on Thursday, December 12th, the wind gradually grew less boisterous, and as we neared the land, steering for the passage, died away, leaving us at its mouth in a dead calm; but we down boats, and every man “pulled with a will,” and soon towed the old ship in, and at 7 P.M. we once more dropped anchor, weary with labor, but refreshed at the sight of the land, and the prospect of “stretching our legs” on shore once more.
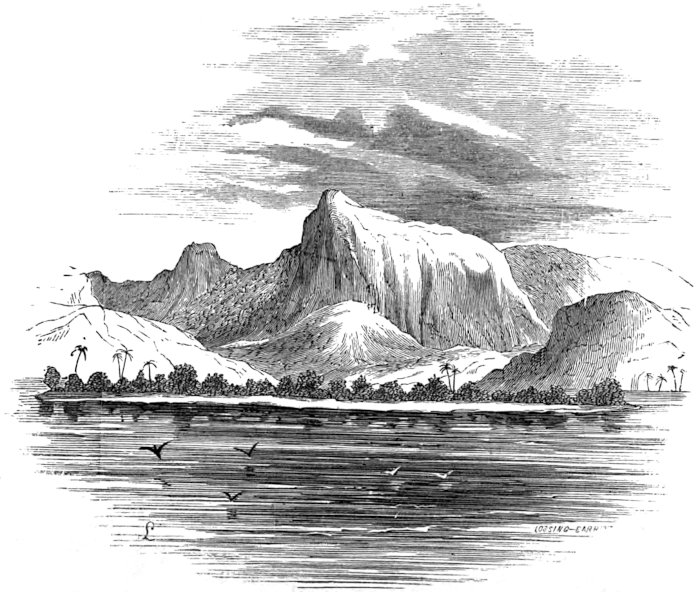

His majesty King Tocasaw, alias King George, accompanied by his eldest son, the Canker, heir-apparent to the throne, and some of the most distinguished chiefs, came off to visit us and welcome us to their island.123 King George is a fine, intelligent-looking native of about fifty. His court dress, which is only worn on great occasions like the present, consists of—a red woolen shirt! Canker has the appearance of a shrewd, unscrupulous fellow, with a most rascally expression of countenance. He is second in command to the king. Cæsar, the king’s brother, is also an intelligent-looking chief, and appears to be full and running over with fun. We were much surprised to find them speaking such good English.
The next morning, on looking about us, we found ourselves in a most beautiful harbor, completely shut in from the sea, lying about fifty yards from the shore. The beach is entirely covered with cocoanut-trees, and the mountains, rising with a gradual slope, expose to view the brilliant foliage of the bread-fruit and mangrove trees.
This island is entirely surrounded by a reef, varying from a few rods to half a mile from the shore. Through the reef Nature has left an opening of about fifty fathoms, or one hundred yards, which admits of the passage of ships of the largest size. The main island is some thirty miles in circumference, and on the north side the shore forms a deep lagoon. Immediately in front of this lagoon is the “small island,” which extends from one extreme point of the bay to the other, being separated on the westerly side from the large island by a few hundred feet of shallow water, of not sufficient depth to admit the passage of a craft of any size, and this is bordered by the reef. On the easterly side of the small island is the passage.
The highest peak of the large island is about two thousand feet above the level of the sea. The king and most of the high chiefs reside on the small island, with many of their tribes, forming quite a settlement. We called at the palace to pay our respects to his majesty.124 He appeared very pleasant and kind to us, and, after presenting us to the queen and two princesses present, set before us such fruit as the island produces. The bananas that grow here are certainly the most delicious we ever tasted, being very small, and are called “sugar bananas.” The productions of this island are the cocoanut, bread-fruit, banana, mummy apples, dittoes, plantains, layees (a coarse species of banana), oranges, yams, and tarra. The bread-fruit serves as their principal food. It is rendered very palatable by being split open and baked, and tasted very good to us, after having lived on hard bread, “duff,” and “salt horse” for nine months. From the tree they manufacture all their culinary utensils and canoes. The island abounds in game, wild pigeons and wild hogs forming the principal part.
After partaking heartily of the fruit the king had set before us, we left, promising to call and see him often during our stay, as he gave us a cordial invitation to do so. We then proceeded to call upon some of the chiefs. On rambling over the small island we found numerous canals cut through in all directions, which at low tide would be nothing but small streams, but at high tide of sufficient depth to float the largest canoes. These canals, as well as some of the roads, are walled up from fifteen to thirty feet high. They are well built, and range from six to nine feet in thickness. We noticed many large stones, which would weigh several tons, placed in the wall some distance from the ground. There is something very mysterious about these walls and canals. As the natives know nothing about them, they say the Evil Spirit built them; and one of the most intelligent chiefs on the island informed us that the oldest records or traditions they have give no account of them whatever.
We also came in contact with what appeared to be the ruins of a large building. It was surrounded by a 125 stone wall, six or eight feet high, on all four sides, with but one entrance, which was by stone steps. We then came to a second wall, somewhat smaller, but similar to the first; and, on ascending a few more steps, came to a level place paved with large flat stones. In the centre were two square deep pits, from eighteen to twenty feet deep, walled up with stone. The natives know nothing concerning this pile of ruins, and only answer your questions with the English word “Devil.” We think there is no doubt but that this island has once been the stronghold of a band of pirates, as every thing about it would seem to indicate. The admirable situation, beautiful and snug harbor, with but a small entrance, in which a vessel might easily be completely shut out from view at sea; the mild and salubrious climate—all these combined would render it a desirable rendezvous. This supposition is not improbable, as it is well known that the Pacific, years ago, was infested by herds of Chinese and Malay pirates, and these very natives bear a strong resemblance to the Malays.
About twenty-five or thirty years ago the island was governed by a king, who, from the accounts given by the chiefs, must have been a perfect tyrant; and during his reign two or three ships were taken and plundered, and all hands massacred. This tyranny had the effect of creating a rebellion, which was headed by Tocasaw, the present king. After a severe struggle the rebels came off victorious, and Tocasaw was crowned “King George.” He is very mild in his rule, and appears to seek the welfare of his subjects, who love him much. They are under complete subjection, however, and whenever in the presence of the king or chiefs, whether in the roads or houses, they immediately stoop low, and remain in this posture until he passes or bids them go about their business. The chiefs pay the same homage to the king as the natives. Even his own children 126 crouch down in his presence, and bend their heads like so many whipped spaniels.
The queen is a small, shriveled-up old lady, and looks as though a good strong norwester would blow her away. She is a very greedy creature, and just as vicious withal, and is thoroughly detested by those who are so situated that they can speak their mind freely, without fear or favor.
They have six children; the eldest son, Canker, as we have already remarked, is next in rank to the king. He is about twenty-six years of age, and is reported to be a perfect villain, yet is very kind to the natives under him. He is a shrewd fellow to trade, and is always begging from the sailors. The second son, Aleck, is a young man about nineteen, and is a remarkably intelligent native. He is universally beloved by all, both chiefs and natives. He speaks better English than any native on the island, and appears to have a strong desire to know “all ’bout ’Merick.” Although so young, he is the father of three fine children, two noble boys and a girl; and his wife is a very kind, good-natured creature. He resides on the north side of the island, and has a beautiful place. The other children of the king are young, two daughters and two sons. Even these children command the same respect from the common natives as the chiefs, yet they play with them in common.
The first, or war-chief; is Sekane, who is the king’s half-brother. He also is a very intelligent native, very active, and is considered the king’s prime minister and counselor. Next comes Cæsar, who is also half-brother to the king—a large, noble-looking native. He is the grand executioner, and when any poor native has violated a law, the punishment of which is death, he officiates. There are two or three other high chiefs, possessed of no remarkable traits.
The natives are rather diminutive in stature, but active 127 when occasion requires. They live in great simplicity. The females are remarkably good-looking; but, owing to their practice of squatting to their work, and remaining in that posture most of the time, are very awkward in walking. Their ears are bored when quite young, and the hole is made larger by inserting in it a roll of leaves, which causes it to enlarge as they advance in years. They generally have them fitted with a bunch of flowers, of which they are passionately fond. Many of them have their noses pierced, and flowers inserted therein. They are generally employed making tappas, or, as they call them in English, “Strong’s Island trowsers,” for the chiefs to whom they belong. Tappa is manufactured from the fibres of the banana-tree, colored with different barks to suit their taste, and woven, by means of a small but ingenious loom, into bands of four or five feet in length, and eight or ten inches in width, with the different colors very ingeniously and beautifully intermixed. The body and principal part of the tappa is black, and comprises all the dress worn by the men or women, from the king down. Sometimes, however, the king and chiefs indulge in the luxury of a calico shirt; but the “court dress,” the red woolen shirt, is only worn on great occasions. The females, also, will sometimes sport a gingham shirt, if they are lucky enough to be presented with one by the chief to whom they belong. Their crinoline, however, is not very extensive.
The men are employed cutting wood for their respective chiefs, building houses, making canoes, gathering fruit, etc. Their food consists principally of fish, bread-fruit, fayees, cocoanuts, and other fruit. The fish are generally eaten raw, and smell rather high before they use them.
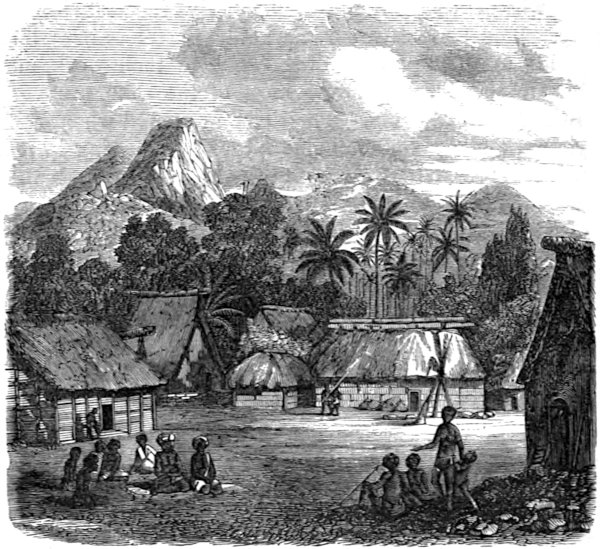

Their houses are built of bamboo, thatched with cocoanut leaves. The king’s house is very large, being fifty or sixty feet high, and about forty feet square. Some of the chiefs have also very large, roomy houses. The common ones for the natives are from thirty to forty feet high, and about twenty feet square. They are kept very neat. In the centre of the house is a square stone fireplace. The king and chiefs have large cook-houses, where all the cooking of the different tribes is done, and each family is served once a day. Each chief has from fifty to two hundred natives under him, including men, women, and children.
No one of the natives is allowed more than one wife, and when the marriage ceremony is performed (which is done by the king for the chiefs, and by the chiefs for the common natives), the girl is “given away” by the one who officiates, and is then tabooed. The penalty of breaking this taboo is death; therefore there is not 129 much fear but that she will remain faithful to her husband.
Each chief is allowed a certain portion of land, which is cultivated by the natives under him. The produce is taken to the king, who retains a portion for himself and ships, if any are in the harbor, and the remaining portion is distributed to the chiefs for their tribes. Their sports consist of songs, dances, and feasts. They do not appear to be a very warlike people, as they have no weapons of any account, and but four or five war-canoes. These are about sixty feet long and three wide. They are supplied with large outriggers to prevent their capsizing, and will carry from sixty to seventy natives. They are built very true and sharp, the bow and stern considerably elevated, and are fancifully decorated with shells and other ornaments. The smaller canoes are generally bread-fruit-tree logs shaped properly, and burned and dug out. They build them of all sizes, from those that will carry but a single person to larger ones that will carry twenty. It is indeed surprising to see with what dexterity they manage them.
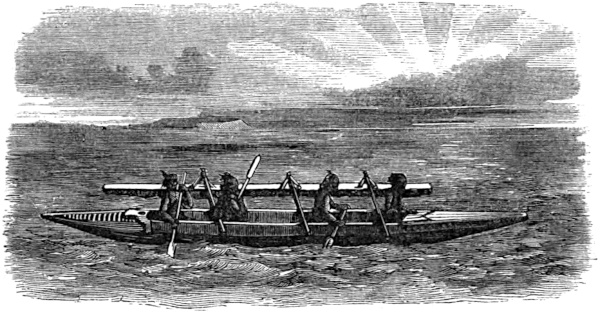
On this island is a root, which grows wild, called “carva.” They pound this root, extract the juice by130 squeezing it in their hands into cocoanut-shells, and then drink it. By taking a sufficient quantity, it operates very similarly to opium, causing a sleepy intoxication. It tastes very much like the extract of sarsaparilla root. This is a great article with them, and, on calling from house to house, you are first presented with a shell of carva. There are those on the island who have used it so much that they resemble in appearance the worst class of opium-eaters.
There is a tree here which is a great curiosity, being a species of the banyan-tree of India. Its branches, bending to the ground and taking root, make beautiful shady groves, and pleasant retreats from the sultriness of the scorching sun.
In the matter of religion the natives have a singular belief. Their deity, whom they call “Blueskin,” was thus described to us by Aleck: “All the same white gal, only he got wing all the same pigeon,” which is as near a description of an angel as we could have given him. They say, “If man be good, he go there,” pointing to the sky; “s’pose he no good, he stop here,” pointing to the earth. It is certainly very singular where or from whence they received these ideas; nevertheless, they sincerely believe them. They have no regular places of worship, neither have they any prescribed form. Some years since a famine visited the island, and swept off many of the inhabitants. According to their traditions, a great quantity of eels, which had never before been seen by them, suddenly made their appearance, and prevented them from entirely perishing with hunger. They have now great veneration for these eels, and they are tabooed, as they believe Blueskin sent them; and, although the waters abound with them, they will neither harm them nor suffer them to be harmed, if in their power to prevent it.
They also believe in evil spirits. Once per year, or 131 oftener, if any thing remarkable transpires, the high-priest is followed by his train of natives, carefully and plentifully oiled with cocoanut oil, wreathed with flowers, and each one carrying fruit of some description to appease the angry spirit, while the priest blows away upon a large conch-shell, making a most hideous noise, to which is added a continual wail by his train, which sounds truly mournful. They go along the beach, and to each chief’s house, taking what has been collected as an offering to Blueskin, generally consisting of pure white tappas and the general productions of the island. These articles are deposited by the priest in a house, tabooed to all but himself, on the mountain, and are left there for Blueskin to take whenever he chooses. The priest only enters this place once a year, or when the island appears to be threatened with some dire calamity. At such times he goes in and has a talk with Blueskin.
On the death of any person, all the friends and relatives meet at the house of the deceased, where they join in singing, wailing, screeching, and weeping for about twenty-four hours, after which the body is buried with much solemnity, with the head to the west. We inquired the reason of this, and were answered, “Very good; ’nother day’s sun he come all right.” The articles most highly prized by the deceased while living are always buried with them. A small fence is erected around the tomb of a native, and the friends every morning carry fruits and flowers, and place them on the grave, for they believe the spirits of the dead linger for a time upon the earth before departing for the skies. If the deceased is a chief or a member of the royal family, a house is erected over the grave, and all the chiefs on the island remove to the place, build small houses, and remain there for three months, the usual term of mourning, during which time they present offerings very bountifully, and with a great deal of state. After the132 ceremony of offering the fruit every morning, the nearest related chief makes a feast, and all the chiefs gather and eat, and drink carva. The females are excluded from these and all other public feasts. The women belonging to the departed chief have their heads shaved, and present a most comical appearance; also all the relatives cut their hair short.
One Saturday evening a native from the island of Rotumah, called Rotumah Tom, came on board with a large number of fine pigeons for our Sunday dinner, which we found very fat, and fine eating. We received a present of a mess of flying-fish also, on Sunday morning, from the king, which were caught the previous night. He is very kind to us, sending bread-fruit, smoking hot, every meal, for all hands, and other food which the island produces. A favorite dish with them is “poey,” and is prepared as follows: They bake a quantity of tarra (which is something like our potato), and then pound it on a large flat stone, mix in some roasted bananas, and, after working it sufficiently, grate up the meat of old cocoanuts, and, inclosing the gratings in leaves, by squeezing extract the white milky substance, and cover the poey in such a manner as to resemble frosting. Some of the poey is made from the banana and bread-fruit, and is truly excellent. After it is prepared it is placed on large banana leaves, and is then ready for consumption.
We were fortunate in being at the island at this time, as Monday, December 16th, was the day for the annual visit of the high-priest of Blueskin, with his train, and we had an opportunity of witnessing the whole affair. The occasion was one of great excitement among the natives, they looking upon the proceedings with a great deal of solemnity and awe. Our crew were all ashore, and appeared to be highly amused, nearly all going to the opposite side of the small island from the harbor to133 meet “Blueskin” and his train as they arrived from the large island. When we expressed to some of them our intention of joining the procession, they exclaimed, almost horror-stricken, “What for? ’spose you do all the same, Blueskin he strike; kill ’em very quick!” Nevertheless, some ten or twelve of our men did join the procession, and “howled” in the most scientific manner possible, to assist in driving the evil spirits from the island, without interruption from Blueskin. Yet we imagine the high-priest thought if there were any greater “evil spirits” than some of the “Emily Morgan’s” men, it was high time they were driven off. After making the tour of the island, and consigning every thing evil to the spirits of the deep, the priest proceeded to the house of young Aleck, and, after many ceremonies, gave him a new name, “Zegrah,” which is considered a great honor, and raises his rank a peg or two.
Our Pitt’s Island native, Friday, could hardly suppress his astonishment and laughter during the whole proceeding, and, on our asking him his opinion of the show, exclaimed, “What for all the same? All the same Kanaka pool!” We proceeded to the house of Cæsar, where a feast was to be held after the ceremonies at Zegrah’s, as we will now call him. We had received an invitation the day before, so that we felt ourselves “perfectly at home” among the “nobility.” On arriving, we found his large cook-house filled with natives, who were waiting for the ceremonies to commence. Cæsar was seated on a mat in one corner, with some of his petty chiefs about him. He very kindly offered us seats at his right on the mat, and we accordingly “squatted.” He asked us, “You been see Blueskin?” and on our replying in the affirmative, he wished to know how we liked him. We gave him our opinion in as few words as possible, and expressed ourselves as being highly pleased with the performances. 134 He laughed heartily, and appeared to treat the whole thing as a good joke—an excellent humbug. He now clapped his hands twice, and, speaking in his native language, the petty chiefs passed the leaves of different articles to him, and at the same time others helped the natives. We ate heartily of poey, baked bananas, bread-fruit, sugar-cane (which we had forgotten to mention grows here in great abundance), cocoanuts, fish (which were baked for our company, as they know white men will not eat them raw), with large shells of carva to wash it down. After these courses had disappeared, the dessert made its appearance in the shape of an animal of some kind, piping hot, which had been baked whole. We supposed it to be a wild hog, and were about to partake, when, curiosity getting the better of our appetites, we inquired if it was “hog.” Cæsar replied, “No, dog;” at the same time urging us to help ourselves, and saying “very good.” We did not doubt it; but, suddenly recollecting that we had eaten very heartily, concluded that we wouldn’t “indulge,” and excused ourselves by saying we were full, and could eat no more. He seemed loth to let us off in this manner, but, finding it no use to urge us, gave it up. It was evident he was not pleased in our refusing to partake of his favorite dish, but we could not go “dog.” After he finished his “dessert” of baked dog, he sent several choice parcels to his wife and daughters, and women belonging to his tribe, and after washing, which they always do at the close of a meal, we retired to his house, and enjoyed a quiet smoke, spinning yarns, singing songs, etc., which appeared to greatly amuse Cæsar, and then stretching ourselves upon the large cool mats, enjoyed a refreshing sleep.
The next day we called upon Zegrah, and, after talking with him some little time, he urged us to take up our quarters with him as long as the ship remained;135 said he had a nice, comfortable house, which he would taboo to the natives, and give us, and we should have every thing at our command. When we wished to go aboard the ship a large canoe was at our service, with natives to paddle. Of course we thanked him for his kindness, and accepted his generous proposals. We accordingly went into our “hotel,” and arranged our beds, etc., which consisted merely of mats spread upon the bamboo floor, with pillows which we had brought from the ship, and soon found ourselves in comfortable, pleasant quarters, but a short distance from the beach, with a fine sea-breeze, and the never-ceasing roar of the breakers sounding in our ears, as the huge rollers come combing, dashing, breaking along over the rocks. It was, indeed, to the lover of nature a magnificent scene.
On going home the first evening we thought best to take a stroll across the island, then take the sand-beach to the house. On arriving at the beach, behold! it was high tide, and we must either climb stone walls or take the water, which was some three feet in depth. We concluded to wade it, and prepared ourselves accordingly by assuming Strong’s Island costume, and then “pitched in.” Occasionally a roller would come booming along, dashing over and almost taking our feet from under us. It was just dark, and as we were plodding along, consoling ourselves with the thoughts of a good night’s rest after we reached our “hotel,” we suddenly perceived a large shark dart between us toward the wall, turn himself round very easily, and then swim away. We made all the noise possible to frighten him, and then ensued some of the tallest “walking in the water” that we had ever seen. We could only go ahead. There were high stone walls along shore, water ahead, water behind, and water to our right; so we e’en made the best of it, and “put” as fast as our legs would carry us through three feet depth of water. We were fortunate enough to escape 136 with whole limbs, and arrived safely at our stopping-place, congratulating ourselves upon our escape from “John Shark.” Friend Zegrah had prepared for us a quantity of baked bananas, roasted fish, etc., and, setting them before us, with plenty of fruit, we had a very sociable and jovial time. His wife was present, and seemed to enter into the spirit of the evening with a hearty good-will. Zegrah himself, as we before remarked, was young and full of fun, but, living on a remote part of the island, was very lonesome, and made us promise to spend all the time we possibly could with him, and he would pilot us over the island.
The next morning, Wednesday, December 18th, “Sail ho!” was the cry. On looking, we saw a ship off the passage, and presently a boat made its appearance and came ashore. The ship proved to be the “Planter,” of Nantucket, full, bound home. Captain H. came ashore in the boat, and brought his clothing and some goods. He informed the king that he wished to reside on the island for a short time, as he did not like to go to America at present. We learned the following particulars in regard to Captain H. and the “Planter:” While the ship was cruising off Pitt’s Island, a barrel of bad meat had been opened, which created considerable dissatisfaction among the crew, and they finally threw it overboard, and said they would do no more work until they had good meat. The captain told them they should have no more until the regular time, as they had no right to throw the other overboard. Upon this, the men refused duty. The captain ordered them to work, but they firmly refused. He then ordered them to come aft, and this they refused to do, when he ordered the mate to go forward and bring the ringleader aft. Upon this, one of the crew threw out a threat that, if he came forward and laid his hands upon any of them, they would break his head, or something to that effect. The captain, thinking137 it time something decisive was done, ordered some muskets to be loaded and brought on deck. They were accordingly brought, and he then told the men distinctly and firmly that unless they went below he would fire. Some one of them replied, “Fire, and be hanged to you!” After waiting a sufficient time, and repeating his orders, he fired, and one of the mutineers instantly fell dead, the ball taking effect in his brain. The men instantly rushed pell-mell for the forecastle. The mate now came forward, and ordered them up one by one, and, being perfectly tamed, they came and submitted to being placed in irons and stationed aft. The body, after a suitable time, was buried. Upon the men promising to resume their duties and behave themselves if liberated, the irons were taken off, and they were allowed to go forward.
These events transpired but a few weeks before the ship visited Strong’s Island, and the captain, thinking it better to wait a year or two before returning home, wished to remain on this island during the interim. The king, after some conversation with our captain, gave his consent, and, accordingly, Captain H. had his property transferred from the ship to the shore, leaving her in command of the mate. The ship did not anchor, but the things were brought ashore in boats.
When the last boat was about leaving the shore, “Smut,” alias the blacksmith, and our friend Mackey, stepped in, and, accordingly, stepped out, as that was the last we heard of them. We were sorry to lose Mackey, as in doing so we lost one great source of amusement; but he was gone, and, before it was known on board that they had deserted, the “Planter” was off, with square yards and a stiff breeze.
Some of the crew one day started for the shore in a small canoe, and before they had got half way it capsized, slightly spilling them out. They had a fine ducking, as well as a long swim for it. The same day, we,138 in company with another shipmate, undertook to navigate one of the canals in a small canoe, but, not exactly understanding the crooks and turns of the “ditch,” had the misfortune to be capsized in the mud, and received a good soaking before we “made the land.”
Hardly a day had passed since our arrival in port that we had not turned our eyes large-islandward, and longed for a stroll among its mountains, valleys, and groves, but had delayed the intended visit from the want of a suitable guide. On Friday, the 20th, however, that want was supplied by Zegrah offering his services for the occasion. We accepted them with pleasure, and, in company with two other shipmates, crossed the channel in a canoe. In low tide this channel is fordable. We found the houses were not so large nor comfortable as on the small island, nor so neatly kept, and are more scattering. We encountered many ruins and walls here also, but no canals. After rambling over hills and rocks, through woods and swamps, and finding ourselves completely covered with mud, we made our way back, having encountered nothing worthy of note, and our bright anticipations, which we had long cherished, just about as near realized as thousands of others that we have had. But we must learn wisdom by experience, we thought, and thus consoled ourselves.
Our man Friday we find a capital fellow to stroll on shore with, he having a perfect fund of wit and drollery to draw upon at pleasure. Wherever we went we introduced him as the brother to the king of his island, and he was accordingly treated with the greatest respect, which amused him infinitely. We found him very useful in our rambles also; for, when we were thirsty, he was always ready to ascend a cocoanut-tree, and pass down a sufficient quantity of the rich nuts to satisfy the thirst of all. One day, while he was thus engaged, a native came, running and hallooing, to see who was 139 taking cocoanuts that were tabooed. Of course, the boys all ran; and one of the crowd was in such haste to get over a stone wall with an armful of cocoanuts, that he lost his balance, and wall and all fell, plunging him almost out of sight in a mud bath. Friday, however, sat in the tree, perfectly at his ease, laughing heartily at the mishap. The native sang out to him, “Come down; no good; king taboo!” Friday coolly replied, “No saba” (no understand), and again commenced throwing down the nuts, taking particular pains, however, to hit the poor native as often as possible, who would cry out, “Wa-a-a, wa-a, what for all the same? No good.” He finally beat a retreat, leaving Friday master of the field, and the boys laughing at the manner in which he had driven the “Kanaka pool,” as he termed him, from the ground. When he came down he found himself in a quandary. He had got more cocoanuts than he could conveniently carry, and leave them he would not; and, as the boys were all supplied, he was in a fix. At last, however, his eye brightened, and exclaiming, “I fix ’em,” he stripped off his pants, reducing himself to the costume of the “king’s court,” and filling each leg with cocoanuts, marched along. We took the “spoil” to our quarters at the “hotel,” and deposited them there. We would here state, that when the king or chiefs wish to reserve any particular place or house from the intrusion of the natives, they place the taboo upon it; and, as the penalty of breaking this is death, they consider it sacrilege almost to disobey, or think of molesting the place. It was thus that our quarters were rendered perfectly safe from intrusion. Zegrah tabooed the house, and no native dare enter it without our permission. The natives are very kind and hospitable to those who treat them well, but inclined to pilfer if a good opportunity presents itself. Most of them are notorious beggars, and are constantly teasing for a “small piece ’bacca.”
140
On Sunday morning, December 22d, we found that our third mate and another man had deserted in the course of the night, taking with them all their clothing. All hands rejoiced that the third mate, the great bully, had left, and the captain shipped two men instead of the deserters. These men had been on the island some months.
But we had been some time in port; all our wood, water, and fresh provisions were on board, and we were ready for sea. Accordingly, at five A.M. on Monday, December 23d, we weighed anchor, and left this beautiful harbor, some with sorrowful hearts, and others rejoicing that they were once more rolling on “the deep blue sea.” But we did not immediately leave the island. The captain had a little more business to transact, and we “stood off and on” the harbor for two days, close in sight of the land.
The next day after weighing anchor, the bark “Mary Frazier,” of New Bedford, Captain Haggerty, entered the harbor, so that our island friends were not left alone. She was from the Arctic Ocean, where she had taken thirteen hundred barrels whale oil in one season. We ascertained by her that our two deserters had escaped from the island in the bark “George Champlin,” Captain Swain, which vessel had been lying in the lee harbor. In the place of our third mate who had deserted, and his office become vacant thereby, the captain placed Mr. Smith, whom we took from the ship “Marcus,” as the reader will recollect, in exchange for the boat-steerer, who left us on account of his ill health. All hands were much pleased with the exchange, as Mr. S. was a noble man, and a sailor every inch of him. But scarcely had we left port, and on the next day succeeding that in which we learned of the escape of his predecessor, before he was taken violently ill with a burning pain in his stomach. For several days he continued growing141 worse, becoming deranged, and continually vomiting, until Tuesday, December 31st, the last day of the year, he departed this life. He died struggling very hard.
This sudden death cast a gloom over the whole ship’s company. But a few days since, and he was the perfect embodiment of health. Little did he or any of his shipmates imagine that one brief week would find him clasped in the cold arms of death. Little did poor Smith imagine that he would so soon be called upon to obey the dread summons. Mr. S. had followed the sea from his youth, and had arrived at the age of about thirty, without ever experiencing sickness of any kind. He was a most excellent and thorough seamen, understood well his business, was peaceable and friendly to all, and while on board had conducted himself in such a manner as to take a firm hold upon the affections of his shipmates. He had secured the confidence and esteem of the captain and officers, as well as the respect and good-will of the men. He was prompt in the discharge of his duties, always performing them in a cheerful manner. But he has gone from our midst. Suddenly he was taken from us to that bourne from whence no traveler returns.
Little does the landsman know the sweet comforts the dying sailor is deprived of. Separated from the home of his heart by thousands of miles, tossed to and fro on a sick couch, with no kind father to watch over and soothe the anguish of his pain; no loving mother comforting and praying for the salvation of the dear son; no dear brothers or sisters to sympathize and cheer the lonely hours with their presence—none of these to smooth the dying sailor’s lonely pillow, alleviate his wants, assuage his grief, and comfort his mind by divine teachings; none of their cheerful countenances to light the dark valley of the shadow of death. Yet every thing was done that was possible to do for Mr. S. to alleviate his sufferings and comfort his mind. But all142 was of no avail. There is little doubt but he was poisoned at Strong’s Island. But his bodily sufferings are o’er, and instead of departing upon the soft, downy bed, with his dear ones hovering over him, he yielded his spirit to the God who gave it from his rolling couch, and the last sounds that reached his ears were the moanings of the wind, and the hoarse murmur of the waves, impatient, as it were, to receive their victim.
At four P.M. we shortened sail, hauled aback the head yards, hoisted the ensign half-mast, and called all hands to “bury the dead.” The gangway board was removed, the body sewed up in a sheet, and weights attached to the feet, and then laid upon a plank. The services commenced by the captain reading a portion of the Holy Scriptures, then making some excellent and touching remarks, followed by a prayer. He then read the burial service, and when he said “we now commit this body to the deep,” the end of the plank was raised, and the body of poor Smith was consigned to its watery grave, there to rest till the morn of the resurrection, when the last trump shall sound, and the sea shall give up its dead. The body rapidly disappeared beneath the blue wave, and, on glancing around, the tear was seen in the eyes of all those hardy men—those men who had faced death without a blanched cheek or a fainting heart—as they took their last look at the body of their late shipmate. On the land, in the city or town, a death is hardly noticed, and is not felt; but on board a ship, with but a small circle, as in our case, of about thirty, living together as one family, and shut out from the world, as it were, one snatched from our small company is seriously missed, and death serves to bind the remaining still closer together, as the loss just experienced shows us all the uncertainty of human life, and no one knows who will next be called upon to pay the last sad debt of nature. May we all be prepared, that, should 143 Almighty God see fit at any time to remove us from this world of sin and sorrow, we can go with willing hearts—that we may “render up our account with joy, and not with grief.”
How different the “New-year” at sea from that at home, were our thoughts this “New-year’s morning” on first awakening. But we wished all on board a “happy New-year,” and then the good folks at home came in for a share of our prayers, and we could not but think that, while they were enjoying the choicest viands, our “New-year’s dinner” must consist of hard bread and salt junk, with a “plum duff” for dessert.
We were again bound for the Group, to try our luck for whales. And we had our “luck,” for we only saw them twice during the whole cruise of three months, and they were then going “eyes out” to windward. We did not even “grease an iron” that cruise.
By this time our man Friday had become somewhat civilized, and was able to speak pretty good English. After trading at the island one day, we managed to gain some very interesting accounts from him in regard to it and its inhabitants. It lies in latitude 3° 02´ N., longitude 172° 46´ E., the northernmost island of the King Mill Group. The natives are very friendly, and have 145 not yet learned the knavery of the other islands. The chief in command is called king, and is assisted by a number of chiefs. The king is allowed as many wives as he chooses, but the chiefs and natives but one. They have no religion, yet they are very superstitious. They believe in ghosts, and that the spirits of the dead visit them. Their evil spirits they call “jentsh,” and they hold that when they do any thing wrong the “jentsh” haunt them; and if they are afflicted in any manner, either by sickness or otherwise, it is punishment imposed upon them by the evil spirits, who are sent to torment them. Friday declared to us that he had often seen and conversed with these spirits, and upon being contradicted he flew off; and said, “S’pose me pool? s’pose me no got eye? me no all same Strong’s Island Kanaka pool; me saba plenty.”
If a native dies, they roll the body in a mat, and the relatives sit around the corpse and wail and mourn until the body is in a state of putrefaction. They never leave their places, their food being brought to them. The climate is so warm that it does not require much time for the body to decay. When it reaches this state, it is sewed up strongly in the mat, and buried, if a male, with his war-club and spear, to protect him in the spirit world; but if a female, nothing is buried with it, as they believe the females need no war-like instruments to protect them from danger. Like the inhabitants of Strong’s Island, they believe that if the person who dies is good, he goes “up there;” but if he was bad, he remains in the ground, and is forever tormented by the “jentsh.”
Their houses are built of bamboo; are large and roomy, some of them having two or three lofts or stories, and are kept very clean and neat. The natives are very cleanly, but very few of the men wear any clothing. The females wear a tappa, about two feet in 146 width, about the loins. They subsist principally on cocoanuts, a species of bread-fruit called jack-fruit, tarra, wild fowl, and fish. The king is a large, corpulent native, apparently about forty-five years of age, and is called “King George,” which appears to be the name of every “king” we have yet heard of in this part of the world. The lingo (for we suppose it can not properly be called a language) in the various islands of the group is nearly the same, so much so that natives from the various islands can understand each other.
Their weapons of warfare are principally spears, though war-clubs are sometimes used. The spears are made from cocoanut wood, and are very long, and pointed at both ends. They handle them with a great deal of skill, and will throw one from forty to fifty feet with remarkable precision. Their mode of battle is very singular. Both parties approach each other, and, when within proper distance, throw their spears and then run. If one party get the advantage, and throw their spears first, and any take effect in the opposite ranks, those that have received the spears make great haste to get out of the way. These battles seldom last long, though a great deal of time is spent in manœuvring, and great preparations are made, but the contest is soon decided.
We had now cruised three months without getting a drop of oil, and the “old man” concluded to try his luck on Japan. Wanting wood and water, however, more than we had on board, for a long cruise, we steered for Strong’s Island again, and on Saturday, March 29th, we sighted it. The next day we entered the harbor, and at 11 A.M. we came to an anchor. To our great surprise, we found the bark “Mary Frazier” still in port, she having been “windbound” for three months. We also found the bark “Maria Laura,” of Hobarton, Captain Mansfield, in port. On going ashore, we found that many improvements had been made by Captain H. He had147 built three nice large houses. The king, too, had caught the spirit, and built himself a new house; and, in fact, a general spirit of improvement and go-aheadativeness seemed to have taken possession of all.
In the evening of the day on which we arrived, we had the opportunity of attending a singing-school, which the king had authorized to be instituted for the purpose of teaching the children the native songs of the island. As a matter of course, we could understand nothing that was sung, but we were pleased with their voices, which were very sweet, and they appeared to keep excellent time by clapping their hands.
The next day, Monday, the king, in his court dress, with all the royal family excepting Canker, came off to dinner to the ship. Canker evidently felt his guilt, as he appeared to keep out of the way of any of the ship’s company. We had no doubt, when Mr. Smith was first taken, that he had been poisoned, and circumstances pointed strongly to Canker as the guilty person. It appears that our chief mate, with Mr. S. and Canker, had been gunning, and, on returning, the mate and Mr. S. commenced bantering with Canker in sport. However, he did not take it in that manner, but appeared quite offended. On arriving at his house he seemed to have regained his good-will, and invited them to drink some carva with him. They of course accepted, and it was accordingly ordered, and brought in two large shells. The mate noticed this, and asked Canker why he did not drink with them. He replied, “Never mind; me no drink; me too much sick.” This was something so unusual, as the general practice among them is for the chief to drink first, that the mate refused unless Canker would drink, suspecting all was not right. Canker refused even to taste it, and exclaimed, in high dudgeon, “You think carva been poison? Strong’s Island no got poison.” Mr. S. laughed at the fears of the mate, and148 drank off his carva and in a few moments drank that which had been prepared for the mate. Two days from that time poor Smith was taken ill, as we have related, and soon died, leaving no doubt in the minds of all on board that he had been poisoned by this unscrupulous Canker.
His wife having died since we left the island, on our return we found all the chiefs living on his place. They feast every day. We called on our old friend Zegrah, who seemed very much pleased to see us, gave us a hearty welcome, and accompanied us to our “hotel,” where we regaled ourselves on fruit, fresh fish, etc. Upon mentioning the circumstances of the death of Mr. S. to him, he remarked, “Canker bloody rascal!”
The next day, Tuesday, April 1st, we called upon Canker. We found him remarkably sociable, and his first question was, “Where Mr. Smith?” We told him he was dead; whereat he raised his hands with horror, and exclaimed, “How long ship sail, he die?” We told him “three days,” when he replied that he was very sorry, as Mr.S. was a good man. Now the scamp had been made acquainted with all these particulars before. We asked him if he had not heard of his death, and he replied “no,” but we knew he lied. After some farther conversation, he asked us, “What make Mr. S. die?” We told him plainly that he was poisoned, but said nothing of our suspicions as to the guilty person. He immediately commenced denying that he had poisoned him, and said, “Strong’s Island no got poison.” As no one had hinted or charged him with doing it, we regarded his denials as very suspicious. After remaining in deep thought, apparently, for some time, he again asked, “How long he been make sick, he die?” meaning, how long after he was taken sick before he died. We thought this suspicious also, as we had but just informed him that he died three days after the ship sailed, and we determined149 to try him on another tack, and see what he was driving at. We replied to him, therefore, “One week.” His countenance immediately brightened, as though a happy thought had suggested itself, and he said, “S’pose me make poison carva he drink, he no live one day, he die too quick.” We asked him how he made poison carva. He replied that he put in the juice of a certain plant. We reminded him that he had said but a few moments before that “Strong’s Island no got poison.” This seemed to completely stagger him, and he appeared lost in deep study. We now left, well convinced that his highness, Mr. Canker, was a consummate villain, and that he had poisoned Mr. S.
Our fourth mate, Mr. F., concluded to try his luck gunning one pleasant day on the large island. After climbing stone walls, rambling over mountains, and wading marshes, he thought, as game was scarce, he would take a short nap. He was hardly asleep before he felt some one about his person, and sprang to his feet just in time to see a Kanaka running off with his sheath-knife in his hand. He instantly raised his gun and fired at the black rascal, but his shot did not take effect; so the native only ran the faster, and got clear with the knife.
The crew of the “Mary Frazier” were a disagreeable set of men, always boasting and quarreling among themselves and with their officers. Quite a number of the different ships’ companies were on shore one evening, rolling in the ball-alley, which had been built by Captain H., and a disturbance occurred between the mate of the “M. F.” and one of her crew. The man, who was a large, two-fisted fellow, was blustering about, threatening to knock the mate “into the middle of next week;” but, as he was taken no notice of by any one, after suffering the superabundant flow of gas to escape, sneaked off, leaving the others to enjoy their exercise.
On the evening of Thursday, April 3d, we attended a 150 dance at the king’s house, given by some New Zealand natives. Their faces and bodies are tattooed in a very singular manner, and look truly frightful. Their gestures are fierce, songs wild, and their dancing is little more than keeping time by changing their position.
On Monday, April 7th, we attended a grand feast given by the king. All the chief’s on the island were present. Every thing was served up in the highest style of “Strong’s Island fashion,” and the white men from all three ships were heartily invited to partake, which they did of every thing except “dog.” After the feast was over the “plate” was cleared away, and room made for a grand dance, which was led off by the king and followed by the chief’s, the women singing, and keeping time by clapping their hands and beating an instrument resembling a tambourine. The old king flew around quite lively, and each one appeared to do his utmost to excel. At the close of each dance the white portion of the audience would cheer the performers in the most approved style, which seemed to please them greatly. The natives appeared much amused, whether at the dancing or cheering we could not say, but probably a little of both, as they showed a broad grin all the time. Old Cæsar tried very hard to see how high he could kick his heels, and, at the same time, keep his balance, but a misstep brought his foot down on a piece of banana-skin, and his heels flew up, and down he came with a crash that seemed as if he had gone through the floor. Upon seeing this, the king and all the dancers stopped to have a hearty laugh, the white men shouted and cheered, the natives grinned, and the house was “brought down” completely. But Cæsar was not to be frightened in that way, and he got up and went at it again with redoubled energy. After dancing some two or three hours, “all hands” took a shell of carva and separated.
The crew of the “Mary Frazier” had been bragging 151 and boasting, since we had been in port, that they had better boats, and could pull faster than either of the other ships’ boats. Knowing what braggadocios they were, our men took no notice of them, nor did the crew of the English bark for some time, until finally they challenged the Englishmen to a race, and the challenge was accepted. The flag-boats were stationed one mile apart, and the boat that pulled around these stationary ones three times and came out ahead was to win the race, making a pull of six miles. The crew of the “M. F.’s” boat were down quite early in the morning on the day of the race, six large brawny fellows, stripped to the skin, and “eager for the fray.” About 9 A.M. the Englishmen lowered their boat, the same number of men composing her crew, but with a far different appearance, being perfectly cool, and making no boasting display. Our boys, thinking they might as well be “counted in,” though not thinking of winning, five of them, with the second mate, jumped into the waist-boat, and “struck out” for the starting-place. The boats were now ranged alongside, the signal was given, and away they flew like arrows from the bow. The “Mary’s” boat soon left the others behind, our “plug” being distanced by both. Each crew bent their backs to it, sending the boats through the silvery sheet with great speed. The Englishmen’s boat seemed to skim over the surface of the water with the ease and grace of the swan, the crew taking it perfectly easy. The first flag-boat was rounded, and the “Mary’s” boat was some distance ahead. But now was “the tug of war.” The good-natured Johnny Bulls awoke from their lethargy, and the cry rang out, “Pull, my hearties, pull!” and every stroke lessened the distance between the two boats, our own boat gaining on the “head boat” about as fast as did the Englishmen. But all was excitement; the men in each host were straining every nerve, and, at the end of the third mile, the Englishmen152 passed the other boat, and, before the fourth was reached, ours passed it also. But still on they pulled, determined not to give up, yet dropping farther and farther astern, until, at the end of the sixth mile, the English boat was a mile ahead of the “Mary Frazier’s,” and our own about half a mile ahead. The Johnny Bulls now gave three cheers for their own boat, and “three times three” for ours, not so much for the victory as that the boasters had been so badly beaten. Our boys were not interested in the race at all, only pulling for the “fun of the thing,” and they were more surprised than any one else to find that they could beat the “crack boat” of the “M. F.;” and her crew were so mortified that they said no more about “fast boats.” Thus were the boasters beaten.
On Saturday, April 19th, the king gave another grand feast and dance, to which we were all invited as usual. After some time spent in dancing by the chiefs and king, the old black “doctor”[3] of the “Maria Laura” struck up with his violin, and all hands joined in a regular breakdown. This pleased the king and natives very much, they laughing heartily and exclaiming, “What for all the same ’Meriky fashion?”
As we before remarked, Captain H. had built a ball-alley on the island, and the king and chiefs spent a great part of their time there, and had become very expert players. The king might often be seen “rolling a string” with one of the foremast hands of the different ships.
The “Mary Frazier” had now been in port nearly four months, the “Maria Laura” two months, and ourselves one month. The three ships were ready for sea, and had been for weeks, but the wind blew constantly into the passage—a fair wind to enter port, but impossible for a ship to leave. At length, however, on the morning of Wednesday, April 23d, the wind died away and153 it fell a dead calm, and the old man determined to make the effort to tow the ship out of the passage. Accordingly, we “hove up” anchor and down boats, and commenced to tow. When at the mouth of the passage a breeze sprang up, taking us “all aback,” and swinging the ship around. We were rapidly drifting into the breakers, when the pilot, Rotumah Tom, immediately sprang into a boat alongside, and, pulling for the weather side of the passage, with the end of a line in his hand, which he had taken with him, he plunged down and made it fast around a coral rock, came up, and made signals to “heave away” on board. This was the work of almost a moment; the ship was within but a few feet of the breakers, and we held our breath, expecting every instant to see her strike. But by sharp, quick work, and the good judgment and activity of Rotumah Tom, we soon cleared the breakers, and, warping up to our old anchorage, “let go” again.
The other ships also dropped anchor, and congratulated us on the narrow escape of the “Emily.” We felt thankful to God for the escape, narrow as it was. To have been wrecked there and then would have been truly lamentable.
The next morning a light breeze sprang up from the southward, and all three ships left Strong’s Island, bidding them adieu. The breeze increased as we dropped the land, and with a fair wind we headed west-northwest for Guam.
Sunday, May 4th, we arrived at Guam. This is a beautiful island, of rather high land, and resembles the American coast more than any land we saw during our wanderings. The surface presents a rolling appearance, the land looks fertile, and it is interspersed with dense foliage. This island is the principal one of the group of the Ladrone Islands.
These islands were invaded in 1554 by the Spaniards, but their conquest was not completed till the year 1592, although they had, during the different years of their invasion, resorted to their usual sanguinary means. It was not until they had destroyed an immense number of the inhabitants that they could bring the warlike Ladrones to a state of subjection. When the conquest was finished, they compelled the subjugated people to leave all the other islands which form the group, and reside on only two of them, Guam and Rotta, which placed them completely under the observation of their jealous invaders. They also forced them to receive the Roman Catholic religion, which continues to be the only one tolerated on the island. The Spaniards have managed ever since to keep the people in a state of subjection, although the spirit of revolt still lies dormant in their breast, ready to burst forth at the first favorable opportunity.155 They speak the Spanish language fluently; in fact, they can speak no other, or they have no knowledge of the one formerly spoken on the islands.
All hands were busily engaged getting off recruits for the coming season on Japan, which consisted of yams, sweet potatoes, melons, shaddock, and bananas, which grow here in great abundance. The island also produces tamarinds, oranges, limes, cocoanuts, citrons, and papaw apples, all of the finest quality. The inhabitants here enjoy perpetual summer; the climate is mild and salubrious, and, were they free from Spanish oppression, might be a happy and contented people.
We found a Scotchman—Captain Anderson he called himself—who had resided here many years, and accumulated quite a little fortune trading with ships, etc. He informed us that Captain Luce, of the “Boy,” of Warren, together with his boat’s crew, had been massacred by the natives at M‘Gaskill’s Island but a short time previous. The captain went ashore for the purpose of trading with the natives for fruit, fowl, etc. He had visited the island before, and always found the natives friendly and peaceable. As he did not return to the ship, the officer in charge kept close in to the land, and fearing there had been foul play, early in the morning he stood in, and, by the aid of the spy-glass, discovered the natives dressed in the clothing belonging to the boat’s crew. They saw a white man coming off in a canoe and making signals to them. When within hailing distance, he reported that the captain and boat’s crew had been murdered; that he had resided on the island some time, and was not afraid they would attack him. Upon learning this sad news, the ship proceeded to the cruising-ground in charge of the mate.
Every thing being in readiness, on Monday, May 5th, we left Guam for the Japan ground, to cruise over a trackless waste of waters for five or six months in pursuit156 of dollars in the shape of sperm whales. Nothing out of the usual routine of ship’s duties occurred for nearly two months. All was monotony; the same process day after day—not even a sail nor a whale to vary the scene. At length, however, on the morning of Sunday, June 22d, our ears were startled by the cry of “Sail ho!” from the mast-head. It was a dead calm—not a breath of air stirring—and the sail was just visible from aloft. About 4 P.M. a breeze sprang up, and brought the stranger with it. It proved to be the “Boy,” and a boat’s crew came on board. They confirmed the report relative to the massacre of Captain Luce and his men. They also reported that a Nantucket ship cruising on the ground had lost a boat and crew by being taken down by a whale. It was supposed the line became foul, and, before it could be cut, boat and crew disappeared beneath the surface, as they were never seen or heard from afterward.
We now found large quantities of albicore and skipjack around the ship. These fish are very good eating, tasting much like fresh cod, and there were thousands of them to be seen in every direction. All that was necessary to take them was to tie a piece of white rag on a hook, and then sit on the bulwarks and trail the line along the top of the water, the fish jumping at it as fast as one wished to haul them in. We have seen as much as ten barrels of them caught in one day. They weigh from five to fifty pounds. It is singular, but they follow a ship as long as she remains in those latitudes.
At length, on the morning of Saturday, June 28th, the welcome cry was heard from masthead, “T-h-e-r-e she b-l-o-w-s!” All were aroused, and it was not long before our boats were down and after him, for it was a “lone whale.” The bow boat soon fastened, and just as all hands were congratulating themselves that we should soon have a whale alongside, the irons drew, and the157 whale left for parts unknown. “Just our luck,” was the exclamation, and all returned to the ship with long faces, and “slightly” discouraged. It was now eight months since we had taken a drop of oil, and we were twenty months out, with but three hundred barrels. The prospect of two thousand barrels in four years looked very dark just then. However, the old man endeavored to console us by saying, “It is a long lane that has no turning, boys!”
And we found this adage true, for the next morning we lowered down, and in less than an hour had a hundred-barrel sperm whale alongside, which caused every face to brighten, and before the decks were fairly cleared up we took another, which made us eighty barrels, making one hundred and eighty barrels in less than one week, more than half as much as we had been twenty months in getting. Thus it is; whaling is more a lottery than any thing else.
While cutting in the last whale, we discovered a ship running down to us, which soon came within hailing distance, and proved to be the British bark “Medina,” from Hong Kong, bound to San Francisco, with a load of Chinese emigrants.
We were now enjoying beautiful weather. During the days hardly a cloud was to be seen, and the atmosphere as clear as a bell. The nights were lovely, warm, and pleasant, and many of the crew preferred bringing their mattresses on deck and sleeping in the open air to sleeping below. One night Portugee Manuel, among the rest, was thus quietly taking a nap, but it happened to be his watch on deck, and he did not feel disposed to keep awake when he should. One of the watch, thinking to have a little sport, tied him fast to a large hog who was quietly reposing not far off, and then, taking a rope’s end, commenced belaboring the porker, who started up and off, dragging the “Gee” very unceremoniously158 with him. This somewhat surprised Manuel, who was not accustomed to this novel mode of locomotion, and, on being released, he swore vengeance (in Portuguese) against hogs and Yankees.
We again raised whales on Monday, July 28th, and gave chase as usual. The waist-boat soon fastened to a fine long fellow, who did not like to be trifled with, it seemed, in such a manner, and commenced thrashing about in a way that threatened destruction to the boats in the vicinity. After working himself into a towering passion, he ended the fracas by knocking the waist-boat “higher than a kite,” and sent the crew flying in all directions. The men were soon picked up, and, when the whale saw the mischief which he had done, repenting, we suppose, he remained quiet, and submitted to the “killing process” with a very good grace, and “gave up the ghost” in the usual style. The body was towed to the ship, and the “funeral ceremonies” were performed in short order, his beautiful coat soon converted into sperm oil and stowed away in the hold.
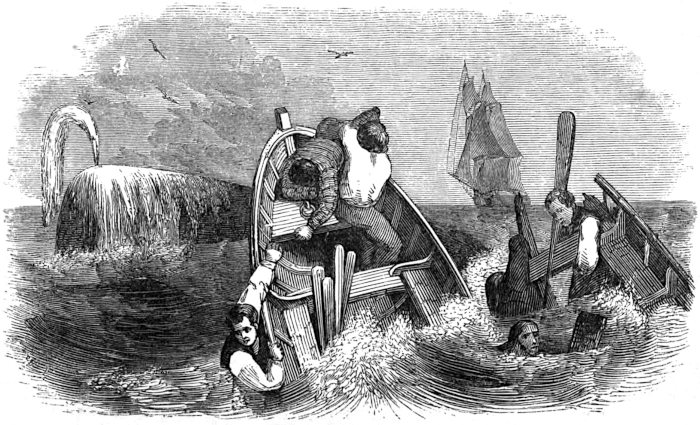
In the many books which have been written of whaling voyages, we recollect nowhere to have seen a natural history of the sperm whale, and we trust it will not be uninteresting to the reader if we give it in the present volume. It can not but be instructive, at all events, and, being satisfied on that point, we shall proceed; and, first,
The Food of the Sperm Whale.—This food consists almost wholly of an animal called by whalemen “squid,” and by naturalists the “Sepia octopus.” This squid forms the principal part of the sustenance of the sperm whale when at a distance from the shore, or what is termed “off shore ground.”
Manner of Feeding.—It appears from all that we could learn from the oldest and most experienced whalemen that we met, and from the observations we have been enabled to make upon this interesting subject, that when the whale is inclined to feed he descends a certain depth below the surface of the ocean, and there remains in as quiet a state as possible, opening his long and narrow mouth until the lower jaw hangs down almost perpendicularly. The roof of his mouth, the tongue, and especially the teeth, being of a bright, glistening color, must present a remarkable appearance, which seems to be the incitement by which his prey are attracted, and when a sufficient number are within the mouth, he rapidly closes his jaw and swallows the contents. This is not the only instance of animals obtaining their prey by such means,162 when the form of their bodies, from unwieldiness or some other cause, prevents them from securing their prey in any other manner, or by the common method of the chase. The crocodile frequently employs stratagems of the like nature. Covering himself in mud, and lying still on the bank of some stream, he opens his enormous jaws, when hundreds of smaller reptiles, attracted by the mucus or slime which covers his exterior, become the easy prey of the artful machinations of their scaly deceiver.
The sperm whale is frequently subject to deformity of the lower jaw, two instances of which we have seen, in which the deformity was so great as to render it impossible for the animal to find the jaw useful in catching its prey, or even, one might have supposed, in deglutition; yet these whales possessed as much blubber, and were as rich in oil as any of a similar size we have seen before or since. In both these instances of crooked jaws, the nutrition of the animal appeared to be equally perfect. In both cases the jaws were bent on one side. It would be interesting here to inquire into the causes of this deformity; but whether it is the effect of disease, or the consequence of accident, would be difficult to ascertain. Old whalemen affirm that it is caused by fighting. They state that the sperm whale fights by rushing head first one upon the other, their mouths, at the same time, wide open; their object appearing to be the seizing of their opponent by the lower jaw, for which purpose they frequently turn themselves on their side. In this manner they become, as it were, locked together, their jaws crossing each other, and in this method they strive vehemently for the mastery. We have never had the fortune to witness one of these combats, but if it be the fact that such take place, we need not wonder at seeing so many deformed jaws among sperm whales; for we can easily suppose the enormous force exerted on these occasions,163 taking into consideration, also, the comparative slenderness of the jaw-bone in this animal. From these facts it may at least be surmised, with a great degree of probability, that the mode of procuring food as above stated is the true one; for with a jaw so much deformed, the animal would seem incapable of pursuing his prey, and would consequently gain but a very precarious subsistence, did not its food actually throng about its mouth and throat, invited by their appearance, and attracted in some degree, as is supposed, by the peculiar and very strong odor of the sperm whale.
The teeth of the sperm whale are merely organs of prehension. They can be of no use for mastication, and consequently the fish, etc., which he occasionally vomits present no marks of having undergone the process.
The manner of the suckling of the young ones is a matter involved in some obscurity. It is impossible, from the singular conformation of the mouth, that the young one could seize the nipple of the mother with the forepart of it, for there are no soft lips at this part, but instead the jaws are edged with a smooth and very hard cartilaginous substance; but about two feet from the angle of the mouth they begin to be furnished with something like lips, which form at the angle some loose folds, soft and elastic, and it is commonly believed by the most experienced whalemen that it is by this part the young whale seizes the nipple and performs the act of sucking, and which is doubtless the mode of its doing so.
Swimming.—Notwithstanding his enormous size, we find that the sperm whale has the power of moving through the water with the greatest ease, and with considerable velocity. When undisturbed, he passes tranquilly along, just below the surface of the water, at the rate of about two to four miles per hour, which progress he effects by a gentle oblique motion from side to side 164 of the “flukes.” When proceeding at his common rate, his body lies horizontally, his “hump” projecting above the surface, with the water a little disturbed around it, and more or less according to his velocity. This disturbed water is called by whalemen “white water,” and from the greater or less quantity of it an experienced whaleman can judge very accurately of the rate at which the whale is going from the distance of three or four miles.
In this mode of swimming the whale is able to attain a velocity of about eight or nine miles per hour; but when desirous of proceeding at a more rapid rate, the action of the tail is materially altered. Instead of being moved laterally and obliquely, it strikes the water with the broad flat surface of the flukes in a direct manner, upward and downward, and each time the blow is made with the inferior surface the head of the whale sinks down to the depth of eight or ten feet, but when the blow is reversed it rises out of the water, presenting then to it only the sharp, cutwater-like inferior portion.
The blow with the upper surface of the flukes appears to be by far the most powerful, and as, at the same time, the resistance of the broad anterior surface of the head is removed, it is the principal means of progression. This mode of swimming with the head alternately in and out of the water is called by whalemen “going head out;” and in this way the whale can attain a speed of ten or fifteen miles an hour, and this latter is believed to be his greatest velocity.
The tail is thus seen to be the great means of progression, and the fins are not much used for that purpose; but occasionally, when suddenly disturbed, the whale has the power of sinking suddenly and directly downward in the horizontal position, which he effects by striking upward with the fins and tail.
Breathing.—All the cetacea, as is well known, are warmblooded 165 animals, and possess lungs, and, consequently, require a frequent intercourse with atmospheric air, and for this purpose it is necessary that they should rise to the surface of the water at certain intervals. The majority of this class of animals do not appear to perform this function with any regularity, and it is in this respect that the sperm whale is remarkably distinguished among the cetacea; and it is from his peculiar mode of “blowing” that he is recognized, even at a great distance, by experienced whalemen. When at the surface for the purposes of respiration the whale generally remains still, but occasionally continues making a gentle progress during the whole of his breathing-time. If the water is moderately smooth, the first part of the whale observable is a dark-colored pyramidal mass, projecting two or three feet out of the water, which is called the “hump.”
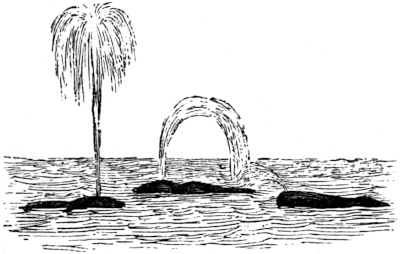
At very regular intervals of time, the nose, or “noddle-end,” emerges at a distance of from forty to fifty feet from the hump in the full-grown male. From the extremity of the nose the spout is thrown up, which, when seen from a distance, appears thick, low, and bushy, and of a white color. It is formed of the expired air, which is forcibly ejected from the spout-hole, acquiring its white color from the minute particles of water previously 166 lodged in the chink or fissure of the nostril, and also from the condensation of the aqueous vapor thrown off by the lungs.
The spout is projected from the spout-hole at an angle of about forty-five degrees, in a slow and continuous manner, for the space of about three seconds of time. If the weather is fine and clear, and there is a gentle breeze at the time, it may be seen from the masthead of a moderate-sized vessel at the distance of five or six miles. The spout of the sperm whale differs much from that of other large cetacea, in which it is mostly double, and projected thin, and like a sudden jet; and as in those animals the spout-holes are situated nearly on the top of the head, it is thrown up to a considerable height in almost a perpendicular direction. When, however, a sperm whale is “gallied” or alarmed, the spout is thrown up much higher and with great rapidity, and consequently differs much from its usual appearance. The regularity with which every action connected with its breathing is performed by the sperm whale is very remarkable. The length of time he remains at the surface, the number of spouts or expirations made at one time, the intervals between the spouts, the time he remains invisible “in the depth of the ocean buried,” are all, when the animal is undisturbed, as regular in succession and duration as it is possible to imagine.
In different individuals the times consumed in performing these several acts vary, but in each they are minutely regular, and this well-known regularity is of much benefit to the whaleman; for, when he has once noticed the periods of any particular sperm whale which is not alarmed, he knows to a moment when to expect it again at the surface, and how long it will remain there.
Immediately after each spout the nose sinks beneath the water, scarcely a second intervening for the act of 167 inspiration, which must consequently be performed very quickly, the air rushing into the chest with astonishing velocity. There is, however, no sound caused by the expiration or spout; in this respect, also, differing from other whales, for the “fin-back” whale and some others have their inspirations accompanied by a loud sound, as of air forcibly drawn into a small orifice. This sound is called by whalemen the “drawback,” and when heard at night near the ship, convinces the listening watch of the species to which it belongs. In a large “bull” sperm whale, the time consumed in making one inspiration and one expiration, or the space from the termination of one spout to that of another, is ten seconds, during six of which the nostril is beneath the surface of the water, the inspiration occupying one, and the expiration three seconds; and at each breathing-time the whale makes from sixty to seventy inspirations, and remains, therefore, at the surface of the water eleven or twelve minutes. At the termination of this breathing-time, or, as whalemen say, when he has had his “spoutings out,” the head sinks slowly, the “small,” or the part between the hump and flukes, appears above the surface of the water, curved with the convexity upward; the flukes are then lifted high into the air, and the animal, having assumed a straight position, descends perpendicularly to an unknown depth. The act is performed with regularity and slowness, and is called by whalemen “turning flukes;” an act, too, which is always noticed by those at masthead, who call loudly, when they disappear below the surface, “T-h-e-r-e goes flukes!” The whale continues thus hidden beneath the surface from sixty to seventy minutes; some will remain an hour and twenty minutes. If we take into consideration the quantity of time that the full-grown sperm whale consumes in respiration, and also the time he takes in searching for food and performing other acts below the surface of the ocean, we168 should find that a seventh of the time of this huge animal is consumed in the function of respiration.
The females being found generally in large numbers and in close company, it is difficult to fix the attention upon one individual, so as to ascertain precisely the time consumed below the surface. However, as all in one school generally rise at the same time, it may be observed that they remain below the water about twenty minutes. They make from thirty-five to forty expirations during the period they are at the surface, which is about five minutes, and they thus consume about a fifth of their time in respiration, a proportion considerably greater than that of the adult males.
When disturbed or alarmed, this regularity in breathing appears to be no longer observed. For instance: when a “bull,” which, when undisturbed, remains at the surface until he has made fifty expirations, is alarmed by the approach of a boat, he immediately plunges beneath the surface, although he may not have performed more than half the usual number of his expirations. He will soon rise again not far distant and finish his full number of respirations; and in this case, also, he generally sinks without having assumed the perpendicular position before described. On the contrary, he sinks suddenly in the horizontal position, and with remarkable rapidity, leaving a sort of vortex in the place where his huge body lately floated.
When urging his rapid course through the ocean in that mode of swimming which is called “going head out,” the spout is thrown out every time the head is raised above the surface, and under these circumstances of violent muscular exertion, as would be expected, the respiration is much more hurried than usual.
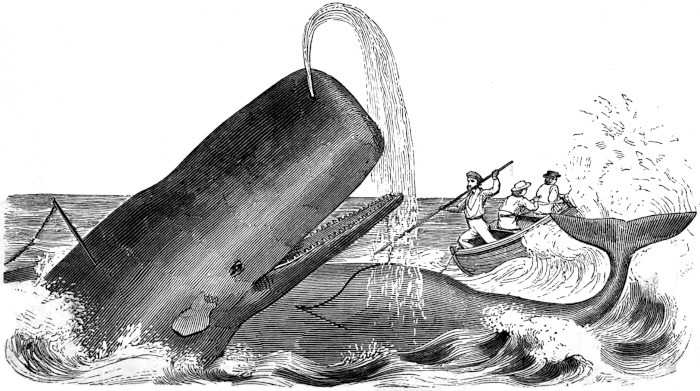
171
Other Actions of the Sperm Whale.—When in a state of alarm, or gamboling in sport on the surface of the ocean, the sperm whale has many curious modes of acting. It is difficult to conceive any object in nature calculated to cause alarm to this leviathan; notwithstanding which, he is remarkably timid, and is readily alarmed at the approach of a boat.
When seriously alarmed, he is said by whalemen to be “gallied,” and in this state he performs many actions very different from his usual mode, as has been mentioned in speaking of his swimming and breathing, and many also which he is never observed to perform under any other circumstances. One of them is what is called “sweeping,” which consists in moving the tail from side to side on the surface of the water, as if feeling for the boat, or any other object that may be within reach. The whale has also an extraordinary manner of rolling over and over on the surface, and this he does when “fastened to” from a boat. At times they place themselves in a perpendicular posture, with the head only above water, presenting, in this position, a most extraordinary appearance. When seen from a distance they resemble large black rocks rising out of the midst of the ocean. This posture they seem to assume for the purpose of surveying more accurately or more easily the surrounding expanse. A species of whale, called by whalemen “blackfish,” is most frequently in the habit of assuming this position.
The eyes of the sperm whale, being placed in the widest part of the head, of course afford the animal an extensive field of vision, and he appears to view objects very readily that are placed laterally in a direct line with the eye, and when they are placed at some distance before him. His common manner of looking at a boat or a ship is to turn over on his side, so as to cause the rays from the object to strike directly upon the retina.
Now, when alarmed, and consequently anxious to take as rapid a glance as possible on all sides, he can much more readily do so when in the above-described172 perpendicular position. Occasionally, when lying at the surface, the whale appears to amuse itself by violently beating the water with its tail. This act is called “lop-tailing,” and the water lashed in this way into foam is termed “white water,” and by it the whale is often recognized from a great distance.
But one of the most curious and surprising of the actions of the sperm whale is that of leaping completely out of the water, or of “breaching,” as whalemen term it. The way in which he performs this extraordinary motion appears to be by descending to a certain depth below the surface, and then making some powerful strokes with his tail, which are frequently and rapidly repeated, and thus convey a great degree of velocity to his body before he reaches the surface, when he darts completely out. When just emerged and at its greatest elevation, his body forms with the surface of the water an angle of about forty-five degrees, the flukes lying parallel with the surface in falling. The animal rolls his body slightly, so that he always falls on his side, and seldom breaches more than twice or thrice at a time. In very clear weather, on the Japan ground, we have seen the breach of a large whale at a distance of sixteen miles; but, as a general thing, eight or ten miles is the distance that a breach may be discovered from masthead.
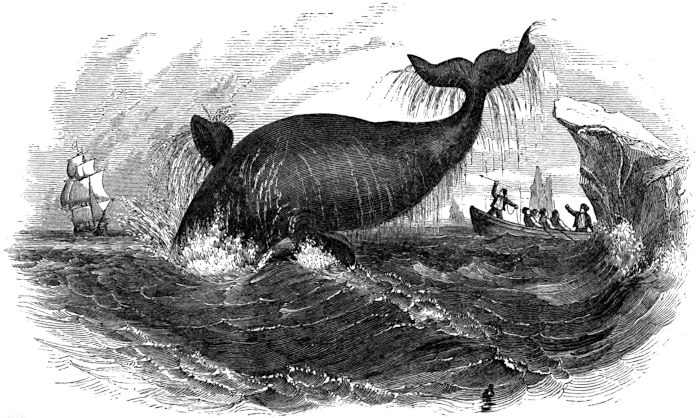

175
It is probable that the sperm whale often resorts to this action of breaching for the purpose of ridding itself of various animals which infest its skin, such as large “sucking-fish,” and other animals which resemble crabs. Of the former of the parasites, some fix themselves so closely to this convenient carrier that they sometimes adhere to the skin of the whale for several hours after its death, and then suffer themselves to be forced off by the hands of the whalemen. It is not improbable, also, that some of these actions may be resorted to in the whale endeavoring to avoid the assaults of the swordfish, by which they are sometimes attacked. There is also an animal called a “killer,” which, in company with the swordfish, attack the whale. The latter will goad him from below, while the former leaps out of the water and falls upon him from above, the attack thus intimidating the whale, and giving the swordfish an opportunity to inflict its wounds.
Herding.—The sperm whale is a gregarious animal, and the herds formed by it are of two kinds; the one consisting of females, the other of young bulls not fully grown.
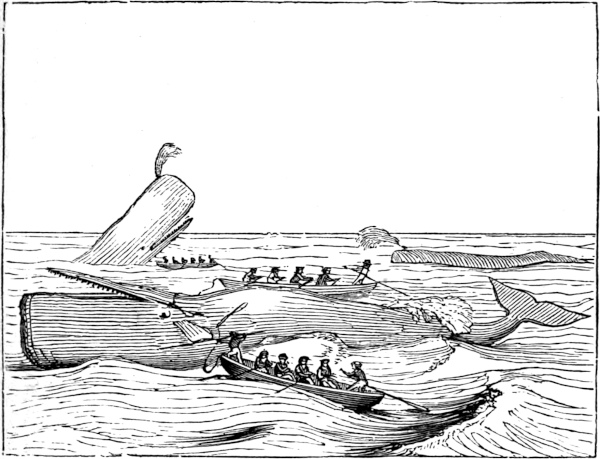
These herds are called by whalemen “schools,” and occasionally consist of great numbers. With each school of females are always from one to three large males, the lords of the herd. The males are said to be extremely jealous of intrusion by strangers, and to fight fiercely to176 maintain their rights. The full-grown males, or “large whales,” almost always go alone in search of food, and, when they are seen in company, are supposed to be migrating from one feeding-ground to another. The large whale is generally very incautious, and if alone, he is without difficulty attacked and easily killed, as he frequently, after receiving the first blow from the harpoon, appears hardly to feel it, but continues lying like a “log of wood” on the water before he rallies or makes any attempt to escape from his enemies.
Large whales are sometimes, but rarely, met with remarkably cunning and full of courage, when they will commit dreadful havoc with their jaws and tail. The jaw and head, however, appear to be their principal offensive weapons.
The female breeds at all seasons, producing but one at a time, except in a few instances, in which two are produced. Her time of gestation is unknown, but is supposed to be about ten months. Their young, when first born, are about twelve or fourteen feet in length, and five or six in girth. The females are much smaller than the males, being considered not more than one fourth the size of the adult large whale. They are very remarkable for attachment to their young, which they may frequently be seen urging and assisting to escape from danger with the most unceasing care and fondness. They are also not less remarkable for their strong feeling of attachment to each other; and this is carried to so great an extent, that, should one female of a herd be attacked and wounded, her faithful companions will remain around her to the last moment, or until they are wounded themselves. This act of remaining by a wounded companion is called by whalemen “bringing to,” and whole schools have been destroyed by dexterous management, when several ships have been in company, wholly from these whales possessing this remarkable 177 disposition. The attachment appears reciprocal on the part of the young whales, which have been seen about the ship for hours after their parents have been killed.
The young males or “young bulls” go in large schools, but differ remarkably from the females in disposition, inasmuch as they make an immediate and rapid retreat upon one of their number being struck, who is left to take care of himself. They are also very cunning and cautious, keeping at all times a good look-out for danger. It is consequently necessary for the whaleman to be extremely cautious in his mode of approaching them, so as, if possible, to escape being seen or heard, for they have some mode of communication one to another, through a whole school, in an incredibly short space of time. They are consequently much more troublesome to attack, and more dangerous and difficult to kill, great dexterity and dispatch being necessary to give them no time to recover from the pain and fright caused by the first blow. When about three fourths grown, or sometimes only half, they separate from each other and go singly in search of food.
All sperm whales, both large and small, have some method of communication with each other by which they become apprised of danger, and this they do, although the distance may be very considerable between them, sometimes amounting to six, seven, eight, or even ten miles. The method by which these communications are carried on remains a curious secret.
It has been before stated that the food of the sperm whale consists almost wholly of an animal of the cuttle-fish kind, called by whalemen “squid,” and by naturalists “Sepia octopus;” and at times, when he is near the shore, he feeds upon small fish, which are denominated “rock cod,” and which sometimes approach the size of a moderate salmon.
But the instances in which fish of this description have been ejected from the stomach of the sperm whale are but rare, while every day’s experience proves that its common food consists of that division of molluscous animals which naturalists have denominated “Cephalopoda,” and of which the “Sepia octopus,” or “sea squid,” appears to be the most common.
A few words on the natural history of this highly organized and remarkable animal can not fail to be interesting to the reader, as it has excited the attention of naturalists for many ages, from the remarkable nature of its formation and peculiar habits.
Endowed with all the five organs of sense, it is second to no inhabitant of the mighty waters in the complete elaboration of its organs, which has constantly rendered it a great object of attention to the anatomist and physiologist.
Dr. Roget, in his Bridgewater Treatise, under the head of “Cephalopoda,” states that “we now arrive at a highly interesting family of mollusca, denominated Cephalopoda, and distinguished above all the preceding orders by being endowed with a much more elaborate organization179 and a far wider range of faculties. The Cephalopoda have been so named from the position of certain organs of progressive motion which are situated on the head, and, like the tentacula of the polypus, surround the opening of the mouth. These feet, or arms, or tentacula, if we choose to call them so, are long, slender, and flexible processes, exceedingly irritable and contractile in every part, and provided with numerous muscles, which are capable of moving or twisting them in all directions with extraordinary quickness and precision. They are thus capable of being employed as instruments not only of progressive motion, but also of prehension. For this purpose they are, in many species, peculiarly well adapted, because, being perfectly flexible as well as highly muscular, they twine with ease round any object of any shape, and grasp it with prodigious force. In addition to these properties, they derive a remarkable power of adhesion to the surfaces of bodies from their being furnished with numerous suckers all along their inner sides. Each of these suckers is usually supported on a narrow neck or pedicle, and strengthened at its circumference by a ring of cartilage. Their internal mechanism is more artificial than the simple construction already described; for when the surface of the disk is fully expanded, it is formed of a great number of small, slender pieces, resembling teeth, closely set together, and extending from the inner margin of the cartilaginous rings in the form of converging radii to within a short distance of the centre, where they leave a certain aperture.
“In the flattened state of the sucker, this aperture is filled by the projecting part of a softer substance, which forms an interior portion, capable of being detached from the flat circle of the teeth when the sucker is in action, and of leaving an intervening cavity. It is evident that by this mechanism, which combines the properties of an180 accurate valve with an extensive cavity for producing rarefaction, or the tendency to vacuum, the power of adhesion is considerably augmented. So great is the force with which the tentacula of the cuttle-fish adhere to bodies by means of this apparatus, that, while their muscular fibres continue contracted, it is easier to tear away the substance of the limb than to release it from its attachment. Even in the dead animal we have found that the suckers retain considerable powers of adhesion to any smooth surface to which they may be applied.
“The octopus, which was the animal denominated polypus by Aristotle, has eight arms of equal length, and contains in its interior two very small rudimentary shells, formed by the inner surface of the mantle. This shell becomes much more distinct in the loligo, where it is cartilaginous, and shaped like the blade of a sword. The internal shell of the common sepia is large and broad, and composed wholly of the carbonate of lime; it is well known by the name of cuttle-fish bone. Its structure is extremely curious, and deserves particular attention, as establishing the universality of the principle which regulates the formation of shells, whether external or internal, and from which structures differing much in their outward appearance may result. It is composed of an immense number of thin calcareous plates, arranged parallel to one another, and connected by thousands of minute hollow pillars of the same calcareous material, passing perpendicularly between the adjacent surfaces. This shell is not adherent to any internal part of the animal which has produced it, but is inclosed in a capsule, and appears like a foreign body impacted in the midst of organs with which, at first sight, it appears to have no relation. It no doubt is of use in giving mechanical support to the soft substance of the body, and especially to the surrounding muscular flesh; and this probably contributes to the high energy which the animal displays 181 in all its movements. It has been regarded as an internal skeleton, but it certainly has no pretensions to such a designation; for, although enveloped by the mantle, it is still formed by that organ, and the material of which it is composed still carbonate of lime. On both these accounts it must be considered as a true shell, and classed among the productions of the integuments. It differs, indeed, from bony structures, which are composed of a different kind of material, and formed on principles of growth totally dissimilar. Besides tentacula, the sepia is also provided with a pair of fleshy fins, extending along the two sides of the body. The loligo has similar organs of a smaller size, and situated only at the extremity of the body which is opposite to the head. They have been regarded as the rudiments of true fins, which are organs developed in fishes, and which are supported by slender bones; but no structure of this kind exists in the fins of the Cephalopoda. In swimming, the organs principally employed by cuttle-fish for giving an effective impulse to the water are the tentacula. These they employ as oars, striking with them from behind forward, so that their effort is to propel the hinder part of the body, which is thus made to advance foremost, the head following in the rear. They also use these organs as feet for moving along the bottom of the sea. In their progress under these circumstances, the head is always turned downward and the body upward, so that the animal may be considered as literally walking on its head!
“The necessity of this position for the feet arises probably from the close investment of the mantle over the body; for, although the mantle leaves an aperture in the neck for the entrance of water to the respiratory organs, yet in other respects it forms a sack, closed in every part except where the head, neck, and accompanying tentacula protrude.
“In the calamary, as well as the common sepia, two 182 of the arms are much longer than the rest, and terminate in a thick cylindrical portion, covered with numerous suckers, which may not inaptly be compared to a hand. These processes are employed by cuttle-fish as anchors, for the purpose of fixing themselves firmly to rocks during violent agitations of the sea; and accordingly we find that it is only the extremities of these bony tentacula that are provided with suckers, while the short ones have them also along their whole length. The other genera of cephalopodous mollusca are, like the sepia, provided with tentacula attached to the head. They comprehend animals differing exceedingly in size, some being very large, but a great number very minute, and even microscopic.”
Other animals of this kind inhabit shells, one of which is the nautilus, which, says Roget, “possesses a shell exceedingly thin and almost pellucid; probably for the sake of lightness, for it is intended to be used as a boat. For the purpose of enabling the animal to avail itself of the impulses of the air while it is thus floating on the water, Nature has furnished it with a thin membrane, which she has attached to two of the tentacula, so that it can be spread out like a sail to catch the light winds which waft the animal forward on its course. While its diminutive bark is thus scudding over the surface of the deep, the assiduous navigator does not neglect to apply its tentacula as oars on either side, to direct as well as to accelerate its motion. No sooner does the breeze freshen and the sea become ruffled than it hastens to take down its sail, and, quickly drawing its tentacula within its shell, renders itself specifically heavier than the water, and sinks immediately into more tranquil regions beneath the surface.”
Sir William Jardine, in speaking of the food of the sperm whale,[4] ventures to suggest to those who may 183 have frequent opportunities of observing whether this whale may not also frequently resort to the medusæ, and minute fish which in so remarkable a manner supply food to some of the smaller, as well as the other genera of the gigantic whales. That there is an abundant supply of this sustenance, both in the Antarctic Ocean and the more smiling latitudes of the southern seas, can easily be proved by a reference to Lesson’s Statements, and also to the Journal of Captain Colnett, who, when near the southern point of America, observes: “During this forenoon we passed several fields of spawn, which caused the water to bear the appearance of barley covering the surface of a bank.”
Arbigny also remarks that “there are immense tracts off the coast of Brazil filled with small creatures so numerous as to impart a red color to the sea.” “Statements of this sort,” observes Sir William, “could easily be multiplied; and hence we can not but suppose that this kind of food, which is ascertained to afford such rich nourishment to the other great cetacea, may very possibly be appropriated by the sperm whale to the same purpose.”
This is an unaccountable error on the part of the compiler of the Naturalists’ Library. The apparent banks above mentioned, and which we have ourselves frequently seen in various parts of the ocean, are certainly formed by myriads of medusæ and other small animals, which form the sustenance of the Balæna mysticetus, or right whale’s food, which consists of animals of the shrimp kind, and other minute creatures, which are closely congregated and swarm in those animated “banks,” but of which the sperm whale never partakes; as it is not “very possible,” but quite impossible that he could do so, however inclined he might be, on account of the organization of his feeding apparatus, which may be readily seen when its form is referred to.
184
The Sepia octopus, or “sea squid,” sometimes reaches an enormous size. In the Philosophical Transactions for 1758 (777), after having given an interesting description of a specimen sent for examination, the editor states that “it can, by spreading its arms abroad like a net, so fetter and entangle the prey they inclose when they are drawn together as to render it incapable of exerting its strength; for, however feeble these branches or arms may be singly, their power united becomes surprising; and we are assured Nature is so kind to these animals that if, in a struggle, any of their arms are broken off, after some time they will grow again. It is evident,” he continues, “from what has been said, that the sea polypus or octopus must be terrible to the inhabitants of the waters in proportion to its size, for the close embraces of its arms and adhesion of its suckers must render the efforts of its prey ineffectual either for resistance or escape, unless it be endowed with an extraordinary degree of strength.”
A gigantic Cephalopoda was discovered by Drs. Bank and Solander, in Captain Cook’s first voyage, floating dead upon the sea, surrounded by birds, who were feeding on its remains. From the parts of this specimen which are still preserved in the Hunterian Collection, and which have always excited the attention of naturalists, it must have measured at least six feet from the end of the tail to the end of the tentacles.
But this last we must imagine a mere pigmy when we consider the enormous dimensions of the one spoken of by Doctor Swediaus,[5] whose tentacula or limbs measured twenty-seven feet in length. But let the doctor speak for himself: “One of the gentlemen,” says he, “who was so kind as to communicate to me his observations on this subject (ambergris), also, ten years ago, caught a sperm whale that had in its mouth a tentaculum of the Sepia octopodia nearly twenty-seven feet 185 long! This did not appear its whole length, for one end was corroded by digestion, so that, in its natural state, it may have been a great deal longer. When we consider the enormous bulk of the tentacula here spoken of, we shall cease to wonder at the common saying of the fishermen, that the cuttle-fish is the largest fish of the ocean.”
In Todd’s Cyclopedia of Anatomy (529), treating of Cephalopoda, in an admirable paper by Mr. Owen, it states that “the natives of the Polynesian Islands, who dive for shell-fish, have a well-founded dread and abhorrence of these formidable Cephalopods, and one can not but feel surprised that their fears should have, perhaps, exaggerated their dimensions and destructive attributes.”
The same learned writer, after having beautifully described another animal of this order, observes: “Let the reader picture to himself the projecting margin of the horny hook developed into a long, curved, sharp-pointed claw, and these weapons clustered at the expanded terminations of the arms, and arranged in a double alternate series along the whole internal surface, and he will have some idea of the formidable nature of the carnivorous onychotenthis.”
This species of Cephalopoda is thus armed with those kind of teeth at the termination of the tentacles in order to secure the agile, slippery, and mucous-clad fishes on which it preys; and there is an instance recorded in the works of a celebrated author on Excursions in the Mediterranean, by which we perceive that these terrible creatures sometimes prey upon men. The author says: “In those shallow waters are caught great quantities of fish, by forming curved lines or palisades some way out to sea with palm branches, by which the fish that come up with the high water are retained when it recedes. The horrid polypus, which is, however, greedily eaten, abounds, and some are of enormous size. They prove, at times, highly dangerous to bathers.
186
“An instance of this occurred a few years since. A Sardinian captain, bathing at Jerbah, felt one of his feet grasped by one of these animals; on this, with his other foot he tried to disengage himself, but this limb was immediately seized by another of the monster’s arms; he then endeavored to free himself with his hands, but these also were firmly grasped by the polypus, and the poor man was shortly after found drowned, with all his limbs strongly bound together by the arms and legs of the fish; and it is extraordinary, that where this happened the water is scarcely four feet in depth.”
Other species of these surprising animals, as the calamaries, or “flying squid,” as they are termed by seamen, have the power of propelling themselves through the atmosphere. “There is good reason for believing,” says Mr. Owen, “that some of the small, slender-bodied subulate species of this genus are enabled to strike the water with such force as to raise themselves above the surface, and dart, like the flying-fish, for a short distance through the air.” We have seen very frequently, both in the North and South Pacifc, tens of thousands of these animals dart simultaneously out of the water when pursued by albicore or dolphins, and propel themselves, head first, in a horizontal direction, for eighty or a hundred yards, assisting their progression probably by a rotary or screwing motion of their arms or tentacles, which they have the power of thus moving with singular velocity. This species also, as well as the large onychotenthis, we are led to believe, often serves the sperm whale for food. We have seen, on several occasions, very large limbs of the latter species of squid floating on the surface of the ocean, appearing as if bitten off by some animal, most probably by the sperm whale; for, when these remains have been seen, we always looked out most anxiously for those animals, and have seldom been disappointed in seeing them within a few hours afterward.
At the close of our first “season” on Japan, we found ourselves with two hundred and fifty barrels more of oil than when we came on to the ground, and we felt greater encouragement, though we were yet very poorly off, being nearly two years from home, with but five hundred and fifty barrels. However, the weather admonished us that we must be leaving those regions; and accordingly, on the 10th of September, we pointed the “Emily’s” head to the southward, and, crowding on the “kites,” we were soon in pleasant weather, making passage to our old ground, the Group.
On the morning of Thursday, September 18th, we were aroused by the soul-cheering cry of “Land ho!” In a moment all hands were in the rigging to catch a glimpse of the land. All strained their eyes with eager excitement to once more view a green spot. We had now been cruising nearly five months, and during that time we had seen nothing that resembled land, and but two ships. Sailing in the midst of the vast North Pacific, and cruising week after week, month after month, nothing new, nothing to change the monotony so usual to shipboard, all at once rose to our view a188 beautiful island densely covered with dark green foliage, the tall cocoanut-trees nodding a welcome as they waved their sweeping branches to and fro; and as we drew near to the land, the neat huts of the natives peering through the leafy opening, with the white sand-beach, a delightful clear atmosphere, with a fine breeze, the old ship standing on in majesty, all combined to make it a scene refreshing to behold—one of beauty and loveliness. Truly have these islands been denominated “breathing-places for sailors.” After beating about, enduring gales and storms, and meeting with no living beings upon the trackless ocean, to be ushered into the presence of one of these lovely “sea-girt isles” fills the beholder with the most joyous feelings, and convinces him that he is yet in the land of the living. We found ourselves, almost unconsciously we might say, offering our thanks and praises to the Giver of all good for His protecting power through the dangers and storms of our voyage thus far, and trusting that we should ere long be restored to those we so dearly loved.
But we were now to cruise for a few months among these islands. On Tuesday, September 21st, we were in sight of Henderville’s Island. At sunset, being about eight miles distant from the land, the wind died away, leaving every thing calm, the surface of the water unruffled, not a breath of air stirring, and the sails idly hanging or flapping themselves to and fro. The current was rapidly setting us in-shore. About eight o’clock we lowered a boat, and found we were drifting toward the reef at the rate of two miles per hour. The lights of the native fishermen along the reefs were plainly visible, and the roar of the breakers came to our ears in thunder tones, that sent a thrill through every heart, sounding like a death-knell, or the roaring of some monster anxious for his prey. That land which had appeared so beautiful to us but a few days previous was 189 now hateful to our sight, and oh! how we longed for “plenty of sea-room” again. That island might truly be a “breathing-place” for us, but we feared it would be our last “breathing-place,” for we well knew the disposition of its natives, and were well aware that, should our ship be lost, there was no mercy to be expected from those rapacious savages. Serious thoughts for once filled the mind of every man on board: the visions of those happy homes far away—were we never to visit those homes again? The memories of the many happy days spent with friends—were we never again to enjoy them? After battling the elements thus far, after passing through so many dangers, were we thus to perish—to be thus massacred by a horde of merciless savages, and no one, perhaps, to tell our friends when and how we died? Oh! it was horrible to think of, and caused a shudder of anguish to pass through our every frame. And yet nothing but the interposition of a kind and merciful Providence could avert this fate. Slowly but surely were we drifting into those fatal breakers, and one hour more, one short hour, we felt must decide our fate. Oh, for a breeze! in vain we look for it; in vain we wished for it. All was calm and unruffled.
As a last resort, the boats were ordered out, and all hands sprang into them as they never sprang before, and commenced towing the ship. For four long hours did those noble men work at the oars, a battle between life and death, each seemingly striving for the mastery. We were just able, by this constant tugging at the oars, “to hold our own,” to stem the current. About one o’clock in the morning a breeze sprang up, and never, never was wind so welcomed. All hands gave one simultaneous shout, “We are saved!” and returned to the ship with joyous hearts. We could not but thank our heavenly Father for thus preserving us from the horrible fate that at one time seemed so certainly to await us.
190
Glad indeed were we to be delivered from this fate, and we now directed our course toward Ocean Island. On the morning of Thursday, September 25th, at daylight, the welcome shout was heard, “There she blows! A large whale!” Instantly the boats were down, and all hands gave chase. We discovered the whale had been fastened to by some other ship, as he had two irons in him, with a long line trailing behind. The larboard, or mate’s, boat soon fastened; the whale sounding heavily, a signal was made for “more line,” and the bow boat ran down, and passed to them their line; the whale continued to sound, taking out nearly eight hundred fathom (4800 feet), until the irons drew. In a short time the whale made his appearance; the boats again renewed the chase. After some considerable manœuvring and provoking dodging on the part of the whale, the waist-boat fastened. Away he went again, railroad speed, and after treating the boat’s crew to a ride that caused them to exert every muscle to hold their hair on, the irons again “came home.”
This only served to increase the excitement, and again the several boats gave chase with redoubled energy and ardor. About sunset the captain’s boat drew near; he stood in the head of the boat, determined to make the old fellow show the “red flag.” He was now close on; all were looking with breathless anxiety. They neared him, and the captain darted; the second iron followed the first in an instant, and he shouted “We are fast!” and turned round to roll up the sail of the boat. The old man was the spryest man in the ship, and before he could roll up the sail (which usually occupies about a minute), the last flake of line went out of the boat, and away went the old veteran with four hundred fathom (2400 feet) of our line and two harpoons. This was the last chance, it being near sunset, and they gave up the chase, at the same time respecting the intelligence and191 sagacity of the whale in not allowing himself to become a prey to the frail boats. He probably felt himself insulted by being pestered with such small trash, as well as the idea of being melted up for grease.
The men came on board hungry, thirsty, and tired, having pulled and worked from 6 A.M. to 8 P.M., with but a couple of cakes of hard bread and about a quart of water each to refresh themselves with through the day. The weather was intensely hot; they were exposed to the equatorial sun, which was directly over them; and yet they thought of none of these things till they came on board with no whale. Thus ended the chase of the largest whale we had yet seen, and which our boys christened “Ocean Island Dick.” The captain asserted that for the many years he had followed the sea (about thirty), he had never seen so large a whale as this one. Never mind; he has got the ship’s mark, in the shape of two irons, that will be apt to trouble him some before he rids himself of them.
Saturday, September 27th, we were at Ocean Island. The king himself, with quite a number of natives, came off, bringing with them nothing but pumpkins to trade. One of the boys remarked that he “supposed they considered themselves ‘some pumpkins!’” They were of an excellent quality, but were, in reality, our crooked-neck squash. They raise them in great quantities, and it is the principal article of trade with the ships. This island is certainly the most beautiful one of the group, the land being moderately high, and presenting a very even surface.
On leaving here we shaped our course again for Strong’s Island, which we saw on Wednesday, October 8th. As we neared the land the wind died away, leaving us becalmed, which continued for four days and nights. How provoking it was to lie there, about sixteen or eighteen miles from the land, during all this time, 192 and feel ourselves thus imprisoned! During the day-time the surface of the water would scarce be disturbed by a ripple, and presented the appearance of a vast mirror, with a green islet by the way of decoration. After having been shut up in the ship for six long and weary months without setting foot on shore, to be thus kept in sight of a green “breathing-place” for four days and nights, and feel that you could not reach it so long as the calm continued, was tantalizing; it was not strange that we wished for a strong breeze, one that would put us into the harbor in two or three hours.
At length our wishes were gratified; and on Sunday morning, October 12th, we again dropped anchor in our old resting-place. In the afternoon we went on shore, and, on arriving at our “hotel,” found Zegrah and his wife, who gave us a hearty welcome, having been expecting us. In the evening they gave a feast in honor of our arrival.
The next two or three days we spent as usual, rambling over the island, through canals and over walls—through swamps and ditches in search of adventure. As we have before observed, we found the natives very kind and hospitable, always welcoming us in a hearty manner; and, from their actions, we should judge they were really glad to see us again. Wherever we visited, they spread before us the numerous fruits of the island, urging us to eat, and insisting that we should drink a shell of carva with them. We can never forget their kind, simple-hearted hospitality, and we have often looked back upon our visits there as green spots in the desert of life, refreshing and cheering.
Since the death of Mr. Smith, whenever we had been at this island, Canker would never come near the ship. This we thought strange, as the first time we were there he was on board nearly every day. Still, he appeared very kind to any of the ship’s company when they called 193 upon him, making them presents of fruit, etc., as if wishing to reinstate himself in their good graces.
On Thursday, October 16th, the king came off to the ship to dinner. On sitting down at the table, he happened to cast his eye upon a dish of greens, which had been sent to the ship by Canker, and cooked by the steward. He instantly took the dish, and then went upon deck, examined them minutely, and threw them all overboard. He then inquired if there were any more on board, and on being answered that a large quantity had been cooked for the men, he ordered them to be thrown overboard immediately. He then asked, “Who been makey send all the same on board?” On being told “Canker,” his anger scarcely knew bounds. He raved and appeared so excited we feared he would do himself some injury. After a little while he became more calm, and said, “Captain, you look out that Canker; he too much bad man; he no good. I no like speak too much; he my son.” It was evident there was a struggle going on in the heart of the good old king. He loved his son notwithstanding his faults, and to thus have evidence of his bloodthirstiness angered him, and it was some time before he fully recovered himself.
It was, indeed, a diabolical scheme of this Canker’s. Some one of the crew had injudiciously told him, in jest, that “a large man-of-war was on its way to the island to inquire into the death of Mr. Smith, and that, if the captain or any of the crew should tell them he had poisoned Mr. S., the man-of-war would hang him.” This he believed, and, feeling his guilt, he determined to remove all evidence of it by putting the whole ship’s company to death by poison. He knew we were all fond of greens, and he chose a day, also, on which none would be on shore, all hands taking dinner on board that day. But, through the interposition of the Almighty, he was 194 prevented from accomplishing his dark and bloody designs. How much had we to thank our heavenly Father for, and how many times did he preserve our lives from threatened dangers, seen and unseen, during those five eventful years of our life!
One evening during our stay, one of our men, by the name of Wilds, whom we shipped on our first visit to this island, had some little disturbance with her Strong’s Island majesty, the queen. Wilds had always been a great favorite with her, and was privileged to do and say as he pleased about the house. He had lived with the king while on the island. This evening he came in with his mats and pillow rolled up under his arm, and commenced joking and teasing the queen; finally, starting to leave, he asked her if he could leave them there until he returned for them. On being answered in the affirmative, he threw the bundle at her in a playful manner, which happened to hit her rather solid, and knocked her down. She screamed, of course (what woman would not?), and imagined herself nearly killed. Poor Wilds at first knew not what to do or say; finally he undertook to apologize, but she would not listen to a word, and ordered him to leave.
This little incident shows what a trifling circumstance will break the friendship of some of these natives, and turn them to as bitter enemies as they were former friends, as in the case of Mr. S. and Canker. Wilds received orders from the queen not to come to the palace again, as she did not like the idea of allowing her royal person to be a target for a common sailor to fire his bundles at. The king, however, when he heard of it, laughed at it as a good joke, and treated Wilds with as much friendship as formerly.
We were now all ready for sea again—wood and water all on board. Thinking, however, that we must have one more ramble before leaving, on Saturday, October195 18th, we started, in company with several of our shipmates, for a stroll among the mountains. During our walk we came to a fine spring running into a large stone basin. The weather being excessively hot, we concluded to lie down in this cool, shady place, and rest. While reclining on these beautiful mossy banks, spinning yarns of homes far away, and of happy days, carrying ourselves, in imagination, to those homes and pleasures, we were very suddenly and unceremoniously aroused from our easy positions by a rushing sound, accompanied by a hoarse roar. It can be imagined that we did not occupy many moments in regaining our feet, and we had scarcely done so ere a large wild boar rushed past with great velocity, deigning not even to bestow a passing glance upon us, the spectators of his race, whose hair stood on end, but kept on his course until he was lost in the thicket.
Some natives, headed by Sekane, the chief soon made their appearance, and stated that they had started the boar from his den by wounding him, and asked us to join in the chase. This we consented to do, as we were anxious to view the sport; but, not exactly understanding the hooks and crooks of wild-boar hunting, took good care to keep well in the rear, and our eyes about us. It was certainly amusing; the slightest noise would cause our company to start for some tree, and on finding that it was merely a false alarm, would look immensely foolish. The natives now wished us to guard a pass that we had arrived at while they went after him. As soon as the natives were all out of sight, we took our stations in small trees, where we were sure that we should be out of reach of the boar’s tushes. After waiting some time, we heard a shouting but a short distance from us. Each now instinctively shouted “he is coming,” and tried to ascend still higher. We were relieved from our fears, however, by seeing the squad of196 natives approaching, with the wild boar lashed in such a manner that he could not escape. He was carried by means of poles run through the lashings of his feet by four natives. They felt very proud of their booty, and exclaimed, “King have big feast now!” He was captured by means of a lasso thrown over his head by one of the natives. Sekane now wished us to form a grand procession and march to the king’s house, where the boar would be delivered to and received by the king in great style, “all the same ’Meriky fashion,” as they termed it. We accordingly did so; and on our arrival, the natives, who had gathered in great numbers, commenced shouting, until we could hardly “hear ourselves think.” The animal was then presented to the king by Sekane, who made a speech, which was very intelligible to us, as we could not understand a word of it, and replied to by the king in the same manner. We were informed, however, by Cæsar that the king praised highly the natives who had captured him, and that he spoke highly of the bravery and assistance the white men had rendered, as Sekane had given him a glowing description of our assistance. This, of course, restored our confidence in our own courage, which had somewhat fallen.
The animal was immediately slaughtered, and preparations were made for a “big feast,” to which the white men were all invited, and those of us who had so materially assisted in its capture were assigned posts of honor by the side of Sekane, who was the “lion of the day.” We now began to think that we had some courage, and many of the boys expressed themselves as ready to proceed on another “wild boar hunt,” provided—the natives would go ahead. The feast passed off with great eclat, and all hands enjoyed it much, dining this time on veritable “hog,” and not “dog.”
But we were now ready for the “blue waters” again, and we must not loiter too long amid the pleasant197 scenes of Strong’s Island. On Monday, October 19th, we weighed anchor and proceeded to sea. The king and Captain H. accompanied us outside the passage, when we took leave of them, and, with a fair wind, shaped our course once more for the Group. We had been treated with such uniform kindness by most of the natives the many times that we had visited this island, and by such marked respect by the king and chiefs, that the remembrance of the happy hours we had there spent, and the pleasant and agreeable scenes we had met, as well as the information we had gained, still clings to us, and furnishes many an agreeable moment for reflection and pleasure.
We were again at our old business of cruising and whaling, but with poor success. On Friday, October 31st, we captured three blackfish. These are a species of whale yielding from one to five barrels of oil, of an inferior quality, and almost black, from which color the fish seems to have derived its name.
Monday, November 3d, we spoke the “Phocion,” of New Bedford, Captain Nichols, and the day following the “Ganges,” of Nantucket, cutting in a sperm whale, which assured us that others were fortunate if we were not, and consoling ourselves that our turn would soon come.
Nothing of any interest transpired for a month from this time, except occasionally lowering for whales and the capture of two, until Wednesday, December 3d, when we again spoke the bark “Belle,” just from Sydney. From them we learned that our carpenter, alias 199 “Chips,” who, it will be recollected, deserted at Pitt’s Island, and left in the “Belle,” had been arrested in Sydney for stealing a quadrant and sextant from a ship there, and thrown into prison. We were now to lose one of our best men, though a Kanaka. For some time past it was evident that Friday had been growing homesick, and he often told us, “I like go see my land.” The captain, being willing to gratify him, and it being uncertain when we should again visit his “land,” consented to his taking passage in the “Belle,” which vessel was going there immediately. Friday was overjoyed at this prospect; his chest was brought upon deck, ready to be lowered into the other ship’s boat. But now came the parting with his shipmates. This was hard for poor Friday, for all loved him, though he had a dark skin. He had been so kind to all on board—so ever ready and willing to do all in his power to serve others’ interests—so quick to learn, and so grateful for any kindness shown, that all hands, from captain to cook, loved and respected him. Many little presents had been bestowed upon him as tokens of remembrance, and his heart almost failed him as he looked around upon those he was leaving behind; the tears gushed from his eyes; but, summoning resolution to his aid, he sprang into the boat awaiting him, and sadly waving his hand to us, was soon out of sight. We can truly say that we have parted with many white acquaintances with less sorrow than we did with Friday, the Pitt’s Island Kanaka.
On Tuesday, December 9th, we spoke the “Bengal,” of New London, an Arctic whaler, who reported quite a number of whalers lost in the Arctic the previous season by the ice. A short time after we spoke the “Lion,” of Providence, Captain Nichols, a brother of the master of the “Phocion,” whom we saw a few days previous.
200
The morning of Saturday, December 20th, broke with very squally, thick weather, and we came very near running down Henderville’s Island, or running well on it. It appeared almost that we were fated to be cast away on this hated place. The “Lion” was on our weather beam, and was running in the same direction. As the squall, which was a severe one, passed off, and the weather became clear, we discovered breakers just ahead. We had “tacked” ship very quick a number of times during the voyage, but never, we venture to say, did the “Emily” go about quicker than then. The “Lion,” being to windward, had more room; she also went about, and we left those parts just as fast as the breeze would drive us.
While trading at Simpson’s Island, on Monday, December 29th, a chief came alongside in a canoe, and wished to “see the elephant”—in other words, cast his lot with us. He was partly induced to do so by seeing on board an old shipmate, for it seems he had been one cruise in the “Planter.” The necessary bargain was soon made, and the captain bestowed upon him the name of Dick Simpson. Dick turned to his canoe, and ordered the natives to go ashore. They appeared loth to part with him thus, but after some very, to us, unintelligible jargon and extraordinary flourishes on the part of Dick, they left, with sorrowful countenances.
The next day we spoke the “John and Elizabeth,” of New London, Captain Chappel. We were now speaking ships day after day, and nearly all of them later from home than we were. From most of them we obtained papers, and many of the crew obtained letters. It was truly pleasant to us to come so frequently in contact with ships from our own native land, separated from it, as we were, by the diameter of the earth—vessels that bore aloft the same stars and stripes that we had so often beheld waving proudly at home—vessels that contained201 Americans, our countrymen; and, although we might not be participants in the mighty events which were transpiring in our native land, yet we could hear of them even in that distant clime. These incidents truly served as bright spots in the storm-beaten mariner’s existence.
And now we come to another New-year. Thursday, January 1st, 18—, has come. Another page has been written in the history of man. The thought came to us on this morning, How many hearts at home have been made desolate, during the past year, by the loss of near and dear friends? How many have been called from this vale of tears to meet their God? Have we profited by the lessons which our heavenly Father has endeavored to impress upon us? To us will come, before another New-year shall roll around, the words, “This year thou shalt die.”
All hands this day held a sort of jubilee, “going in,” as far as our limited means would allow. All appeared to think of but one thing, “We are one year nearer home.” No work was done except attending to the sailing of the ship; all hands regaled themselves on roast chicken, sea pie, plum duff, etc. (which did not amount to much—etc., we mean), for dinner.
The sailor is proverbial for his love of music. We were gamming with the “Phocion” on Wednesday, January 7th, and in the evening the cook of the “Phocion” came on board, bringing with him his violin. He was the blackest man we ever saw—so black that we actually believe charcoal would make a white mark on him. He was not only cook on board the “P.,” but was also the “band.” He was asked down into the cabin to entertain his listeners with his melodious strains, and there requested to play “Hail Columbia;” and whether it was because we were so long absent from the land of Yankee Doodle, or whether we had no appreciation of music, 202 we know not, yet we could discern no track or trace of “Hail Columbia,” as we were wont to hear it in times past. Not relishing it, we requested him to play “Yankee Doodle,” with the “variations.” He commenced, and before the first strain was ended the dogs left the cabin for the deck on the full run, howling, with their paws to their ears; the crockery in the steward’s room seemed to catch the infection, and danced about merrily; the officers, who had retired for their watch below, growled; the din increasing as the darkey worked into the merits of the tune, all tended to create admirable confusion, until we had faint ideas of being spectators and listeners in Pandemonium. The noise increased; the darkey sawed away more lustily than ever; the captain’s wife cried out that she was half crazy, until some person, who had “no soul for music,” threw a large sea-boot with such unerring aim and force, that, striking the “band” full in the countenance, fairly drove his nose in, as it was already as flat as possible; the claret flew, and the darkey, muttering something about not appreciating music, pocketed the insult and started forward for the forecastle.
Here the concert again commenced, with all the “variations.” The men joined in, some singing, some drumming on tin-pans, some dancing, the Kanakas yelling, and the old darkey “coming down” with a vengeance. As these melodious sounds reached the deck, we really imagined ourselves in Bedlam; at all events, we could not but wish the fiddler there with a hearty good-will.
Tuesday, January 20th, we spoke the bark “Alfred Tyler,” of Edgartown, Captain Luce, who reported that a few days previous he had lost a boat and boat’s crew by desertion. They had supplied themselves with provisions and every thing necessary, and it was supposed had steered for Sydenham’s Island. Captain Luce, immediately disguising his vessel by paint, and transforming 203 her into a ship, was in pursuit of the deserters, and felt confident that he should yet capture them.
On Monday, February 2d, spoke the “Hector” again, who reported the “Ontario,” of New Bedford, ashore on the reef at Pitt’s Island, and rapidly going to pieces at last accounts. She had on board twenty-two hundred barrels whale oil, which was mostly stove or drifted about. The “Phocion,” very fortunately being in the neighborhood at the time of the accident, rendered them all the assistance in her power. All hands were saved. The “P.” also picked up four or five hundred barrels of oil, which, in addition to that already obtained, filled her, and she started for home, the captain of the wrecked Ontario taking passage. It was very fortunate that the ship went ashore at this island, as the natives are kind and generous, and rendered all the assistance in their power to get her off the reef, and in obtaining several valuable articles from the ship, which they delivered to their rightful owners. Had she been wrecked on some of the southward islands, she would have been instantly thronged with natives, who would have plundered her of every thing they could carry off, if they did not massacre the entire crew.
The captain and all hands having a desire for more of the Ocean Island “pumpkins,” and being in the immediate vicinity, we steered for Ocean Island, arriving there on Wednesday, February 11th. Quite a number of canoes came off to trade, but the captain, not obtaining a sufficient quantity, sent a boat on shore to obtain a boat-load, if possible.
On this island there is but one place where the natives can procure fresh water, and that is a large cavern some distance below the surface of the earth. By reason of a superstitious belief, no one but women are allowed to descend this cavern; hence the females bring all the water that is required by the natives in cocoanut-shells, 204 as they have no utensils of a larger description. At some seasons of the year the water is very low, and the king places all on an allowance of so much per day. At such times many suffer from the want of it. We remember that at one time of visiting this island, it being in the dry season, the natives came off in swarms to get water to drink, and so numerous were they that the captain was obliged to compel them to desist, as we had barely sufficient to last until the end of the cruise.
There were several white men living on shore here at this time, of the class known as “beachcombers.” From their appearance we should judge them to be of the worst class of society—strong-built, able-bodied men, living here an indolent, lazy life; nothing to do, their victuals brought to them by the females, and swilling a sort of rum made from the cocoanut. The natives, believing by their protestations that they can accomplish any thing, appear to favor them, and each chief has a “beachcomber” to do his trading on the ship. Yet they resort to all manner of deceit, both with natives and with any ship’s company that will allow them to come on board. Whenever a ship heaves in sight, they represent to the natives that the captain is either a brother or cousin of theirs, and promise great things. When they come on board, they generally go about begging among the men, spinning a most pitiful yarn, and, at the same time, taking good care not to take any thing out of their reach, but still reaching very far if occasion requires. If they can find a disaffected person among the ship’s company, they “button-hole” him at once, and persuade him, if possible, to desert, telling him how easily he can live on shore; that they will take charge of and hide him, so that neither the captain nor natives can find him; and represent that they have unbounded influence with their chief, who is always the highest on the island. If they succeed in persuading the man to desert, they will205 promise to carry many little articles ashore for him, with some clothing, as, they say, “You would be suspected if they should see you with a bundle of clothes, but if they see me with them they will readily suppose I have bought them.” After getting all they can, they persuade the man to hide in the bottom of a canoe alongside, throw a mat over him, and the natives, who understand the game that is being played, paddle off to the shore. Presently the man is missed. The captain goes ashore, and offers a reward of ten or twenty pounds of tobacco and some pipes for the recovery of the deserter. The poor miserable Judas then goes to the captain, and informs him that he has discovered the runaway’s hiding-place, and takes him immediately to the place where he has put the man himself, and reveals him to the captain, who orders him to the boat. The poor fellow, not daring to resist, with a feeling of shame, and his head hung down, proceeds to the boat; the captain pays the reward to the villain, who chuckles to think how nicely he has deceived and betrayed both parties.
We have often wondered why it is that masters of vessels, who well know the foregoing remarks to be true, will allow these miserable pests and outcasts to come on board their ships. They are nearly all escaped convicts from the penal colonies of Sydney and Norfolk Island, and the worst class of those convicts. They contaminate all with whom they come in contact; and no person, having the slightest regard for himself, or possessed of the smallest degree of ambition or honesty, would for a moment consent to reside on one of these islands, living in the manner these beachcombers generally do. They are constantly instilling some mischief into the heads of the natives, and teaching them treachery and deceit. Many times, we are sorry to say, has great injustice been done to the shipwrecked or invalid mariner by classing him with these people, but no one despises a beachcomber more than a true sailor.
206
The taboo is also exercised at this island; per example: when their products are very scarce, the king places the taboo upon all trade, thus forbidding them to take off any thing to ships; but should a ship arrive and wish to trade, the taboo may be broken by the captain coming ashore and paying the king a certain amount of tobacco. As soon as the taboo is off, canoes go in great numbers. The appearance of three ships at any one time also breaks the taboo.
The natives here also live in a state of great subjection. The principal authority is vested in a king; the chiefs rank next, each chief having authority over a particular tribe, who are held more as slaves than as free men. The climate is warm, and of an even temperature, the island being forty-eight miles south of the equator. They enjoy alternately the sea-breeze and land-breeze, the thermometer ranging from seventy-five to eighty degrees.
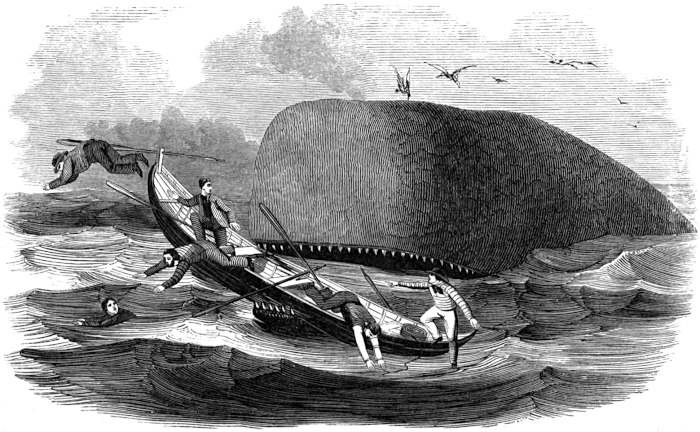

209
The inhabitants are strong, robust-looking, and wear no dress of any description. The houses are similar to those on Strong’s Island, built of bamboo, very large and comfortable, but not kept over and above neat. Their ideas of good and bad are similar to those held by the natives of the Windward Islands of the Group; they have their evil spirits, or “Jentsh,” who, they believe, occupy the deep cavern; but, as females are considered harmless, none but they can descend the cavern and live. They are most expert thieves, and their transactions in this line would shame a London pickpocket. As a specimen: we bought some beautiful shells from one of these gentry at a reasonable price, and very carefully, as we supposed, knowing their weakness for taking things, hid them. Presently the same native we had purchased of came up from his canoe alongside with another assortment, which he offered us. We bought them, at the same time remarking the great resemblance they bore to the ones we had just purchased, and proceeded to stow them away. On arriving at the place, lo and behold! the shells were gone, and, on examining closely, we found that we had purchased the same shells twice. The rascal had watched where we put them, informed another native, who had slyly taken them, lowered them to the former one alongside, who then paddled around the other side of the ship, and came on board with “more shell,” as he said. We were completely sold as well as the shells, and, feeling somewhat indignant, procured a good-sized billet of wood, and proceeded to look for the canoe. But the rascal was too sharp for us again; anticipating punishment, doubtless, he wisely jumped into his canoe and paddled for the shore, leaving us to gaze after him, and laughing probably at the fine trick he had played us. This practice was universal; some of the men bought fowls twice, some mats, and other articles. We came to the conclusion that the example of the rascally beachcombers had not been without its influence upon these natives.
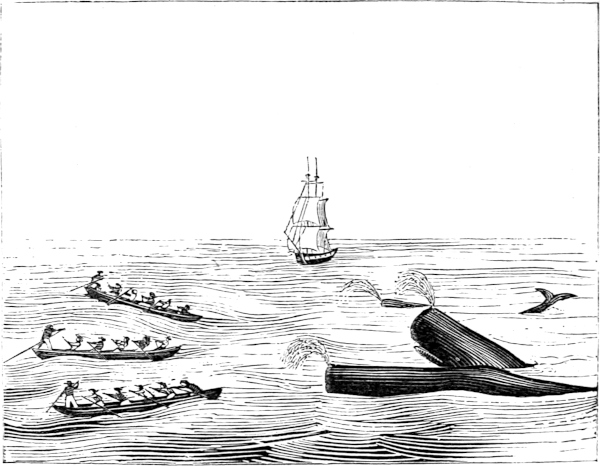

We were now having very good success in whaling, having taken about one hundred and fifty barrels since leaving port. On Friday, February 13th, we saw whales, and lowered all the boats. Each boat soon fastened to a separate whale. The one to which the bow boat fastened appeared inclined to show fight. After running a short distance, he would turn and rush with open jaws for the boat, but the crew were rather too quick for him, and would dodge the enraged monster. Getting tired of this play, he finally sounded. All hands were now watching to see where he would “break water,” and at the same time hauling in slack line. Presently they were all startled by the appearance of a huge jaw, well filled with teeth, coming through the bottom of the boat. One of the crew, who sat immediately over the spot, was thrown into the air in the shape of a spread eagle, and came down into the water not hurt, but badly frightened. The boat instantly filled, as a large portion of her bottom was gone, treating the whole crew to a ducking. The whale, appearing perfectly satisfied with what had been done, left for parts unknown, with the ship’s mark clinging to him. Out of the general conflict we secured two whales, which we took alongside, and soon had their jackets off and into casks.

213
From here we proceeded to Pleasant Island, and sighted it on Thursday, February 19th. The captain struck a bargain with one of the chiefs for five thousand old cocoanuts and twenty-five large hogs, for which he was to pay in muskets, tobacco, etc. On arriving at the ship with the hogs and cocoanuts, they were found to be wanting both in quality and quantity. The captain refused to receive them unless the chief was willing to receive pay in proportion to what he had brought. This the copper-colored rascal refused to do, and demanded payment for the whole amount agreed to be furnished; but the captain was firm, and distinctly told him and his natives that he would pay them for no more than they had brought. At this they became greatly enraged, and the captain ordered them to take their property and leave. This they refused to do, declaring they would not go until they had received pay for every thing they had agreed to bring. We now apprehended some disturbance; the natives were getting excited; we knew them to be the worst and most sanguinary tribe on the island; the captain was becoming angry, and we anticipated quite a little time. As they appeared determined not to go, the captain ordered hogs, natives, and cocoanuts all pitched overboard, and we commenced with the cocoanuts first, throwing them into the water; the hogs soon followed, and the natives, anxious to save their property, went of their own accord, gladly saving us from a personal encounter, in which we felt that we would have fared the worse.
The next day we spoke the “Mohawk,” of Nantucket, Captain Swain. The wife of Captain S. being with him, and being an old friend of Mrs. E., our captain’s lady, they enjoyed a very pleasant visit together.
The “Mohawk” was recently from Pitcairn’s Island, well known as the residence of the descendants of the “Bounty’s” mutineers. We presume that the circumstances of this mutiny may be known to some of our readers, but we shall take the liberty of relating it, as related to us by one who lived upon the island. In 1790, the “Bounty” was sent from England to Otaheite to procure plants of the bread-fruit to introduce into the West Indies. After leaving Otaheite, the crew, or a majority of them, headed by Mr. Christian, the mate, mutinied. They placed the captain, who had the reputation of being a tyrant, with some others, in an open214 boat, gave them provisions and water, and cast them adrift. The mutineers, after cruising about some time, made Pitcairn’s Island. Here they resolved to form a settlement, and, proceeding back to Otaheite, procured females, whom they took with them, and then went on shore, taking all that was valuable from the ship. After doing this they burned her. At first they had much trouble, and murders were committed; but finally, through the influence of one John Adams, the remainder became Christianized. He had taken ashore with him a Bible and Prayer-book. Much attention was paid to educating their children in the tenets of the Christian religion, and before his death Mr. A. had the pleasure of seeing the colony well established, and the people prosperous and happy. At his death he resigned his charge into the hands of one John Moffet, an enlightened Christian man who visited the island, and, being struck with the simplicity and religious character of the inhabitants, became so favorably impressed that he decided to remain there. “At this time,” said our informant, “he lives there, administers the simple code of laws framed for their government by Mr. Adams, and, although a very aged man, is the umpire in all disputes, reads service every Sabbath, and is regarded as a loving father by all.”
We also learned of the death of Mrs. P., wife of Captain P., at this island. The deceased had resided on Nantucket, where she was esteemed by all who knew her as one of those kind ministering spirits who soothe the distressed, comfort the mourner, and alleviate the wants of the poor as far as lies in their power; in short, one of those few persons who are universally beloved by all. Her health being very poor, it was thought a sea-voyage would be beneficial to her; accordingly, she accompanied her husband, who was master of a whaler. After some months, perceiving the health of his wife to 215 be failing, he steered for Pitcairn’s Island. Arriving there, she went on shore in excellent spirits; and, after remaining some days, Captain P., finding that she rapidly regained her health, took an affectionate leave for a short cruise. As soon as the excitement connected with coming on shore had subsided, she commenced failing again, and in a short time her soul took its flight to that better and brighter world, where “all is joy, and peace, and love,” to receive the happy reward which is promised to those who love God; leaving as a legacy the following lines, written while on her death-bed, her form racked with pain, but her soul calm and clear as a summer’s morn:
Her body was attended to its final resting-place with216 great solemnity. The wild winds chant their mournful requiem over her grave, accompanied by the never-ceasing roar of old ocean, as she dashes against the rocky shores of this lovely Pacific isle.
We learned farther from the “Mohawk” that the natives of Covill’s Island (an island just to the northward of Pitt’s Island) had taken a California schooner, and massacred the passengers and crew. It was supposed that there were female passengers on board, as the natives were in possession of sundry articles of ladies’ apparel. In trading with some vessel, they gave California gold pieces for little or no tobacco, showing that they place no intrinsic value upon gold or silver. These natives attempted to take the “Lion” while she was trading there, but did not succeed.
Whenever two whalemen are in company, and whales are raised by either ship, the boats from both vessels lower, and all oil thus taken by either is shared in common. On Monday, March 8th, while in company with the “Mohawk,” whales were raised, and down went eight boats in hot pursuit, each boat seemingly determined on being first boat fast. It was blowing quite fresh at the time, and quite a heavy sea running. The waist-boat from our ship was the first one to fasten, and no sooner had they done so than the gentleman whale knocked the boat into quite a number of pieces, and spilled them out, leaving them “lying around loose.” The larboard boat, happening to be near, took the line and held on to the whale. One of the “Mohawk’s” boats picked up the scattered crew of the stove boat, and brought them on board. The larboard boat was flying through the water at about ten knots, “dead to windward,” against a heavy head sea, which flew over and against her bows with uncommon force. She appeared actually plowing through it, the water forming a high bank of surf each side. The boat soon lost sight of the ship, and they were obliged to cut the line and return, the crew completely saturated with salt water and exhausted by their labors. During this time the bow boat had killed a sixty-barrel whale, which was soon alongside and cut in.
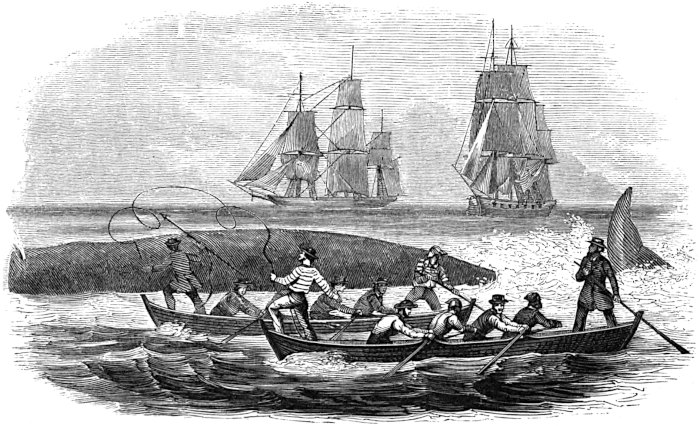
219
Although ancient and modern historians may abound in descriptions of man’s daring by “flood and field,” and the many accidents and hairbreadth escapes which accompany his voluntary exposure to a multitude of dangers, surely the recital of his doings in the chase and capture of that leviathan of the deep, the sperm whale, can be second to none in the interest it must excite in every contemplative mind. It is not in the field, jungle, or thick forest that these hardy adventurers seek their prey, upon man’s natural element, where, should any untoward accident occur, assistance of some kind can be readily obtained; but on the vast ocean, at times thousands of miles distant from any habitable land, where they are not only exposed to the dangers which beset them in their adventures with these monsters of the deep, but to others still more terrible, in which the dreaded typhoon forms no inconsiderable part; or when, near lands distant and barbarous, dangerous reefs, sunken rocks, and relentless savages may surround them on every side, requiring all the moral and physical energy of which our nature is possessed to escape the manifold dangers which beset them, but which the whaleman looks upon without dread, passing among them in his gallant bark, and bearing off in triumph the valuable giant of the ocean.
Even in these latitudes, the equatorial, we often experience heavy, and sometimes terrible gales of wind. On Wednesday, March 10th, having just cleared our decks from the last “fare of oil,” a heavy gale set in from the westward, which continued for four days, with scarcely a moment’s interruption. The “Mohawk” lost 220 some of her sails, and had her bow boat swept off the cranes. We lost our foretopsail and mainsail, which were literally blown into ribbons. The weather was very thick, the rain descending in torrents, accompanied with heavy thunder and lightning. On Sunday, the 14th, the gale broke, and the clouds lifting, disclosed to our view, but a short distance to windward, Hall’s Island, which we had drifted past. The sun, making his appearance once more, gladdened the hearts of all, and for the first time in four days we took an observation, and found that we were in long. 174° 36´ E., having been drifted by the current from long. 171° E., with but ten miles difference in latitude, being about two hundred and sixteen miles to the eastward of the spot where we took the gale. We very narrowly escaped going ashore the previous night, although unconscious of it at the time. The weather was very thick, and it would have been impossible to have seen land any distance; but, by the safe guidance of an ever-merciful Providence, the two ships were swept through a passage between Knox’s and Hall’s Islands not more than ten or twelve miles in width, and dangerous to pass through in broad daylight. The first intimation that we were any where in the neighborhood of land was when Hall’s Island broke upon our astonished vision to windward, and then did we see the narrow escape we had met with.
Leaving Hall’s Island astern, with clear and pleasant weather once more, the two ships proceeded in company to Ocean Island, where we arrived on Monday, March 22d. Each vessel sent a boat on shore, and procured about three hundred pumpkins. While on shore, our attention was called to an odd figure we saw approaching us, which we discovered to be a native fantastically decorated. It proved to be a man who had formerly sailed in our ship when the present captain was on his first voyage as master of her. He had been to “’Merick,” 221 where, as he informed us, he procured the suit of clothes which he then wore. It consisted of pants which would have buttoned twice round him, but about six inches too short; in lieu of suspenders, they were held up by a piece of spun-yarn passing over his shoulder, and again made fast. His shirt was of calico, of the largest figure and most gaudy colors, with a collar that nearly eclipsed his head, and a cravat of calico, with colors “to match.” His shoes were about fourteen inches in length, and both lefts; his vest, which was intended to be white, had probably been made for a boy, as it was about a foot too short; his coat of blue broadcloth, with large brass buttons, a “swallow-tail” cut, with the waist between his shoulders, the sleeves lacking some inches in length, and the collar nearly reaching to the top of his head, upon which was a very tall, bell-crowned hat, with a very narrow rim. This whole walking machine was surmounted by a huge umbrella. It is probable that some Yankee had given the poor fellow this suit while he was in “’Merick,” and he appeared to feel very grand and proud, but complained that it was very hot. He informed the captain that he had returned to the island a rich man, as he had a whole keg of tobacco, besides some pipes, beads, calico, etc.; also, his complete suit, of which no other native on the island could boast. The king kept very close to the great man, wishing to be considered as his nearest friend, and took quite a fancy to his dress; but of no use; the native felt his superiority over the “niggers,” as he termed them, and scorned even the friendship of the king.
After obtaining a sufficient quantity of pumpkins we returned to the ship, and both vessels took their departure for Guam, preparatory to a season on Japan.
With a strong breeze and all sail out, we were not long in reaching the Ladrone Islands. Tuesday, April 6th, at daylight, saw the island of Rota, bearing west half north, distant thirty miles. In the afternoon, in company with a boat from the “Mohawk,” we went on shore and procured a few hogs, yams, and fruit. This island is one of the most magnificent in appearance from the sea that we have yet seen. The land is moderately high, and thickly covered with evergreen foliage, with an occasional opening, showing the marks of cultivation. The town is built on a level spot of ground, with great regularity and neatness; the houses are all whitewashed or painted, and the streets kept clean. The inhabitants are very courteous and friendly, and evince quite a degree of civilization. They have a fine-looking church here, Roman Catholic, of course, which is built of stone, and looks much better on the outside than the inside. The governor received the captain, dressed in full uniform. He is a tall, noble-looking Spaniard, but the223 dress appeared as if it were made for some more bulky personage; perhaps he wore it ex-officio. One of the boys exclaimed, on seeing him, “The old governor’s clothes set like a purser’s shirt on a handspike.” His palace, as they term it, is a very comfortable-looking stone building, the calaboose adjoining it.
The next morning we were close in to the island of Guam. We took a pilot and proceeded to Umata Bay, where we dropped anchor about three P.M. Umata Bay is the watering-place for all whalers who refit at Guam, as it is the only point on the island where fresh water can be readily obtained. It is called a bay, but it is merely a roadstead, as ships anchoring here are exposed to the sea in all directions except the eastward.
Both ships’ companies were at it next morning rafting water, and made the old hills resound to the chorus of the merry song as they bent back to the tugging oar.
We took the opportunity of visiting the town of Marisa, situated three miles below Umata Bay, and found a very pretty village. The houses are all on one street, which is very long. One peculiarity we could not but notice: the street was swept very clean, and we observed many Spaniards of both sexes engaged in sweeping it, probably paying the penalty of breaking some law. The church here is a fine edifice, and contains two large bells, which ring out merrily for vespers. Although the governor has his permanent residence at Guam, yet he occasionally leaves the “heat and turmoil of city life,” and, taking his family for a visit to the “country,” spends a week or so in this village, where he has a large palace. After rambling around to our entire satisfaction, and spending the day very pleasantly, we returned with a fine breeze, the boat fairly flying through the water. We felt quite fatigued in consequence of our jaunt, but, after a refreshing rest, awoke next morning ready for another day’s tramp.
224
We improved the day in visiting the town of Umata Bay, and a short ramble in the mountains back. The village differed but little from that of Marisa: the same long street, swept clean; the same white houses; and, were it not for the absence of the palace and the difference in the country adjoining, one would almost imagine himself in the same village.
At two P.M. on Saturday, April 10th, we took on board the last of five hundred barrels of water, hove up the anchor with a will, and steered for the port of Apia. We arrived here the next morning, where we cast anchor. This is the anchorage, and the only safe one, for ships refitting at Guam, and is situated seven miles from the town or village of Guam, which is the capital of the group. The port of Apia is a fine bay, situated on the west side of the island, protected from the sea by a reef running across, with an entrance of about half a mile in width. This island, like nearly all in the Pacific, is surrounded by a coral reef. In the centre of the bay is a small island, on which is a fine-looking fort, with five or six guns mounted for the protection of the commerce of the island. We found several ships lying at anchor here, from some of which we obtained quite late news from home.
It is customary for ships that refit here to allow their men to go on shore and remain a week or ten days at a time, as the distance is so great—seven miles from town—that one day’s liberty at a time would be worth but little. Accordingly, on Monday, April 12th, the starboard watch were given a week’s liberty, while the other watch remained on board to paint ship. On landing, what was our surprise to see a large number of cows standing near, and, to our astonishment, we were informed that they were there for our accommodation, if we chose. For the sum of fifty cents we could enjoy a fine horseback ride on a cow “up to town.” As there were225 men from four ships going in company (nearly sixty of us), we all entered into the spirit of the affair, and each man selected his “horned beast” and mounted.
And now ensued a scene that beggars description. Leather thongs were made fast to the horns for the rider to hold on by, and the Spaniard, who led off on a noble animal, seeing all was ready, shouted “Arriva!” and away he went on the full run, the others following; the men having no saddles, some were rolling from side to side, some had seated themselves “wrong-end first,” and all, instead of hanging on to the thongs, reach forward, and, grasping the horns, hang on like grim death; the cows, with their heads stretched forward to the utmost, their bells jingling, each one bellowing and snorting, and their riders, instead of sitting upright, stretched in a horizontal position, their legs extended, and yelling like so many wild Indians; the old Spaniard shouting and singing in Spanish, and the whole cavalcade upon the full run—all this produced one of the wildest scenes imaginable. As the procession entered the town, Spaniards of both sexes, men, women, and children, rushed to the street, shouting and laughing at the “Americanos.” The old Spaniard kept on, and, after having made the circuit of the town, brought up at the “Grand Plaza” in front of the governor’s palace, the poor riders being almost insensible from the continual and deafening din that surrounded them.
They halted here, and all hands joyfully dismounted; the Spaniards crowded around to congratulate them on their good riding, but, paying no attention to them, they “vamosed” in search of a boarding-house. By the laws of the island, every white man or foreigner must have a boarding-house, and be within doors at eight P.M. This is necessary, that good order may be preserved in the night-time, and tends to prevent many disgraceful scenes that would otherwise occur.
226
The police here are very vigilant. Every person who keeps a boarding-house is compelled to report the names of his boarders, and about eight P.M. the captain of the police goes around to see if all are in. If any are absent from their respective houses, they are found and marched home; and should they be saucy, or show any belligerent spirit, off they go to the calaboose. This also tends to prevent desertions, as the governor allows no white man to remain on the island unless sick. There are a few old residents here who are exceptions, they being citizens.
Loving an early morning walk, five A.M. the next day after our arrival on shore found us “up and dressed,” and out. It was truly a lovely morning, the sun shining brightly, birds singing sweetly, and the church bells ringing merrily. As we walked along the banks of a quiet stream, how did these sounds bring up in our minds similar scenes at home—our own peaceful stream, the feathery songsters, and the old church bells. But the roar of the surf dashing over the breakers reminded us that many, many miles of “deep blue sea” separated us from our homes, and that many days must pass ere we could again live over those happy days, and our present musings be realized.
The inhabitants of this island are of the Malay race, intermixed with the Spaniards. They are generally very kind and hospitable to the stranger, often inviting him to their houses, and setting before him refreshments, fruits, etc.; but if offended, they are revengeful to a sanguinary degree. Many of them carry short, thick swords, called “choppers,” by their sides, which they use for clearing their small farms and other purposes. With these choppers they frequently commit horrible outrages, inflicting, in the heat of passion, terrible wounds upon each other, or upon any one who may chance to give them cause for affront, fancied or real.
227
It was at this island that Captain Stevens, master of an English whaler, was murdered a few years since, in a cowardly and brutal manner. He was set upon by a gang of desperadoes, under direction of the then governor, with whom Captain S. had had some difficulty. The miscreants stole into his room and took his pistols, which were lying on the table, and, on going out to ascertain who had committed the theft, he was attacked and fairly cut to pieces, the wretches not desisting until they had murdered him. It is reported that the governor was punished by his own government and removed from the island.
An amusing incident occurred a few years ago, illustrating the bravery of the governor and the army. The master of an American whaler, being ready for sea, and some of his men being imprisoned in the calaboose for some trifling breach of the laws, went to the governor and demanded his men, stating that he was ready for sea, and should sail at four P.M. His excellency replied that he could not have them unless he paid the fine imposed, which was a very large amount. The captain, thinking, from the large amount imposed for so slight a breach committed, it a mere plan to extort money from him, replied that he would pay no money to the governor, whereupon the latter replied that “he could not have his men.” The captain took his leave, saying that if the men were not on board at four P.M., he, the governor, must suffer the consequences. He now proceeded to his ship, weighed anchor, left the harbor, and at four P.M. was opposite the town. When within about a quarter of a mile of the shore, and directly opposite the palace, he hauled aback his main-yard, ran up the stars and stripes, and commenced to bombard the palace with one six-pounder, which was all the cannon he had on board. Almost within range of the palace, and situated at the water’s edge, was a stone fort with several228 guns mounted. The brave commander did not see fit to return the fire, when he might have blown the ship to atoms. After half a dozen shots had been fired, a flag of truce was seen on the fort. He ceased firing, and a boat was soon seen approaching the ship containing his men and a file of soldiers, the commandant of whom gave him the compliments of the governor, who, he said, had sent his men, and requested him to cease firing, as one shot had taken effect in the palace, and actually lodged in his private room. The captain took his men and departed. The governor still preserves the ball, and frequently exhibits it to visitors as the one the Yankee skipper fired at him.
We had received an invitation to attend mass with some of our Spanish friends, and, arousing ourselves at four A.M. on Wednesday, April 14th, we proceeded to the church. It is a fine-looking stone building, very large and massive, with a chime of bells in its tower. On entering, we found it well lighted, and filled with Spaniards of both sexes. It is beautifully furnished inside, many of the ornaments and holy vessels being of gold and silver. The services were solemn and impressive, and, although they worshiped in a different manner from us, yet we could not but feel a devotional sentiment within us as we listened to the beautiful chant, and witnessed the devout worshipers at their devotions. It seemed to bring us nearer to the land of Christianity, accustomed as we had been, for months past, to attend no place of public worship.
On arriving at our boarding-house after mass, we found some delicious “toddy” awaiting us. This, when fresh from the tree, is a palatable and pleasant drink, and is highly beneficial to a person coming ashore after a long cruise on salt water, and living mostly on salt provisions. It is procured by a person called a “toddy-cutter,” who ascends to the top of a cocoanut-tree in the 229 shade of the evening, and cuts a number of notches at the root of one of the limbs, hanging a long piece of bamboo underneath, which in the morning is found filled with the delicious beverage. After collecting his several bamboo vessels, he proceeds to distribute them at the different boarding-houses, supplying all who may wish with this excellent beverage. It is needless to say that the “toddy-cutter” was very liberally patronized while so many seamen were on shore. There are no intoxicating qualities in the toddy, no more than in a glass of soda or lemonade.
The streets of Guam are very wide and straight, and are kept clean. The houses are built compactly of wood and stone; those built of wood, which comprise the greater number, are elevated on frame-work and posts four or five feet above the ground. They are mostly of one story, painted white, and are neat and orderly in appearance. The stone houses are built in a substantial manner, and look very solid and comfortable. The governor’s palace is a long stone building of two stories, with nothing remarkable about it to indicate it as the palace of the governor of the great island of Guam. The west end of it joins the calaboose, which is a solid stone building of one story, and they are both guarded by sentries. Immediately in front of both buildings is the “Grand Plaza,” in the centre of which is the cock-pit.
The inhabitants here delight in the cruel exhibition of cock-fighting, and manifest great interest in the combats. Not being satisfied with seeing these noble fowls destroy each other with the weapons which nature has given them, they place on them steel spurs shaped similar to a scythe, which are made very sharp. Armed with these destructive weapons, the contest is soon decided, as the first blow frequently kills the unlucky bird. These exhibitions always take place on the Sabbath, as that is their grand gala day. At the time appointed230 the arena is opened, a ring made, and no person allowed inside the rope but the judges and owners of the cocks. The space around is completely thronged with old, middle-aged and young men, who enter into this cruel sport with the greatest animation. Even the governor is always present, witnessing the combats, and betting as freely as any one. The fowls are large, noble-looking animals, of the Malay breed, and upon two being brought into the ring, the betting commences with great excitement, from a rial to a dollar, and more, according to the wealth of the parties. One Spaniard holds up his finger, and shouts out the name of the fowl he chooses to bet on; another, seeing him, raises his in the same manner, and names his favorite; and so on around the ring. The signal is given, and the cocks, being let loose, fly at each other, and, as we before remarked, the combat is soon terminated. Those who have lost now pay over the stakes, and two more fowls are entered. This continues through the greater portion of the afternoon, and it is surprising to see the large quantity of noble-looking fowls slain.
On the east side of the Plaza is a fine-looking stone building used as a seminary, which is supported by the Church, for the purpose of educating those who can not afford to attend private schools, and of protecting and educating the orphan. This institution is the pride of the island, and may well be considered as such, for it is productive of great and lasting benefit. The scholars manifest much interest in their studies, and their behavior and accomplishments would compare favorably with many similar institutions in our own land, where the opportunities of a good education are so general.
A few months since the prisoners confined in the calaboose, about one hundred in number, attempted to take the palace. Their plans were all laid; a part were to attack in front, the remainder in the rear. The object231 was to obtain possession of the arms and ammunition contained in the palace, and then to make an attempt to capture the island. The plot was discovered, however, just in time to frustrate it; and, after some severe fighting, during which about twenty-five were killed, the remainder were secured, and sent to Manilla for trial, and were there hung.
While walking through the town one evening, we heard the sound of music issuing from a building near by. On presenting ourselves at the door, we were invited in, and found the room filled with females, with but one or two exceptions. It was the hour of vespers. At one end of the room was the image of the Virgin Mary and the Crucifixion. Those chanting were on their knees, with their hands crossed on their breasts, the very picture of humility and meekness. As their sweet voices mingled in the beautiful chant of “Ave, Sanctissima,” we could not but be struck with the solemnity and sublimity of the scene. If woman be all she is represented to be, lively, charming, and angelic, she is certainly more than this when engaged in offering devotion to Almighty God, and imploring the aid of the divine Savior. The females of Guam are remarkably fair-looking: keen black eyes, long, flowing black hair, smooth complexion, and possessed of a robust and well-rounded form; their step light and elastic, and very graceful in their movements. One of these dark-eyed beauties in the attitude of prayer, her hands beseechingly clasped, her loose hair flowing luxuriantly around her well-rounded shoulders, and her countenance expressive of meekness and innocence, would form a model for the chisel of a Powers.
After vespers we passed a very pleasant evening with these lively, chatting beauties, from whom we learned much of interest in regard to the island; and we must confess to a slight feeling of regret when we heard the232 bells peal forth the hour of eight, compelling us to say to them “Adios.”
The next day we had planned for a stroll in the country round, and before 6 A.M. were on our way, with two Spanish lads about eighteen years of age as guides. We passed several farms on our route, and, from appearances, we should judge the occupants to be well skilled in agriculture. About five miles northeast of the town we came to the ruins of a large stone building, which, our guides informed us, were the remains of a monastery, and built, as they said, “very many year ago.” On examining an arch or gateway, we found the keystone marked 1636. The stones appeared regularly hewn and well fitted. It would seem from this that the art of masonry was understood here more than two hundred years ago, as this building must have been erected under the supervision of a master mason, well-skilled in the use of the square, level, plumb, and trowel.
Near this pile of ruins is a large stone reservoir, about thirty feet in length, twenty-five in width, and thirty to forty in depth. At this time it had about three feet depth of water in it. This reservoir was probably built at the same time as the monastery, as our guide said, on asking him when it was built, “Tiempo Casa Dios” (at the time of the building of the house of God).
After walking some distance farther, nothing of interest presenting itself, we set out on our return. When within about one mile of town, we noticed several large sheds filled with tobacco, which is grown here in large quantities. The inhabitants, however, do not understand manufacturing it otherwise than into cigars. All smoke here—men, women, and children; and we must confess that it detracts somewhat from the beauty of a young lady to see her promenading the street with a huge cigar in her mouth, puffing away most lustily; but this spectacle is so common here that one soon becomes accustomed to it.
233
The betel-nut is chewed by “all hands,” giving a reddish cast to the teeth, of which they all seem very proud. The young Ladrone beauty prides herself as much on the bright-red appearance of her teeth as the American ladies do on the pearly whiteness of theirs.
On arriving at our boarding-house we found ourselves covered with mud, and possessed of alarming appetites. It is useless to add that we did ample justice to the fine dish of curried chickens, with all the “fixins to match,” which was set before us.
Not forgetting our old friend, Captain Anderson, we called upon him next day, Friday, April 16th, and learned some very interesting and amusing facts connected with the history of the island, one of which we will relate as he gave it to us: Some years ago Captain A. and a few more English residents contrived a plan to make themselves possessors of the island. They secretly worked, step by step, at the same time insinuating themselves into the good graces of the governor. Their plans worked to a charm, and, when they were fully matured, they quietly took possession of the palace, the governor having been made, as Captain. A. expressed it, “as drunk as a boiled owl.” As they now had possession of all the arms and ammunition, it was an easy matter to subdue the natives, which they did in short order, without loss of life on either side, covering themselves with glory. As a matter of course, the new lords and masters must have a glorious jollification over the affair, and at the same time agree on a governor. This latter, however, proved no easy task, as all were equally anxious to “serve their country” in being chief dignitary of the island. After consulting and debating some hours, and finding they were no nearer a decision than at first, they decided to have a spree, and whoever should remain sober the longest, and see the others all laid out, should be the honorable governor. Accordingly, at it234 they went; bottle after bottle disappeared; one by one they voluntarily relinquished their seats and quietly rolled under the table. After a short time no one remained in his seat but Captain A., and he, feeling elated at his success, drank a few bumpers to “Captain Anderson, the future governor of the distinguished island of Guam.” But, as he said, “he was born under an unlucky star.” So it proved, as the bumpers he drank to his own good health keeled him over, and he took his place among his comrades.
The Spaniards, who had been watching these proceedings with no small degree of interest, seeing how matters stood, and the would-be governors gloriously drunk, very adroitly bound them hand and foot. The dethroned governor was, of course, immediately reinstated, and the next day these noble spirits were arraigned for trial. Being convicted of treason, they were sentenced to be placed on a raft, taken out to sea, and then cast loose, leaving them at the mercy of the winds and waves. This was accordingly done; and, after drifting about several days, they were safely landed on the island of Tinian (one of the group.) Here they resided some time; finally, expressing their sorrow for what they had done, the governor pardoned them, and permitted them to make Guam their future residence, on swearing allegiance to the government and promising to be true and loyal citizens.
The week was now closed which had been given to one watch from each ship for liberty. Accordingly, they returned to their respective ships, and the other watches came on shore—about the same number of men. They arrived in due form and procession; and, as we could now look on and witness the performance, we enjoyed the scene with a hearty good-will. As soon as they dismounted, we were among the first to offer our congratulations on their grand and imposing entrée. 235 How natural for men, on finding themselves taken in and done for, to watch and enjoy seeing others victimized. Thus it was in this case; all would speak highly of their merry ride, particularly when in the presence of the uninitiated.
As we before remarked, Sunday is the grand gala day of the inhabitants here. Among other things, we witnessed a parade and review of the army stationed here by the governor, numbering, officers, high privates and all, twenty-five. They do duty as policemen as well as soldiers. They were not a very formidable-looking body of men; some were dressed in white, and some in blue, with fancifully decorated cloth caps. A portion of them were armed with muskets, the remainder with spears. However, they performed their evolutions very well, although we do not believe their commander ever studied Scott’s Tactics.
At the close of the morning service every one appeared preparing for the afternoon sports. At an early hour the space around the cock-pit was crowded with young and old, anxiously awaiting the sport, as they term it, to commence. At two o’clock the fighting began between two noble-looking fowls. The betting ran high, but the battle was soon decided by one of the cocks receiving a home-thrust that pierced his heart. The fighting now continued in this manner until about thirty were slain. In the evening nearly every house was thrown open to receive calls from “Americanos” and others, who were entertained with music and refreshments.
A kind of liquor called “aguadente” is distilled here, very intoxicating in its qualities, yet the effects are not as bad as are those of the poisonous liquors sold in this country. We expected to see the “Americanos” nearly all drunk on this day, as we knew it would circulate pretty freely; but to their credit be it said, not one of236 them became intoxicated. They all seemed to shun it, whether it was because it was the Sabbath, or for what reason we know not, but “all hands” continued sober through the day.
The following morning, on strolling along the beach, we found several “Caroline Island” canoes had arrived during the night. These canoes are about forty feet in length and six feet beam, quite deep, and will carry from fifteen to twenty tons. They are provided with an extensive outrigger to prevent their capsizing, and carry a large mat sail. When under full sail in a strong breeze, being very sharp in their construction, they skim along over the water with amazing velocity. The natives are large, robust fellows, with no clothing but the tappa, or a fine mat worn across the shoulders in the form of a scarf. Each canoe carries one family, and they appear to live in a very peaceable and happy manner on board their diminutive craft. Their island homes are about four degrees to the southward. On inquiring of them through a Spaniard, as interpreter, how they found the island, they replied, pointing upward, “Stars by night, sun by day.” Their cargo consists of hats, mats, and shells. In return, they take tobacco, pipes, calico, and aguadente. These canoes ply regularly between the Caroline Islands and Guam.
The time had now come for all hands to return on board. Another week had flown, and we must leave the land for the water again. But the boys wished to have a “grand time” before leaving, and the last day each one appeared to be determined to make the most of. Long Manuel, our Portugee, appeared very much troubled by the width of the various streets he was attempting to explore, while our Kanakas were singing their native songs with considerable mirth and high-larity. In the evening they all assembled for a dance at one boarding-house at an early hour. They had secured237 the services of four Spaniards as fiddlers, and on their arrival at it they went. Eight o’clock came, and with it also came the chief of police, ordering them to cease dancing, stop their noise, and disperse. On hearing this, Tom W., the ship’s wag, who had “imbibed” pretty freely, proceeded to “argue the point” with the policeman, who could understand but little English. He continued to lay it down in a very emphatic manner, using language that seemed to completely nonplus the Spaniard, who would occasionally refer to the boarding-house landlord, and inquire what the man was talking so earnestly about. The landlord, who well understood what was up, replied that Tom was praising the island and their rules and regulations. This the Spaniard believed, as Tom would occasionally introduce into his speech the words “Bueno Espaniolo” (excellent Spaniards), and end it by inviting him to drink. This part the policeman could understand without any difficulty, and, after having drunk several times, he became as merry as the rest, and, finding he could do nothing with them, departed.
In a short time a file of soldiers made their appearance. The sergeant, who could neither speak English nor understand it, informed the landlord that he must disperse the sailors and shut up his house. The landlord, however, shut the door in his face, and told Tom what was going on, who, instantly seizing a bottle, ran out and offered it to the officer; but of no avail; he was not to be bribed in so easy a manner. Tom now turned his attention to the soldiers, and passed the bottle so freely among them that the sergeant ordered them to cease drinking. However, another bottle was soon produced, and a more merry lot of soldiers was never seen. In vain the officer endeavored to put a stop to the proceedings; they were now all in the house, and had entered into the spirit of the evening; and while all hands, 238 sailors and soldiers, were dancing, Tom very carefully took all their muskets and hid them in a quiet place.
Thus matters moved along, the noise and fun increasing, until the hour of twelve, at which time the guard were to return to head-quarters, make their report, and be relieved. As the bell tolled forth the hour, they seemed to regain possession of their senses; visions of the guard-house floated across their minds, and they well knew it was their doom unless they immediately departed. But now all was confusion: “Where is my musket?” was the general cry; but no muskets were to be found. They raved and swore, but all to no purpose; no one could tell what had become of them. On hearing the sound of the first relief bell, they rushed for the door pell-mell, and found their officer had already taken his departure. They waited no longer, but ran down the streets at full speed. As soon as they were out of sight, Tom took the muskets, carried them to the river, and, wading to a considerable depth, safely deposited the “government arms,” and then returned to the house, where the dance was kept up without farther interruption.
The next morning all hands took leave of the goodly city of Guam, and returned to their respective ships.
One evening before our departure a delegation from each ship in port visited the fort near the anchorage. We found it a solid piece of masonry, mounting six guns of eighteen pounds calibre. It is entirely surrounded by water, and guarded by a few soldiers. About 2 A.M. the several delegations returned, and at daylight a small army was seen approaching. Wondering what could be the cause of this, we were all on the qui vive for news. We soon learned that they had come to retake the fort! It appears that the whalemen had gone for a lark, and had driven the soldiers ashore from the fort, taken possession of it, unshipped the guns, and turned239 things around to their own liking—spilling things generally. The conquering army approached the premises very cautiously, and, after considerable manœuvring, entered, but found the premises vacant, thus obtaining a great and bloodless victory. No doubt they considered it a great achievement, and had it proclaimed as such among their countrymen.
Every thing being now “shipshape and Bristol fashion,” we took our departure for the Japan ground, determined to give battle to the sperm whale this season as we had never before done, knowing that every whale that we now captured shortened our voyage materially.
Nothing of interest transpired on the passage, unless we may speak of continued boisterous weather, until Wednesday, May 4th, when we sighted Bailey’s Island, one of the Bonin Group. Here we sent a boat on shore, and procured a load of sweet potatoes, watermelons, green corn, etc., and about twenty large turtle, which abound here in great numbers. We need not say that “turtle soup” soon became no luxury with us.
We cruised around these islands about a month, taking two large whales in the mean time, which cheered us considerably, although we were far from doing as well as we had expected. The usual course of Japan whalemen is to cruise in the vicinity of the Bonin Islands during the month of May and the early part of June, and then work gradually to the eastward until the close of the season in September, when they are compelled to leave from the severity of the weather.
On Wednesday, June 2d, we saw another whaleman from “Yankee Land,” the “James Allen,” Captain Newcomb, of New Bedford. He bore down to us with the ever-beautiful “stars and stripes” waving proudly from 241 the mizzen-peak, and passed our stern in gallant style. We had a very interesting gam with them, although hard at work putting the dollars in our ship’s hold in the shape of sperm oil.
The next day we saw several large water-spouts, which are very common in these latitudes. They passed some distance from us, and we were very careful to give them a wide berth, as several ships had lately suffered from them, having their spars and rigging severely injured.
These latitudes are also very often visited by fearful hurricanes, called “typhoons.” On the 18th of June we experienced the “tail-end” of one, as seamen call it. As we had received warning from the barometer, sail was taken in, and every thing secured in a substantial manner. The violence of the wind seemed to sweep every thing before it, forcing the old ship almost on her beam ends. The sea appeared like moving mountains; occasionally it would dash against her sides, giving her a shock that would cause her to tremble in every part. The heavy and labored rolling of the ship—the creaking of the timbers—the wind shrieking through the rigging—clouds of spray flying with almost the rapidity of lightning—clashing of the backstays—dashing of the waves, intermingled with the hoarse shouting of the sailors, made night hideous, and rendered the scene altogether indescribable. All longed for morning, and when daylight appeared a most awful yet grand sight presented itself. The gale was still howling in all its fury; a lull for a few moments would ensue, then heavy and sudden blasts would follow in quick succession, striking the ship with such force as to make every plank in her shake and tremble. She would plunge headlong into an immense abyss, and then rise rapidly to the top of a mountain wave, showing a fearful chasm on either side, which threatened to ingulf her and finish the scene. 242 Every thing conspired to render our situation an awful one; and yet it was a grand, glorious sight. At noon the gale broke, and its fury soon abated, leaving us once more with pleasant weather.
We recollect reading, during our wanderings, in a newspaper which we procured from the States, in some ship, a letter written by some European tourist, in which he complained sadly of the “monotony of a voyage across the Atlantic,” which occupied ten long weary days. We thought, at the time, we would like very much to have the writer take one cruise in a whaler of seven or eight months, where he would see nothing but blue water for six of those months. We hardly think he would complain of the “monotony of a voyage across the Atlantic” again. We were now cruising where, day after day, week after week, nothing but blue water was visible around us; the same dull round of duties; not even a brother whaleman hove in sight with whom we could enjoy a friendly gam. To add to all this, we could see no whales; the captain and all hands were getting discouraged, and feared we should have to leave the ground in September with but little more oil than when we came upon it. At last the captain appeared to wake up, and offered a bounty of twenty dollars to the man who should first raise a whale.
At length a laughable incident occurred, which served to enliven our dull life somewhat, and keep us from sinking entirely into a state of nonentity. Several of the crew, one calm day, were out on the jib-boom, endeavoring to hook some fish which were around the ship in great numbers, that they might indulge in the luxury of a mess of fresh fish for dinner. One of the number, in hauling up a large albicore, lost his hat overboard. Spanish Jack being on deck, sang out,
“What you give me get your hat?”
“Two heads of tobacco,” shouted the man.
243
In a moment Jack was overboard, and in a few seconds had the hat. Placing it on his head, he started for the ship. Although it was nearly calm, yet the ship was going slowly through the water, and the breeze happened to be freshening. At every stroke Jack would make he would lose the hat off, and, stopping to pick it up, he found he was losing ground. He now tried a new experiment—throwing it ahead of him, and then swimming to it; then throwing it again, and so on; but even this would not work, as every time he would throw the hat he would go under himself, and come up snorting and blowing like a porpoise. The darkey now began to be frightened. He was all the time losing ground; the ship was leaving him astern; and the captain finally sang out to him, “Never mind the hat; come aboard!” but to no purpose; Jack stuck to the hat, fearing he should lose the reward if he did not get it. At last, however, after repeated threats from the captain, he was under the necessity of abandoning it, and struck out boldly for the ship, shouting, “Santa Maria! Santa Maria! Madre de Dios!” at every stroke. A rope was thrown him, but he was so exhausted he could not hold fast of it; finally one of the ship’s company went down the side and made it fast round his body. Jack was now hauled in on deck more frightened than hurt, and as pale as possible for a darkey to be. On recovering so as to speak, his first words were for the promised reward of tobacco, which were given him, although he had not recovered the hat. All hands had a hearty laugh over this incident, and it seemed to infuse new spirits into every one.
Thursday, July 8th, we spoke the ship “Atkins Adams,” a vessel that left Guam in company with us. She had taken but forty barrels since coming upon the ground.
At length, on Saturday, July 24th, at daylight, was 244 once more heard the welcome cry, “T-h-e-r-e she b-l-o-w-s!” In the shortest possible space of time four boats were down and gave chase. The boat-steerer of the waist-boat darted and missed his aim. This “gallied” the whale, and off he went at railroad speed, the boats returning to the ship. About nine A.M., however, the chase was renewed, and, by skillful management, the bow-boat fastened both irons solid. As the whale was sounding, Spanish Jack, who was one of the crew, from some unknown cause became badly frightened, and managed to throw his paddle into the line-tub. Of course the line, which was running out with great rapidity, became foul, and carried the paddle to the loggerhead, which frightened Jack still more, and his next move was to jump into the tub himself. The boat-steerer, seeing how matters stood, as quick as thought seized the boat-hatchet and cut the line, which alone saved Jack and all hands from certain death. Away went the whale; and, after reflecting upon their situation a moment, the crew commenced berating poor Jack for his carelessness in thus endangering his and their lives, and losing them the whale. As all hopes of capturing him were now at an end, the boats returned to the ship.
On learning the particulars, the captain administered to Jack a slight dose of tow-line tea to prevent any serious consequences arising from his late carelessness. He did not relish the medicine much, but was obliged to take it, nevertheless. It was really provoking; we had been cruising so long without seeing whales, and when we did see them under such favorable circumstances, to lose them from such carelessness was not only provoking, but discouraging.
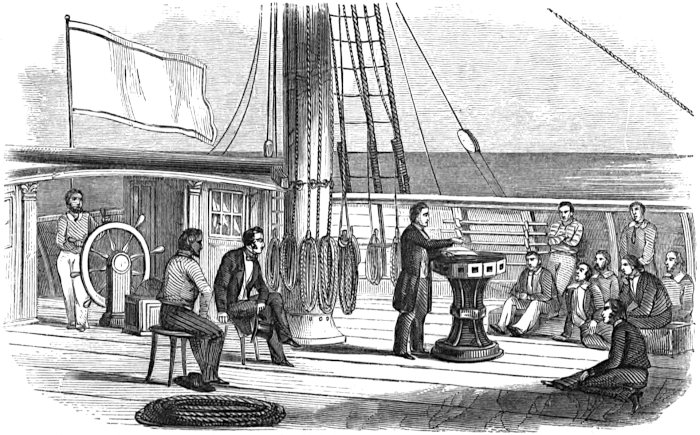

247
The old man, after giving Jack his medicine, proceeded to make a stump speech to all hands, to the effect that “they were now some thirty-three months from home, with only about seven hundred barrels of oil; that the voyage was rapidly drawing to a close; it would soon be time for the ‘Emily Morgan’ to be ‘homeward-bound;’ yet, if they went on at this rate, what would they go home with? A broken voyage; nothing coming to them, and their time worse than thrown away. He hoped the crew would wake up and take some interest in the voyage. If they were only determined to succeed, succeed they would, and they would soon be in ‘Yankee land’ with a good voyage.” At the close of this speech three hearty cheers were given; the men went forward in excellent spirits, threatening the sperm whales on Japan with complete annihilation.
An opportunity soon presented itself; and proved they were in earnest. On Tuesday, July 27th, we raised a “lone” whale, and in less than an hour from the time he was first seen he was lying alongside the ship, dead. On cutting him in, we found him an old veteran covered with scars, and two harpoons in him marked “S. M. N.” By this we knew he had been struck by the “Milton,” who was cruising on the ground. The following day, while cutting in the whale, a sail hove in sight to windward. Some hints were thrown out by the captain that this was the “Milton;” on hearing which, “all hands” struck up a lively tune, and the windlass went round cheerily; blanket-piece after blanket-piece came in on deck, and, just as the last piece swung in clear of the plankshire, the stranger rounded our stern. Instead of the “Milton” she proved to be the “Antelope,” of Newport, Captain Potter. Had it been the former vessel, and any part of the whale remaining in the water, the self-constituted laws of whalemen would have compelled us to have given up the whole of the whale, and this accounted for the hurry we were in to secure the fish ere the stranger came down to us. The result 248 proved our fears to be groundless; nevertheless, the blubber was all on deck, and no one regretted it.
A few days after this we again spoke the “Atkins Adams,” and found that she was about leaving the ground. On inquiring the cause of this resolve, Captain Fish said “that he had seen whales but twice since he had been on the ground, and both times they had steam-engines inside them, and were going like lightning, bound for the ‘Emily Morgan.’” Our skipper encouraged him to remain a while longer, telling him what success we had had, and that the best of the season was yet to come. The following morning, while in company with them, we raised a whale off our lee beam which had the appearance of having been wounded. Seeing us manœuvring, they ran down, but before they reached us we had a dead whale alongside. Without exchanging a word with us, they continued on their course to the southward, no doubt disheartened, and determined to try their luck elsewhere.
We must now mention a very strange incident, and one that but very seldom occurs among whalemen. On cutting in this whale, we found two irons in it marked “S. E. M.” It being our own ship’s mark, and the irons belonging to the bow-boat, and recognized as such by all hands, proved conclusively that it was the same whale which had got our friend Jack into a scrape, and which we had lost nineteen days previous, and about 360 miles to the westward of where we were then cruising.
Such instances are very rare. The only one we ever heard was that of the ship “John and Edward.” While on her outward-bound passage in the Atlantic she struck a large sperm whale, and was compelled to cut from him. She was absent three years, and on her home passage, off the coast of Peru, in the Pacific, captured the same whale. The irons had a peculiar mark, such249 as no other ship carried, and from this they knew the whale. Nothing but the head of the harpoon and about a foot of the shank remained, the other part having rusted off. This proves conclusively that sperm whales do migrate from one ocean to the other via Cape Horn, notwithstanding several learned authors have asserted to the contrary.
On the 15th of September we pointed the ship’s head to the southward with cheerful hearts. This was the best cruise we had yet made, having taken about four hundred barrels of oil. The next season on Japan was to be our last; from thence we were “homeward-bound.” Although it was a long time ahead, yet we felt that every day made it one the less, and every mile of blue water plowed was one the less. Just before reaching the group we lowered and captured a twenty-five barrel whale: this helped to cheer us along our way very much.
Monday, October 11th, we made Pitt’s Island; sent a boat ashore, and found the bark “S.,” of New Bedford, at anchor. The crew of this vessel, including the captain and officers, with ten or twelve beachcombers, were engaged in making cocoanut rum, and all hands, natives included, were as drunk as rum could make them.
The following day we spoke the “Susan,” of Nantucket, Captain Smith. From this vessel we learned that during the past season a fearful tragedy had been enacted at the group. Twenty-five beachcombers residing on Henderville’s and Woodell’s Islands, which are separated by a channel of only a few miles, were murdered by the natives. It appears, from what we could learn, that they had some difficulty with the natives—attempting to do as they pleased—threatening to take the islands, etc. They had also succeeded in effecting a division among the natives, one party espousing their cause, the other opposed to them. Some of the more cunning,250 however, saw through the whole plot, and called a private council of both parties. After much deliberation, it was resolved to put to death all the white men, which was accordingly done. This removed the cause of their quarrels, and they lived at peace again.
We were now steering for Strong’s Island, with fine breezes, beautiful weather, and cheerful hearts. Sunday, October 19th, we spoke the “Atlantic,” of Nantucket, Captain Coleman.
At daylight on Tuesday, the 26th, we were within a few miles of the land. Saw a ship coming out, which proved to be the “Charles W. Morgan,” of New Bedford, Captain Sampson, bound home. Paper, pens, and ink were now in great demand, and, as we wrote a few lines to the dear ones at home, the thought that in one year more we too would be “homeward-bound,” cheered us, and caused us to fancy almost that the time had arrived. But no, not yet could we sing “Huzza, we’re homeward bound!”
At noon we came to anchor in our old resting-place. All hands hastened ashore to see our old friends and exchange greetings. We received a hearty welcome from Zegrah and his wife, who remarked to us that we all belonged to Strong’s Island, we had been there so much. We learned that Rev. Mr. Snow, an American missionary, with his wife, had taken up his residence here; also that Captain Hussey had left the island as master of the whaling brig “Wm. Penn,” of San Francisco.
On visiting among the natives, we discovered a feeling of antipathy to Mr. Snow had arisen among them. We soon ascertained the cause to be what we had at first anticipated. A miserable beachcomber had been telling them that “if the king allowed the missionary to remain, in a short time he would become possessor of the island; that they would have to give every thing251 they obtained to him,” etc. We were surprised that such reports should be so circulated among the natives, as not the least cause had arisen for them, and could only account for it from the fact that it was characteristic of the class. What made the matter still worse was that, when Mr. Snow came to the island, he found this fellow friendless and homeless; his means of subsistence all gone, and begging from house to house. Taking pity upon him, he invited him to take up his abode at his house. Here he found excellent fare, and nothing to do but to eat, drink, and sleep; and, although Mr. S. was very much occupied in making improvements upon his dwelling and land attached, yet he was the last one to offer him any assistance, but, on the contrary, was repaying his kindness by endeavoring to prejudice the natives against him.
Several natives from the Island of Rotumah were residing on Strong’s Island at this time. We attended one of their dances, given by them in honor of our ship’s company. Their singing and dancing excelled any thing of the kind we had yet witnessed. They moved in exact time with the music, and went through the exercises with great precision. During all their dances they use the musket, which they handle with the greatest expertness. The war-dance, in particular, was one of wild and thrilling movements; their hair long, and standing in all directions from their head, even to the perpendicular; their bodies tattooed and besmeared with cocoanut oil, with nothing but a tappa about the loins and a musket by the side, they looked really frightful and war-like. The dance is performed by forming in two lines, and as they sing they perform their evolutions of advancing, discovering and attacking the enemy, wheeling to load their pieces, fronting again, the front rank dropping upon one knee to allow those in the rear to fire over them, while both lines fire in the direction of the252 supposed enemy, and retreat to reload. After performing these evolutions several times, they appear to come off victorious, and start off into a noisy song and dance. We remained until quite a late hour witnessing their performances, and, after all hands had given them three hearty cheers, the assemblage dispersed very peaceably. We returned to our quarters very much pleased with our evening’s entertainment, wishing it were in our power to place the band in Barnum’s hands.
We also attended, a few days after this, a feast and dance given by King George, at which a large wild hog was served up, and every thing “got up” in grand style. To this feast the Rotumah Kanakers were invited, and in the evening they again entertained us with their dances. The king and chiefs appeared highly pleased with their performances, continually exclaiming “very good fashion, that dance.”
Our second officer, Mr. L., had been sick for a number of months, yet he possessed such remarkable energy and perseverance that he would not succumb to it, but did his duty regularly up to the time of our arriving in port; and even then he appeared to feel that when we once more got to sea he should recover; but we all felt and thought differently. We could see that he was wasting away, little by little, and we felt that his days were numbered—that he would never see his home again.
On Sunday, October 31st, divine service was performed on board by Rev. Mr. Snow. For three long years we had not listened to such sounds as came to our ears on that day. It was, to say the least, a pleasing sight to see the weather-beaten tar with a hymn-book in his hand, and to hear all unite in singing the praises of God. The sermon was very plain, yet forcible, reminding us of the short tenure of our lives, and admonishing all to prepare for death. The feeling manner in which Mr.253 S. spoke of death on shipboard brought tears to the eyes of many, as we had not forgotten such a scene among our own small company. King George and the royal family were on board, and appeared to listen to the exercises with a great deal of interest; and when they were concluded, he wished to know of us what the good man had been talking about so long. His majesty appeared to have taken quite an interest in the missionary. He gave him a large piece of good land, built him a nice substantial house, and assisted him all in his power. He was also building a house for himself in the same vicinity.
In conversation with Mr. Snow, he informed us that it was his intention to take the children in charge, teach them the English language, and endeavor to bring them up in the right way. He, of course, anticipated trials and difficulties in his efforts. He did not intend to interfere with any of the old customs of the natives, but show to the rising generation the folly of these customs, that when they came upon the stage of action they would abolish their heathenish rites. We wished him God speed, for we believed him to be a true Christian—one who was actuated by no selfish motive, but by a desire to “do his Master’s will.” We felt, too, that great praise was due to his excellent lady, who had voluntarily surrendered the comforts and luxuries of a home among enlightened people to spend her life on one of the heathen islands of the vast Pacific, to add her mite toward civilizing and Christianizing the poor native. “Verily they will receive their reward.”
We found on shore a native of the New Zealand Islands, who had been left here sick. We visited him several times, once or twice in company with Mr. Snow. He was very sick, and did not expect to recover. The “good missionary,” as he called Mr. S., was doing all in his power to alleviate his sufferings, nursing him with 254 all the love and sympathy of a brother; and Mrs. S. often visited the poor man. He expressed to Mr. Snow his confidence and belief in a dying Savior, trusting in his love and merits; and we doubt not that when his spirit took its flight, it went to those mansions above, where the poor New Zealander is welcomed by Christ and his angels as warmly as the favored Christian of American lands.
The time had now arrived when we were to bid adieu to Strong’s Island and its pleasures, some of us forever. Need we say that we had become somewhat attached to our friends here, who had ever treated us with such kindness? Never shall we forget them; and in future years, when memory shall recall former happy scenes and pleasures enjoyed while roving, Strong’s Island and its simple, kind-hearted natives will stand forth bold and prominent.
On Friday, November 12th, soon after leaving Strong’s Island, we gammed with the “Mohawk,” our old friends, and learned that they had taken eight hundred barrels of oil the previous season on Japan. We could not but envy them, as we were one year from home when they sailed. But we felt that if we could but see the whales, we would soon add to the one thousand barrels we had in our hold.
A few days afterward, at Ocean Island, we spoke the ship “Napoleon,” of New Bedford. The following day we raised whales, and, determined to give them battle, lowered four boats. In less than two hours we had three alongside, and at sundown “started the works” with merry hearts. A few more such lowerings would point the old ship’s head homeward.
But for the present we must steer for a southern port. Our second officer, Mr. Lowe, had been failing in health for many months, and our captain determined to make Sydney, New South Wales, that medical advice and treatment might be procured for him. Accordingly, about the 1st of December, we left the Group, bound for Sydney. But a short time elapsed, however, ere we saw that it was of no use; Mr. L. could not live more than a256 day or two at the farthest. On Saturday, December 4th, he appeared sinking very fast. At his own request we placed him in an arm-chair, that he might, as he said, breathe more freely. With great calmness he described his feelings and symptoms, “gradually growing more chilly, and losing his life by degrees,” as he said. At about 10 P.M. he departed without a struggle. Never did we witness the death-scene where the sufferer was so perfectly composed and resigned. So quietly did his spirit take its flight that it appeared as if he had fallen asleep. Sail was at once reduced, the body laid out, wrapped in a sheet, covered by the American ensign, and placed on the quarter-deck.
The next day, no work, no masthead, no noise; a melancholy stillness pervaded the whole ship. All on board appeared to realize the dispensation that had a second time visited us. We had lost a shipmate that was kind and obliging; an officer that was prompt in the discharge of his duties; a thorough sailor, and a kind, good man—one that was beloved by all his shipmates. At 1 P.M. all hands were called to perform a mournful duty—bury their friend and brother. Our national flag was mournfully waving at half-mast, all sail in, and the ship hove-to. The body was placed upon a plank, with weights attached to its feet. The services were commenced by the captain, who read the one hundred and seventh Psalm, delivered a few excellent remarks, followed by a prayer; and as he repeated the solemn words of the service, “we commit this body to the deep,” the plank was raised, and the body was soon fathoms beneath the “dark blue wave.”
257
As the necessity for our making a southern port no longer existed, we turned our attention to sperm whales, one of which we captured a few days subsequent to the burial of Mr. L. On Monday, December 13th, we spoke the “Roscoe,” of New Bedford, Captain Hayden, who, being an old chum of our captain, sailed in company with us for several days. This event proved very fortunate for us, as the sequel will show; and afterward, in meditating upon our narrow escape, we could but think that a divine Providence was continually watching over and guarding us.
In company with the “Roscoe,” we made Pleasant Island on Wednesday, December 15th. About 11 A.M., when two or three miles from the land, the “Roscoe” about half a mile ahead of us, we perceived her suddenly heave-to and hoist her ensign half-mast, and union down. This we knew to be a signal of distress, and, fearing they were having some difficulty with the natives and needed our immediate assistance, we cracked on all sail and shortly rounded her stern. Captain Hayden informed us that the brig “Inga,” of New Bedford, Captain Barnes, had been taken here a few days previous by the natives, and all of the crew massacred save two; at the same time bidding us beware of the “copper-skinned rascals,” as he termed them. But his warning came too late, for already were our decks crowded with them. We had noticed, as something remarkable, that, after the “Roscoe” had hoisted her signal of distress, all the canoes left her and made for our ship. Not suspecting any danger, we had allowed them to come on board to the number of about four hundred. We were now in a position of extreme danger. As we afterward learned, it was their fixed intention to take our ship the first opportunity, as they owed us an old grudge for throwing their hogs and cocoanuts overboard when on a previous visit to them. That opportunity258 now presented itself. We must confess that things began to wear rather an unpleasant appearance, and we felt satisfied that nothing hardly short of a miracle could save us. Seeing and knowing our situation, Captain Hayden promptly came on board, himself and boat’s crew well armed, bringing with him a white man who had resided on the island many years, and who possessed much influence over the natives. It appears he succeeded in reaching the “Roscoe” prior to any of the natives, and informed Captain H. of the taking of the “Inga;” consequently, no natives were allowed to come on board, and they all pulled for our ship. This white man now informed our captain that he had better get all his weapons of defense in order, lead his muskets, etc., and take them into his cabin, “for,” said he, “these natives are determined to take your ship, if possible; they only await the arrival of one of their chiefs, who fancies you insulted him, and who has sworn to kill you with his own hands, to commence their murderous attack. I have some influence with them, and if I can keep them quiet, and get them away before he comes, I will do so; but if he comes to the ship, nothing can save you.”
The reader may rest assured that this news did not tend to allay our fears in the least, yet each one seemed determined to sell his life as dearly as possible. No undue excitement was exhibited; each one was calm, cool, collected, for we knew the first symptom of fear betrayed would be the signal for the work of destruction to commence. Quietly were all the muskets loaded, and our harpoons, lances, boat-hatchets, and other weapons made ready, so that they could be seized should occasion require. Fifteen or twenty minutes of the most intense anxiety to all hands passed, each one hoping something would transpire to cause the natives to leave. The ships were headed off the land, and sail made; still259 they did not appear inclined to leave, but sat in groups around the deck, intently watching every movement that was made, and earnestly conversing with each other, eying the cutting-spades which hung over the quarter-deck, and evidently longing for some one to commence the fracas. At length a happy thought suggested itself to one of our men. Mounting aloft, he remained a few moments at masthead. Gazing, with great interest apparently, at some object in the far distance, he sang out, with a loud, ringing, joyous voice, “Sail ho! A large man-of-war coming down from the windward under full sail!”
This was sufficient. The natives waited not to hear this repeated, but clambered over the side in the greatest hurry and confusion. Each one seemingly endeavored to be first, and in a few moments our decks were perfectly free from them. As the last native left the ship, one thrilling, deafening hurrah went up from all on board. This was caught up on board the “Roscoe,” and returned with a hearty “three times three.”
We congratulated ourselves on our narrow escape from these merciless savages, and could not but feel thankful to Almighty God for his providence in thus rescuing us. It would have been but a short battle had it commenced. As we have before remarked, the natives of this island are very powerful and robust; and their mode of warfare would have been to have seized the crew and thrown them overboard, while those in the canoes would have held the victims under the surface till they were drowned. Although the man who sang out “Sail ho!” from the masthead did not expect to see one when he started to go aloft, yet he did see a sail, which soon came down to us; and, although not a man-of-war, yet we were none the less pleased to see her. It proved to be the whale-ship “Hannibal,” of New London, Captain Lester.
260
We related to him all the circumstances connected with our late adventures, and he congratulated us heartily upon our narrow escape. The circumstances connected with the taking of the “Inga” were, as nearly as we could learn, as follows: The vessel was near the island, and crowded with natives. While trading with them, Captain Barnes, whether wisely or not we can not say, kept a cutlass in his hand; and, during the transaction of some petty trade, had some high words with a notorious chief; who, fancying himself insulted, seized the cutlass, cut Captain B. through the body, and then tossed him overboard. This was the signal for a general massacre. After killing all but one white man and a native of the Sandwich Islands, whom they took prisoners, they rifled the ship of all they considered valuable, and then attempted to run her ashore. Not succeeding very well themselves, they ordered their prisoners to work the brig to the land, or they would kill them. This they secretly determined not to do; and, bracing the head-yards one way and the after-yards in a contrary direction, caused the brig to remain in nearly a stationary condition. This puzzled them exceedingly; and, fearing a ship might heave in sight, they determined to scuttle her. Accordingly, a chief commenced cutting a hole in her side with an axe, which he let fall overboard after a few strokes. They then determined to set her on fire, which they did, and left for the shore. She probably burned to the water’s edge, as she was never heard from afterward.
We learned that the two prisoners were kept in close confinement on shore, yet kindly treated. We never learned what became of them, yet we trust they were released from the grasp of these murderous villains, as several ships visited the island after having heard of the destruction of the brig, and we know that no whaling captain would leave a thing undone to rescue them.
261
We took from Pleasant Island two men, one a native of the Azores, or Western Islands, and the other a New Yorker. These men begged the captain to take them with him, as they were afraid to remain on the island since the late massacre.
Christmas-day came round in due season, and, although it did not bring us roast turkey, yet it did sperm whales. We captured two fine ones on that day; and, as we finished stowing them down in the hold, New-Year’s-day came upon us, bringing “more of the same sort,” which proved very acceptable.
On Tuesday, January 4th, we spoke the “William Tell,” of Sag Harbor, Captain Taber, who reported that the “Mohawk” had visited Pleasant Island, and purchased several articles belonging to the ill-fated “Inga.” The natives had taken the chronometer apart, and were wearing the wheels and other parts of it around their necks as ornaments. They also reported that, had we been alone at the time of our late visit to Pleasant Island, we would certainly have lost our ship and our lives; nothing prevented it but our being in company with the “Roscoe.” When we heard this, we could but feel that
The following day we spoke the “John Wells,” of New Bedford, Captain Cross. He reported that a mutiny had occurred on board the “William Penn,” by which Captain Hussey had been murdered by a Kanaka. The murder was committed about 4 A.M. Captain H. was in the vicinity of some of the islands of the Group, and, while engaged in looking over the “weather rail” for land, a Kanaka boat-steerer seized a spade and darted it through him, killing him almost instantly. The body was immediately thrown overboard, and the gang (seven or eight of the crew), led by the Kanaka, commenced 262 their murderous work. They killed the steward and cook, severely wounded the mate and second mate, and then, seemingly actuated by some merciful freak, stopped their bloody performances, and promised to leave the vessel quietly if the officers would allow them to take what they wanted. This request was readily granted, as the peaceable portion of the crew and officers were but too willing to have them leave. They accordingly took a boat, and steered for Sydenham’s Island, where the ringleader belonged. The Kanaka took with him a large sum of money belonging to Captain Hussey, and he had not been on shore twenty-four hours ere he was shot by a beachcomber to obtain possession of it. Thus we see the scoundrel met with his deserts.
Captain Hussey also met with the same fate that he consigned one of his own crew to. He murdered his fellow-man in cold blood, and he, in his turn, died a violent death.
The reader must not think, from reading these scenes of violence and murder, that they were continually occurring in this part of our globe. On the contrary, the natives there are generally well-disposed and peaceable; but at this time the islands were thronged with miserable beachcombers—men whose only object and desire appeared to be blood and plunder. The majority of them were escaped convicts from New South Wales, and a more bloodthirsty set of villains never went unhung.
We were now nearly forty months from home, and we found it necessary to prolong the voyage another season. To do this, however, we must have more provisions (bread, meat, and flour) than we now had on board. These could be obtained more advantageously at Hong Kong than at any other port, and our captain accordingly determined to steer for that port. On Sunday, January 16th, spoke her majesty’s brig of war “Serpent,” S. W. Hammett, acting commander. Captain H.263 inquired very particularly concerning the late transactions at Pleasant Island. On taking his leave, he expressed his determination to proceed to the Group, visit all the islands, and rid them of the rascally beachcombers that infested them.
We touched at the island of Rota, one of the Ladrones, on Tuesday, January 25th, and procured a quantity of fruit, hogs, etc. Among the animals was a ferocious wild boar, which the natives had captured on the mountains. He was securely fastened when brought on board, but, as no one knew he was wild, the thongs were cut, and he was set at liberty. This was no sooner done than he made a rush at some of the men, who fled in double-quick time. Turning, he played the same game on another group, until he had complete possession of the deck, all hands taking to their heels, clambering into the rigging, on to the rail, water-butt, and any place that was the most convenient, without stopping to ask questions. Here was a fix—a wild boar had succeeded in taking the ship! His swinish majesty appeared to enjoy the fun hugely, going about the decks making such observations as suited him best, and driving the other porkers around at his pleasure. Once, however, he over-shot his mark. The cook, ensconced in his galley, with both doors closed, felt secure, and would occasionally push one of them ajar and take a look. Porkey finally discovered this move, and, thinking it an unwarrantable intrusion upon his rights, raised his bristles, showed his teeth, and made for the old doctor. Seeing him coming, the old darkey seized a dipper of scalding-water from his copper, and, as Mr. Hog approached within proper distance, bristling for the fight, gave it to him between the eyes. This was too much for his lordship, and a mode of warfare which he least expected. He did not pay the doctor a second visit alive. A number of plans were now devised for his capture—among the rest, that of lassoing him. Portuguese Manuel, who knew 264 all about managing wild hogs, as he said, volunteered to go down upon deck and slip a running bowline over his head. No sooner, however, did his feet touch the deck, than the boar, seemingly mistrusting his evil designs, rushed after him. Away went Manuel, yelling for dear life, with the boar close at his heels. He finally succeeded in mounting the rail, and, thinking the boar still in close pursuit, kept on ascending the rigging with all possible speed, until the mate cried out, and asked him “where he was going?” On hearing this, Manuel looked about him, and, seeing the boar still on deck, descended to the rail, his hair erect, countenance pale (for a Portuguese)—in fact, frightened out of his wits. The crew, scattered about on the rail and in the rigging, presented a truly laughable sight: one or two with their countenances exhibiting the strongest emotions of fear; others with their faces expanded by a broad grin; some cursing the Spaniards for bringing off a “wild boar;” others looking at it as an excellent joke, and laughing heartily at the whole affair. After some time spent in manœuvring, a bowline was slipped over his head, when he was soon choked down, dispatched, and placed in the hands of the cook.
About the 1st of February we experienced a very heavy gale. We were obliged to take our boats in on deck, heave-to, and secure things generally. The steward, not having taken this precaution in regard to his crockery, etc., found it suddenly coming through the pantry door as the ship gave a sudden lurch. The floor was finely strewed with broken dishes, tea, coffee, molasses, and sundry other articles, gloriously mixed in one heterogeneous mass.
On Sunday, February 6th, we sighted Gad’s Rock; also the southern point of the island of Formosa. The next morning the northern Bashee Islands were in sight, bearing W.N.W. Found our reckoning to be latitude 21° 27´ N., longitude 121° 31´ E.
Wednesday, February 9th, brought us in close proximity to the land of the Celestials, as the numerous fishing-junks bore testimony. The same day we sighted Pedro Blanca, which is an island lying near Hong Kong. At 10 A.M. commenced bending the cables, and making other preparations for coming to an anchor. As we neared the land we saw great numbers of pilot-boats steering for us, one of which soon reached us; the pilot came on board, with his long tail, or queu, hanging behind him, and presenting a comical contrast to an old Yankee “Hard-a-lee.” He wanted the moderate sum of forty dollars for taking us into port. Captain Ewer was not so easily gulled as that, and soon gave the old266 fellow to understand that if he wished to pilot us in for twenty dollars he could do so, and if not he could leave immediately. This brought him to his senses, and he very quickly accepted the offer, as numerous other pilot-boats were in sight, and he knew that he would be underbid if they had an opportunity to do so.
The next day found us beating up through the lee passage. At 1 P.M. the wind died away, and the tide commencing to set out, we dropped anchor. At 7 P.M. we weighed anchor, and with a fine breeze beat up to the anchorage. At 8 P.M. we “brought up” in the harbor of Victoria, Hong Kong.
We were aroused from our slumbers the following morning by the familiar strains of “Hail Columbia,” and our first thought was that we were again at home. But this pleasant illusion was soon dispelled; for, going on deck, we found that the music proceeded from the steam frigate Susquehanna, which was lying close to. What joyous feelings did we experience while listening to that soul-stirring air, and beholding our national flag, the glorious “stars and stripes,” floating proudly from the mizzen-peak of such a grand and stately vessel! We could but feel a great national pride to see our beloved country so nobly represented in a foreign clime. On looking about us, we saw the United States sloops of war Plymouth, Portsmouth, and Saratoga; also the Supply store-ship, together forming quite a fleet. Nothing is so cheering to the rover, while in foreign lands, as to see familiar faces, persons speaking the same tongue and claiming the same land of birth, “the land of the free and the home of the brave.” A feeling of patriotism naturally animated us as we beheld our country’s floating batteries, “the right arm of our defense,” and for a moment we forgot that there was any country but “happy, free America!” The harbor was well filled by merchantmen from nearly all nations; also we observed several267 English naval vessels in port, as this is one of their rendezvous. Among the shipping the “stars and stripes” were conspicuous, and we could but notice that they floated from more than half the vessels in port.
Before 9 A.M. the deck of our vessel was crowded with Chinamen of all descriptions. In one corner might be seen the tailor spreading out his fancy clothing; then the shoemaker with his shoes, taking the measures of such of the crew as might want. In another part of the ship might be seen a complete variety store, with all descriptions of lacquered ware, artificial flowers, silk handkerchiefs, etc., all selling for a mere song. Washerwomen running about, engaging the washing while the ship remains in port; bumboats alongside with fruit and confectionery; carpenters, riggers, sail-makers, blacksmiths, etc., each with recommends, looking after and soliciting employment.
The decks now presented a comical spectacle. The bald head of the Chinaman stood out prominent; the honorable tail, neatly dressed, the end tipped with ribbon, was conspicuous in all. Each was dressed according to his calling; the merchant in the finest silks, and the common laborer in the coarsest garments. Our Kanakas had their own sport with them, never having seen a Chinaman before, and regarded them as objects of the greatest curiosity. This was especially the case with Dick Simpson, our King Mills’ native. Not being satisfied with viewing them at a distance, he walked up to one, took hold of the long, braided tail of hair, and cried out, laughing heartily, “Look here! what for all the same? hey? All same big fool. By golly! I no been see all same that, my land!” He then laughed till he could laugh no more, seemingly splitting his sides. The poor Chinaman looked at him in perfect amazement, and, not appearing to relish the joke, jabbered away in his own language. This appeared to astonish 268 Dick still more, and he again broke forth: “What this fellow talking about? see that! By golly! say, long-tail, what you talk about? You no saba noting; more better you go ashore; bimeby me eat you—look out!” Dick had to stop again to laugh heartily, the Chinaman stared so earnestly at him.
By this time the trading had commenced quite briskly, and we overheard the following bargain between one of our boys and a Chinaman. The article was a pair of silk pants, for which the merchant wanted the sum of one dollar and fifty cents:
“No you don’t,” says Jack; “I’ll give you three quarters of a dollar.”
“No can do; no proper,” said the Celestial.
“Well, that’s all I’ll give you; you mustn’t come aboard here to come any of your gouge games; if you do, overboard you go.”
“Three quarters no can catch. S’pose one dollar one quarter, very good, proper.”
“Not a bit of it; three quarters, no more.”
“You no see; pant very good; No. 1; three quarters no can catch plofit; s’pose you like one dollar, very good.”
“Three quarters is all I’ll give you; what do you say, old Chinaman? bear a hand.”
“No; no can do; must catch one dollar.”
“Shiver my timbers! old buggerlugs, if you don’t come to terms pretty soon, I’ll treat you to a salt-water bath; three quarters, or away you go.”
“Well, s’pose must catch three quarters; no good, no proper;” and then, turning to another of the men, said, “S’pose you like catch one three quarters, very good, proper.”
This is a peculiar characteristic of the Chinese merchants. They charge about twice as much as they expect to get for an article; and the only way to trade269 with them is to make them an offer, and not vary one cent from it; they will not let a person go without purchasing.
The mate now came along, and started them all for the shore. They were very loth to go, but after a while we rid the ship of them. As a general thing, they are expert thieves, and will carry off any thing they can lay hold of if not very closely watched.
The captain hired a boat (which is the usual custom), called a “sanpan,” to attend on the ship. These boats are manned by a whole family, as a general thing, it constituting house and home with them. They are generally about thirty feet in length and six in width, with two mat sails. They have a sort of cabin for the accommodation of passengers, which is amidships, or in the centre of the boat. This cabin also serves as parlor, kitchen, sleeping-room, and dressing-room for its occupants. The Chinaman who owned the “sanpan” hired by our captain had a family consisting of himself, wife, wife’s sister, and brother. He had also three fine-looking, bright children, who appeared perfectly contented on board their floating-home.
It is a singular fact that the lowest class of Chinese are not allowed to live on land, but spend most of their lives upon the water. When they possess a certain sum of money they are allowed a residence upon the land, and not until then; but this sum is so large that very few of them ever accumulate it. They are born, live, and die upon the water, never going on shore except to purchase the necessaries of life. One may see floating markets, shoe-shops, tailor-shops, and, in fact, all kinds of mechanical business. We noticed some boats, not exceeding ten feet in length, containing a family of five or six, with all their “household gods,” etc., on board.
But to return to our own “sanpan.” The captain appeared active and intelligent, the females rather good-looking 270 and sociable, the crew (consisting of one man) lazy and indolent. These first class sanpans are hired by ships while lying at anchor for the purpose of conveying the ship’s company to and from the shore, doing the ship’s errands, bringing off provisions, etc., a kind of “man-of-all-work,” for which services they receive from ten to fifteen dollars per month. From this amount, say fifteen dollars, a Chinaman will save ten, which makes it quite a profitable job. It is an excellent plan also for the ship concerned, as it obviates the necessity of lowering her own boats while in port. They sail like the wind, and are quicker in motion than any other boat we ever saw upon the water. One can not look about the harbor but he will see them on every hand, gliding about with the swiftness of an arrow, yet collisions seldom if ever occur. It is surprising to see the ease with which they manage them—two coming from opposite directions with great swiftness, apparently steering for each other’s bows, yet, at the moment when a collision appears inevitable, down goes the helm of one, and they shoot past each other free from harm.
The morning following our arrival a boat came alongside loaded with fresh meat, vegetables, etc. The proprietor of the “market” soon made his appearance, and introduced himself to the captain as “Boston Jack,” a comprador (one who furnishes ships with fresh provisions). He informed Captain E. that he was comprador to the American ships in port, and wished to engage himself as “comprador to the Emily Morgan.” A bargain was soon struck, and he was duly installed in the office. In appearance Boston Jack is about forty years of age, medium height, very quick and active, with a sharp, keen eye, and very polite. The bows he bestowed upon all who honored themselves by speaking to him would have become the most complete and polished French gentleman.
271
Dr. Ball, in his “Rambles in Eastern Asia,” thus speaks of him: “About a mile above Whampoa we called at ‘Boston Jack’s’. This is a Chinaman, an acquaintance that my companions had made in passing before. ‘Boston Jack’ is familiarly known to the European population of Hong Kong as a kind of interpreter and furnisher of provisions for vessels, and a commissioner to provide servants, coolies, and to make purchases of various Chinese articles. He was formerly a pilot, and is still connected with that business, furnishing pilots, etc., and is ready to do any kind of business between the foreigners and Chinese. He is said to be worth a hundred thousand dollars; treated us to beer, and gave us some to take on our way. He had much to say of his son, who lives in New York, and was very polite, inviting us to call again,” etc.
Hong Kong is an island, and not, as is the general impression, a Chinese city. It is a British colony, within a few miles of the Chinese coast. It was Chinese until the treaty after the celebrated opium war ceded it to the English. At that time it was inhabited only by a few fishermen and pirates. It is an elevation of barren mountains, with scarcely any vegetation, and is about twenty-five miles in circumference, and eight in diameter. Its shores are generally bold, and the water deep near the coast. There are, however, several spots with declivities sufficiently gradual for the location of cities. The English government has taken possession of these, and erected fortifications and barracks, where they keep small garrisons of troops. Victoria is the name of the city, yet it is hardly known by any name but Hong Kong.
Victoria is on the north side of the island, built on the base and on the inclination of a conspicuous mountain which overlooks the harbor. It extends about two and a half miles along the edge of the water, and back on272 the side of the mountain half a mile. It has only one principal street, called Queen’s Road, which is near the water, and encircles the island. There are several others parallel with it, and from twenty to forty feet one above the other. The small cross streets uniting them are steep, and at some places have flights of steps by which to ascend and descend. Taking the zigzag streets in their proper order, the highest houses may be reached with a carriage. The houses are generally of two or three stories, though many at the outer part of the city, called bungaloes, are of one story, and look like cottages. Open to the country on the west of the city you will see the steep side of the mountains, with only here and there a poverty-stricken Chinaman’s cabin. The ground is covered with rocks, a little grass, and, higher up, with brush. The white buildings conspicuous here and there are the police stations. Following the road to the east, you enter the part of the city known as Typen-shang, where the lower order of the Chinese reside.
Following the road as it winds round and ascends upon higher ground, we come to the European part—the central portion of Victoria. On the left is a row of Chinamen’s shops, beyond which, along the edge of the harbor, are occasionally the large houses of Europeans. On the right are blocks of European buildings, rising one above another, and as we passed them we could but imagine ourselves once more in a civilized land. Behind these, a little distance up the inclined plane, the mountain rises abruptly, and to the eye nearly perpendicular, and terminating in a peak near three thousand feet high. A scanty vegetation of grass and brambles there appears, but there is little else than rocks, some of which seem to hang by nothing, and may eventually, becoming loosened, roll down and cut their way through the settlements to the water.
Passing along, we come to the principal business part 273 of the city. On the right is a hotel, with blocks of houses occupied mostly by English and Americans, auctioneers, apothecaries, the club-house of the merchants, etc., and back, short streets of Chinese mechanics. Continuing along the water toward the east, after a short interval we see the military quarters, which inclose within a quarter of a mile the showy stone barracks, parade-ground, officers’ residences, in elevated positions, the church, and other buildings. Half a mile farther is another fine block of buildings; then comes the hospital, ship-yard, and a large ship-chandlery establishment. Thus the town or city of Victoria is strung out for two or three miles along the shore.
The population, including Chinese, is about twenty-five thousand. But a small portion are European. Almost every nation is represented here, though there are only a few of each. Besides the English, American, and Chinese, we find the French, Spanish, Portuguese, Persians, Bengalese, Javanese, Manillamen, German, Italian, Russian, Danish, Swiss, Dutch, Belgian, Pole, Arab, Turk, Armenian, Tartar, Siamese, African, and South American.
The streets are filled with Chinese, and you continually see the traveling barber, carrying his barber-shop with him—cobblers, tinkers, pastrymen, men carrying hogs, rabbits, ducks, rats, puppies, etc, already cooked; and along the principal streets you find the brokers, or money-changers, with piles of cash. These cash are a small coin, about one half the size of a cent, of a base metal, and a square hole in the centre, twenty-four of which are equal in value to one of the cents of United States coin. The fortune-teller or conjurer may also be seen, with his charts, covered with hieroglyphics, spread before him, and busily engaged in penetrating the future for some inquisitive Chinaman.
The police force here is composed mostly of English, 274 Americans, and Lascars. They are very effective in preserving order among the Chinese, and a Chinaman stands more in awe of a policeman than any thing else in Hong Kong.
From the ship the town looks beautiful at night. It was New-year’s week with the Chinese at this time, and their part of the town was brilliantly illuminated every evening. The thousand brilliant lamps, with an occasional rocket piercing its way into the clouds above, presented to the beholder a scene of beauty scarcely equaled, reminding him of old legends of enchanted cities. The evening gun of the frigate booms forth, answered from the fort; the bugle call from the barracks sounds sweetly on the calm evening air, and as its soft, gentle tones strike our ear, we almost forget that we are in the land of strangers, and remain musing until we are aroused by the striking of the frigate’s bell, and the hoarse cry echoed over the waters of “All’s well!”
The day after our arrival our ship presented rather a busy appearance. The cooper, with his gang, was preparing casks for water and provisions; others were engaged breaking out the hold and restowing oil, and all hands busy about something; outside a gang of Chinese calkers were busily engaged, and following them were another gang with scrapers and brooms, preparing the ship for an extra coat of paint.
The United States sloop of war “Plymouth” fired a salute on this day, in honor of a visit from the American consul. The report of her heavy guns almost deafened us, and caused our Kanakas to open wide their eyes with astonishment, and exclaim, “I g-o-lly; I never been hear all the same that fore!”
On Sunday, February 13th, the British mail steamer “Wildfire” arrived, having on board Governor Bonham, who had been home to England on a visit. He275 was received by a salute from the men-of-war and the fort, and escorted to his residence by the military stationed here. In the eastern part of the town are situated the barracks; the buildings, which are of stone, are fine, large, and comfortable, and the grounds ample for military evolutions. The 59th regiment of infantry, a company of sappers and miners, and one artillery company, were stationed here at this time. They were composed of fine, healthy-appearing men, and when on parade presented a brilliant appearance.
We found three churches here—one a fine, large Episcopal church, built of stone; a Roman Catholic, and a third a “Union” church, as it was called, attended by persons of all creeds and denominations.
There are also several very fine hotels here, the principal of which is “Brooks’ Hotel.” This is generally the head-quarters of the naval officers. The house is kept on the European plan, is very commodious, and, above all, very neat and clean. Their charges are in proportion, as they intend their guests shall pay for what they have in good round sums.
While on shore shortly after our arrival, Dick Simpson, our “Group” native, saw a man pass on horseback. The poor fellow appeared dumb with astonishment; at length he exclaimed, “What for man, he on big dog! I g-o-lly; I no been see all same that my place; all the same that ’Merica?” On being answered in the affirmative his wonder still increased, if possible, and it proved a hard task to convince him that it was not a dog, but a horse. “Yes, he big dog; ’spose me no saby; he all the same dog,” he would say. In order to satisfy his curiosity, we took him to a horse, and told him to examine for himself. After having expressed himself as satisfied, he wished to know “where he came from.” We explained this as far as lay in our power to do, and after we ceased he chuckled, and told what yarns he would276 spin when he arrived at his “land.” “Kanaka my place all same fool; he no been see nothing!”
As we were the only sperm whaler in port, we attracted considerable attention, especially from the Yankee men-of-war’s-men, as they all lay in close proximity to us, many of whom paid us visits, some to purchase shells, whale’s teeth, and other curiosities, others to learn the modus operandi of the capture of the sperm whale. The particulars of the chase appeared greatly to interest them, as they never before had the opportunity of listening to such narrations, or of inspecting the different apparatus for fastening and killing the whale, hoisting in the blubber, trying out, etc.
During one of these visits from the captain and one of the lieutenants of the store-ship “Supply,” Tom W——, of whom we have before spoken, being full of the old Nick, as usual, “button-holed” the lieutenant at once, and proceeded to show him the ship and whaling craft. He soon had the officer down in the hold, among the greasy oil casks, to show him the manner of stowing down the oil. He kept on a straight countenance, and told his guest he supposed he wished to see the whole show! The lieutenant did not appear to relish the sport, as he had already finely besmeared his coat and pants with dirty grease; and on remarking it, Tom coolly replied, “Oh! that is nothing; you should try a voyage whaling; you would not mind the grease much!” After piloting him through all the dirtiest parts of the ship, he at last brought up in the cook’s galley. The mate, who had been entertaining the captain of the “Supply,” now came in search of the lieutenant, and what was his surprise to see him cozily seated in the “galley” with Tom, who had him by the button-hole, very earnestly explaining how nicely our cooking was done, and the excellent virtues of the stove. The mate now came to the relief of the pestered officer, and was walking off with him, 277 when Tom marched after, called him, extended his hand, and bade him good-by with much warmth, inviting him very cordially to call again. The lieutenant could not refuse his hand, and, returning a slight shake, turned away, looking daggers. However, we believe, on learning the particulars, being too much a gentleman to show anger, he laughed heartily at the joke, and before leaving the ship invited Tom to pay him a visit. Tom thanked him, and promised to avail himself of the honor and pleasure.
On Wednesday, February 16th, Sir William Bonham, the English governor, visited the steam frigate “Susquehanna,” and on leaving was honored by a salute, the cross of St. George at the fore royal-mast head. This vessel is the flag-ship of Commodore Aulick, who was daily expecting the arrival of Commodore Perry to relieve him and take command of the squadron.
The officers on board the several naval vessels in port appeared very courteous and gentlemanly, and possessing a dignity that fully became their position. We felt proud of them as American naval officers, and willing that our navy and our country should be judged by them. There were, however, with them, as with every thing, a few exceptions. The lowest class of naval commissioned officers, familiarly known as “middies,” appeared altogether too large and nice for even the company of the commodore, and would strut about the decks of their ship, or the streets of the city, deeming any one who could not sport an officer’s uniform entirely beneath their notice. We are glad, for the honor of our navy and country, that this class is small, and we would that it were less.
Wishing to visit the barracks of the soldiers and see them in their every-day life, we embraced the opportunity of an invitation from one of the officers, whose acquaintance278 we had previously formed, and paid them a visit. We must confess to a surprise in finding the excellent order and extreme cleanliness that every where prevailed. The rooms were large and well ventilated, and the cots placed in rows along the walls. From all appearances, the soldiers must have easy times and comfortable quarters. They are compelled to drill one hour each day, which usually takes place in the forenoon; from that time until 3 P.M. they are occupied in taking care of and cleaning their arms and accoutrements. From that time until 8 P.M. they are at liberty to go where they please. The evening gun is then fired, and all are required to be within the gates at half past 8, at which time each room is visited, and those absent after 9 P.M. are put under guard as soon as they return, and are punished according to the circumstances of the case.
For their amusement, a very good theatre is connected with the barracks, the actors belonging to the regiment. We learn that this is beneficial, inasmuch as it prevents many of them from seeking pleasure in the numerous drinking-houses which infest certain portions of the city; a pleasure that many of them appeared disposed to seek, but which is generally dear bought, as it is sure to be followed by a punishment proportionate to the offense.
Near the Episcopal church stands the fort, which, from its elevated position, commands the town. The battery is immediately on the beach, and has a fair sweep at the shipping. The authorities find it necessary to keep a strict watch over the Chinese population to prevent an insurrection. They only lack the courage; their hatred of the English is complete, and the will to rise and murder every “outside barbarian” in the city is not wanting in them.
One can scarcely pass through the streets but he is 279 saluted with the cry of “Kum my shop; can sell much too chipp; no wanchee buy sum littley ting?” In fact, the Chinese portion of Hong Kong is a perfect Chatham Street. Going into a shop one morning, we began looking at various articles, the shopkeeper pulling down all his wares to show us. After selecting several articles, and inquiring the sum total of the bill, we were informed it was fourteen and a half dollars. We indignantly turned to leave, when he accosted us with,
“How much can catchee them tings?”
We told him “six dollars.”
“No can do; no can catch plofit, s’pose six dollar.”
“Very good,” we informed him, and again turned to leave, when he called to us the second time, and, after some bantering, told us we might have them for six dollars. Had we not have known the price of such articles previous to this, we might have paid him more than we did, but we knew they were all Jews in trading, and were determined not to allow the rascal to cheat us.
They are great rascals, these Chinese merchants. The currency here is gold, silver, and copper, and they are very cautious in regard to it, being continually on the alert for spurious coin; yet, if they have the opportunity, will put off any quantity of it, and then lie out of it in the most barefaced, impudent manner imaginable. Spanish and Mexican dollars command a premium of from four to six cents; other silver they will not take for its full value. An American half dollar passes for but twenty-five cents among them. On receiving a piece of money, they inspect it very minutely, and if they discover the least flaw or defect in it, they refuse it as bad; or, as they say, “chop dollar—no proper;” yet, if they have the opportunity, will pass the same kind on the purchaser in giving change. If one of them refuse to take such money, it is only necessary to whisper the 280 word “policeman” in his ear, and all is immediately right.
A seaman, who had recently come on shore to live from a California ship, received a bad dollar from one of these merchants. On discovering it, he proceeded to the shop and called for a backgammon-board. Choosing a beautiful one, finished with rich gilt work, he inquired the price. The Chinaman said “three dollars.”
“No, no, John Chinaman; s’pose me no saby you? me live too long Hong Kong; me no fool.”
“Well, s’pose can catchee two dollar, he very good?”
“No, I give you one dollar; proper.”
“Hiyah! how can do! no proper!”
“S’pose you like one dollar, very good; s’pose you no like, very good.”
“Me likey one dollar; two dollar more good; proper; you no see; number one, this fellow; alla same ’nother pigeon (merchant) sell five dollar.”
“Me no give more one dollar; plenty Chinaman speak one dollar proper.”
“Hiyah! Chinaman bloody liar! no speak good; too much lie. S’pose you like catchee one dollar half, proper; s’pose one dollar, no can do.”
“Well, s’pose you no like one dollar, me go ’nother shop.”
“No proper; s’pose you cum my shop, buy plenty, you catchee him one dollar.”
“Oh, certainly. I shall buy you out before I leave.”
Accordingly, he picked up the board, and threw down the same piece he had received from this merchant the day previous. On seeing this the Chinaman flew into a great passion, and called for his board to be returned to him; but it was too late; the purchaser had departed with it under his arm. However, he was not to be got rid of so easily; after the sailor he went, shouting after him to give up his board. The sailor heeded him281 not, but proceeded to his boarding-house, threw the board into his chest, closed it, and sat down on the lid. Presently in came the Chinaman in a hot rage, and demanded his backgammon-board. Upon this the sailor jumped up, seized the Chinaman by the collar, who commenced turning pale, and, shaking him rather roughly, demanded why he gave him “that bad dollar.” The poor fellow protested his innocence, denying the charge. This dodge would not do; so, shouting to a landlord to bring in a policeman, the Chinaman darted for the door, and retraced his steps with all possible speed.
The females are kept under great subjection, being looked upon as little better than slaves. They are not allowed to be educated, but are kept in ignorance. The higher classes dress very richly, wearing many ornaments of gold. In some things we think they show much more good sense than our American ladies. Fashion, with them, does not change every month, yet they all dress in good taste. Their manner of dressing the hair is decidedly superior to that of our own fair countrywomen. On their wrists they wear heavy gold bracelets, generally placed there when quite young, and, were it not for their small feet, they would make a good appearance. This deformity, for we can call it nothing less, causes them to walk as though they were crippled. Many of them are obliged to use the cane to assist them, and they always appear as if it caused them pain to walk. The small feet, we were credibly informed, are confined to the aristocracy. They appear more like club-feet than natural ones, the ankle and foot having both become one. The females are much better-looking than the men. We seldom noticed the high cheek-bones, or eyes so wide apart; and, moreover, their heads are covered by nature’s covering—fine black hair. In complexion they resemble the brunette.
We noticed one very singular fact. As many times 282 as we visited the shops of the merchants, we never saw any females in them, not even belonging to the merchant’s family, who generally reside in the same building. We often wondered at this, so different from our own customs; but then we recollected that we were “outside barbarians,” and could not, of course, be expected to know what was right. On inquiring of “Acowo,” a merchant of high standing, the reason of this custom, his only answer was, “No proper alla same that pigeon; no good.” Very satisfactory, truly!
On Sunday the stores and shops of the Chinese are kept open as usual. They regard no day as a Sabbath. Gambling is carried on to a very great extent among all classes. On entering a shop at almost any time, you will see a number of persons engaged in gambling in the rear portion of the room. The cards are long, narrow slips of pasteboard, with numerous Chinese characters or devices inscribed upon them. The countenances of the players betrayed all the varieties of expression, from that of the fortunate to the unlucky gamester. One may behold the happy and contented look of the winner; again may be seen the countenance livid, lips compressed, eyes glaring, and the whole face betraying the intense excitement of the loser.
It was unsafe at this time to walk the streets of Hong Kong at night, particularly in Typen-shang, or the Chinese portion, or among the boatmen who congregate on the wharves. Although the police were extremely vigilant, very frequently was the pedestrian waylaid, knocked down, and robbed. The boatmen were not to be trusted, as many cases occurred where seamen, returning from the shore to their respective ships at night, were either drugged or knocked in the head, their pockets rifled, and bodies thrown overboard. An officer attached to the steam frigate Susquehanna, while returning to the ship, was thus treated. His body was stripped of its 283 clothing, and then thrown overboard, his murderers supposing him dead. However, the water revived him, and, being an excellent swimmer, he gained the nearest vessel in a weak and nearly exhausted state. Another instance came to our notice while there. The master of one of the American merchantmen in port, while walking through the streets of the Chinese portion of the town in broad daylight, was seized from behind, and his gold watch taken from him. As soon as possible he gave the alarm, and the rascal attempted flight. He was soon captured; not, however, until, seeing escape impossible, he dashed the watch against a stone building, thus destroying it. The punishment for theft, we were informed, is cutting off the hair of the culprit. As this is their greatest pride, they are disgraced forever when they lose their “tails;” and some of them have been known, feeling the disgrace so keenly, to proceed to the grave of a recently-interred Chinaman, rob the dead of its ornamental appendage, and splice or fasten it upon their own in such a manner as to escape detection; then remove to some place where they were not known. Many are seen, however, with no tails, and, like the fox in the fable, are shunned even by their own companions, who have the same desire for plunder, yet lack the courage to carry it out.
While walking through the streets of the city in search of adventure one day, we were startled by a most horrid din, and, looking up, saw approaching a band of musicians, blowing and beating their instruments for dear life. Following this were the bearers of a coffin, which was placed upon a bier, the coffin resembling very much in shape the trunk of a tree, with the larger or spreading part for the head of the deceased, who, we were informed, was the “head” of a family. Next came the mourners—the wife and children of the deceased—dressed in pure white, which is their color for mourning. A284 number of the friends of the deceased, with about twenty American sailors, “slightly elevated,” brought up the rear. The whole procession was going on “a run”—music, mourners, and all hands—“running away from Josh,” as Boston Jack informed us. “Josh” is their evil spirit, and they believe that if they can get the deceased into the ground “in a hurry,” Josh will not trouble him, especially if music is used to frighten him; and we could not but think that the “music by the band,” together with the shouts and yells of the drunken sailors, was enough to frighten his Satanic majesty himself, and drive him out of the city. We stood viewing the procession until they passed from sight, and then came to the sage conclusion that “it takes all kinds of people to form a world.”
They are very strict in their laws about marriage in one sense, and rather loose in another. A Chinaman can have but one wife, who, in marrying, assumes his name; but he is allowed as many handmaids as he chooses to have. Thus they avoid polygamy, and still practice it. Marriage, also, between those bearing the same name is unlawful. The grounds of divorce are seven, some of which are rather amusing. The first is barrenness; the others are adultery, disobedience to the husband’s parents, talkativeness, thieving, ill-temper, and inveterate infirmities. Any of these, however, may be set aside by three circumstances: the wife having mourned for the husband’s parents; the family, since marriage, having acquired wealth; and the wife having no parent to receive her back. It is, in all cases, disreputable for a widow to marry again, and in some instances, especially those of a particular rank, it is illegal.
From the age of ten the females are kept very secluded, and have no opportunity of intercourse with the other sex until they are married. In fact, they never see their intended until the time of marriage. Some of285 them, we should judge, would be sadly disappointed when they come to look at each other for the first time. All that they know of each other before marriage is through their fathers, mothers, or aunts, which, we should think, would be rather unsatisfactory. Yet we are inclined to the belief that they do, by some hook or crook, manage sometimes to get a glimpse of each other’s faces before marriage, else how could the following lines have come into existence, especially the third line of the third verse? It is said to be Chinese, though we rather incline to the contrary:
The birth of a son is an occasion of great rejoicing; the family, or surname, is first given, and then the “milk name,” which is generally some diminutive endearment. A month after the event, the relatives and friends jointly send the child a silver plate, on which are engraven, “Long life, honors, and felicity.” The boys are trained in behavior and ceremonies from their earliest childhood; and at four or five they commence reading. The importance of general education was felt so long since in China, that a work, written before the Christian era,286 speaks of the ancient system of instruction, which required that every town and village, down to only a few families, should have a common school. The wealthy Chinese employ private teachers, and others send their sons to day-schools, which are so well attended that the fees paid by each boy are extremely small. In large towns evening schools are held, that those who are compelled to labor through the day may not be without the advantages of education.
A Chinese school is a great curiosity to an American. They all study aloud, and it appears to cause no confusion with either teachers or scholars, though it would in a Yankee school. But their appearance is the greatest curiosity. Such a set of bald heads with young bodies, their only hair a braided queue hanging down the back—such young faces in the dress of old men, in frocks, leggins, and large shoes, with boys’ motions and actions, and the medley of voices—such a variety of grotesque sounds and tones, is a very novel sight, and would make a laughable picture; but it would be necessary to produce the sounds to give a correct idea of a Chinese school.
Of all the objects of the care of the Chinese, there are none to which they so religiously attend as the tombs of their ancestors, for they believe that any neglect is sure to be followed by worldly misfortune. It is here that they manifest a religious zeal which is hardly shown toward their gods. Their ceremonies connected with the treatment of the dead are of a striking character. Aside from the burial service, of which we have already spoken, there are others commanded by their ritual to be performed. The original and strict period of mourning is for a parent three years, but this is commonly reduced in practice to twenty-seven months. Full three years must elapse from the death of a parent before a child can marry.
287
A pleasing anecdote in relation to filial piety is related of a youth named Ouang-Ouci-Yuen. Having lost his mother, who was all that was dear to him, he passed the three years of mourning in a hut, employing himself in his retirement composing verses in honor of his parent. These are quoted by the Chinese as models of sentiment and tenderness. The period of his mourning having elapsed, he returned to his former residence, but did not forget his filial affection. His mother had always expressed great fears of thunder, and, when it was stormy, would request her son not to leave her. Therefore, as soon as he heard a storm coming on, he would hasten to his mother’s grave, saying softly to her, “I am here, mother.”
The disposal of parental property by will is restricted to the legal heirs. The eldest son has a double portion, or, more correctly speaking, the property may be said to descend to the eldest son in trust for all the younger brothers. Over them he has considerable authority. They generally live together, and club their shares, by which means families in this over-peopled country are more easily supported than they otherwise would be. The constant exhortations in the “Book of Sacred Edicts” point to this usage, and the necessity for it, as they relate to the preservation of union and concord among kindred and their families.
We are informed that the crime of infanticide prevails here to a great extent, especially as regards female infants. They consider it a great tax to bring them up and support them, as they think they receive no particular benefit from so doing. This crime is more common among the poorer classes, who, from their poverty, feel unable to support them. To male children they appear much attached.
We were awakened one morning by the heavy guns of the “Susquehanna,” and at first could not imagine288 the cause. But on gaining the deck and looking around we saw all our national vessels with their gayest colors flying, and smoke issuing from their sides. We then recollected it was the ever-to-be-remembered 22d of February, the anniversary birthday of our dearly-loved Washington, the best and greatest man that ever lived. With great pride did we reflect that, so far from our own dear land even, his name and memory were revered, not only by his own countrymen, but by the descendants of those who would once have gloried in his defeat and death. The English naval vessels also dressed themselves in gay flags, the ever-beautiful stars and stripes flying at the foremast head, and following our own vessels in a national salute of thirty-one guns. Determined not to be outdone by foreigners, after all the men-of-war in port had ceased firing, the “Emily Morgan” hoisted the stars and stripes at the mizzen peak, and other colors at the fore, main, and mizzen trucks, brought her “six-pounder” to the gangway, and belched forth. This proceeding created great astonishment among the government vessels, who little expected to see a whaler saluting the anniversary-day. But why not? we thought, and fired our thirty-one guns, ending with a hearty “three times three,” which made the old harbor ring again. The band from the “Susquehanna” now struck up “Hail Columbia,” which seemed at once to transport us to the home of our beloved Washington, our own dearly-loved home. The house of the American consul was thrown open to visitors, and we embraced the opportunity of calling and paying our respects. We there met many of our countrymen, who appeared to us like old friends, meeting at such a place and on such an occasion.
While rambling through the city, we called at the rooms of a Chinese artist, and there saw some beautiful paintings, mostly landscapes. The portraits were not as well executed, the majority being mere daubs. They289 appear greatly defective in painting the human figure, not having correct ideas of proportion, or arrangement of lights and shades. Some of the paintings representing groups looked really ridiculous; but still, if they have a picture to copy, they do it very finely.
Their powers of imitation, it is said, are not excelled by any people, but they seemingly have no inventive faculties. Yet we saw some things that would go to contradict this theory; and there is an anecdote which was told us by a citizen of Hong Kong, who vouched for its accuracy, that tends rather to disprove it, although the idea carried out was not, perhaps, strictly an original one. At the close of the celebrated “opium war,” some manufacturers at Sheffield, England, hearing of the celebrated imitative powers of the Chinese, sent to Hong Kong a quantity of the finest cambric needles, requesting their agent to ascertain if they could be imitated by the Chinese. The agent, accordingly, took some of them to a Chinese cutler, and, telling him what was wanted, left them. In a few days the needles were returned, with another package precisely similar, except that the needles manufactured by the Chinaman all had eyes nicely drilled and finished in the points of them! The Chinaman called the next day after he had sent the package, and requested the Englishman to send his needles to England, and ascertain if they could be imitated. It is needle-ss to say that Johnny Bull never sent John Chinaman any more cambric needles to imitate.
Still, if you wish an article made, they must have a copy, and that copy will be strictly followed. An anecdote illustrating this is related—the truth of which we do not vouch for, however—of an English midshipman, who wished half a dozen pairs of pants made, of blue cloth. Accordingly, he selected his tailor, gave him the order, and left a pair as a pattern. It so happened that this pair had a small patch on the seat, and was minus290 several buttons; and when the new pants came on board, very neatly made, each had a similar patch, and the same number of buttons missing—the Chinaman charging for the extra sewing. As may be supposed, the middy was in a great rage; but all the satisfaction he could get was that they were made exactly like the pattern left.
The Chinese manufacture a liquor which they call “sam shu,” which is very intoxicating, and of which they drink large quantities. It often happens that they entice our naval seamen to partake of this liquor, and they are as surely robbed as they do partake of it, for it is almost always drugged by them for the purpose, that they may the easier rob poor Jack of his liberty money, or any thing else they can carry off. On awaking, finding himself stripped of every thing by the rascals, there is no resource for him but to return to his ship, which is done. One would think that this treatment once would be sufficient; yet it is practiced upon some many times. Forgetting their former follies, they rush again into the embrace of the soul-destroying, maddening cup.
Having a desire to see something of the domestic life of the Chinese, and possessing a moderate share of what is sometimes termed “impudence,” we, in company with two of our shipmates, invited ourselves to call upon a Chinese family. Selecting a house which had the appearance of having a wealthy owner, we marched to the door, and one of our number rapped. The door was opened by the lady of the house, and in we marched. She immediately motioned us to seats, looking at us, and evidently wondering to what she owed the honor of this visit. The house had a very neat, tidy appearance, as had also the hostess, who, though the mother of eight children, appeared scarcely thirty years of age. They were boys, all but two, and were romping about the291 room, raising “Ned” at a great rate. It being their dinner-hour, she went about her business, leaving her polite visitors to make observations and amuse themselves as they pleased. She soon returned, and placed on the centre of the floor a large dish of boiled rice, another with vegetables, called the children, and seated them on the floor around the “wittles.” After passing us some tea, she took her station with the children, placed a portion of the rice and vegetables on the plate of each one, gave them their “chop-sticks” and told them, as we supposed, to commence. And commence they did. These chop-sticks are two round, slim pieces of ivory, about eight inches in length, which supply the place of both fork and spoon. With the chop-sticks in the right hand and the dish in the left, with its edge close to the mouth, the velocity with which they “fork” down the rice is certainly surprising. They handle these singular sticks with the greatest ease, picking up whatever they wish, and conveying it to the mouth.
The principal food of the Chinese consists of rice, vegetables, and fruit—eating little or no meat. The tea which our hostess had the kindness to pass us was of a most excellent flavor. They drink no tea but black, that being their favorite. It is very different from any we ever drank in America, having a much better flavor. After thanking the lady for her kindness, we took our leave, strolling into the “Josh house,” or temple of worship.
This building is of one story, but covers a large area of ground. It is very fancifully decorated on the outside; and on each side of the entrance is a large sculptured dragon, about twelve or fifteen feet in height. On coming to the gateway, we found the entrance paved with smoothly-hewn stone, and, ascending a few steps, we entered the building. Near the centre of the first room stands, or rather sits, cross-legged, a great, disagreeable-looking 292 bronze idol. It is from twenty to thirty feet high; is represented as very fat, with an immense belly, and laughing, as if very happy. Before him is suspended a lantern, and in it a dim red light is burning, which is never permitted to go out. On a table-like altar in front Josh-sticks were smoking. In front of this table is a large metallic urn for containing the ashes of the Josh-sticks and offerings. Before the altar, in a line, are three stools, covered with little mats, for the worshipers to kneel upon. Above, near the roof, is a Chinese inscription in gilt letters; and each side of a post, extending from the roof to the floor, is lined with the same kind of characters.
On the right were two other gods, facing toward the left, also in a sitting posture, the legs being turned out, and the right foot of each resting on the back of a tortoise. They were about twenty-five or thirty feet high, and eighteen feet in circumference around their middle. They were ornamented with bright and various colors, and gilded and decorated in a profuse manner, appearing more like theatrical characters than gods. Many smaller figures of the human form are about the feet of the larger ones, as if paying them homage. These, also, are richly and handsomely painted, and gilded in a similar manner. All the gods have shrines, kneeling-stools, and Josh-sticks placed before them. The first of these gods, on the right of this room, is represented as a black man, with a huge beard, wearing a crown, and holding a sword in one hand. This is the god of war. The other is the god of music, with a complexion light and delicate, animated features, and regularly trimmed mustaches. He is playing a guitar, and smaller Chinese figures are playing at his feet.
On the left of the room, facing toward and corresponding with those on the right, were two other gods of the same size and style, and seated in the same manner as293 those on the opposite side of the hall. One of them had in one hand a dragon’s egg, with the young dragon just presenting itself, while in its other hand was held, writhing about the arm, a serpent which he was crushing. The other god held a flag, and had a very self-conceited expression of countenance, as if he was a very great character in his own estimation. These are the gods of vengeance and justice.
We passed through a door in the back part of the room into a second apartment. This room contains the greatest number of idols, and is where the principal religious ceremonies are performed. Idols are arranged all round the room, and there are several in the centre. As you enter the door, three huge gods, twenty-five feet high, appear, looking very demurely, with eyes cast downward. Two goddesses, one on each side, stand facing at right angles. They are all very richly dressed—the goddesses particularly so, having crowns on their heads. The others have nothing on their heads but a sort of skull-cap, without a front-piece. The usual amount of vases, Josh-sticks, etc., were standing around, besides various other things, the use of which we did not learn. On the left of the altar was a large iron kettle, used for a drum; and there was also a hollow instrument, made from a peculiar kind of wood, and in the shape of a large sleigh-bell, for drumming purposes. Back of all these idols is a goddess mounted upon an ass, the head of the animal being turned up toward her, as if braying. The gods around the outside of this room were in two rows, and were about the size of men, of various patterns and designs, probably that each worshiper might choose a god for himself.
While examining matters and things in this room, a female approached, and, going to a desk or counter that stood in one part of the room, held a short conversation with a priest who stood there. She then purchased a294 bunch of fire-crackers (such as Young America delights in on Independence days); then advanced to one of the large idols, kneeled down, bowing her head so that it touched the stone floor, three times in succession. She then took two sticks or pieces of wood, resembling oyster-shells, which she held above her head and let fall. This she repeated, bowing her head to the stone floor two or three times, taking particular care, however, not to strike the floor hard enough to break any of the stones, or her head either. Appearing not to be satisfied, she arose, her countenance betraying great anguish. Leaving her angry god, she turned to the goddess, who, she thought, would better understand her feelings, being a woman like herself, and, with her head bowed again, went through the same forms. This time, on arising, she appeared more pleased, and, lighting Josh-sticks, she again commenced, holding the burning sticks in her hand, advancing to the goddess, then receding from it, then bowing to the floor, striking the head, etc., besides much more that was about as foolish. She then lighted the crackers, and threw them around in all directions. At last she took a bamboo box of tablets in her hand, shook it till one fell out, with some Chinese motto on it, which she carried to the priest, who interpreted it, giving her a corresponding slip of paper, which, we suppose, after being burned, entitles her to some thousands of cash in their spirit-world, or admits her to some great honors and privileges. Any person, by paying a few cash, can shake the box and obtain a similar receipt. After chin-chinning the principal god in the room, she departed.
In all the Chinese houses which we visited Josh-sticks are kept continually burning, to drive away the evil spirits, and keep them from harm.
While a part of the ship’s company were on shore enjoying themselves, the remainder, on board ship, were295 continually devising means to “kill time.” On one occasion, Tom W., our old joker, made his appearance on deck, presenting a most comical figure. He had on a pair of pants that came within six inches of his ankles, with a narrow piece of leather passing around the bottom of his feet for straps; a coat with the waist between his shoulders, and the skirts trailing the decks; the whole surmounted by a tall, bell-crowned hat, with narrow rim. About his neck was suspended a boatswain’s whistle. Rigged out in this style, he mounted the “hurricane deck,” and commenced pacing to and fro with great dignity. On board the “Susquehanna” they were exercising the men in loosing and furling the sails, and every time the whistle of the boatswain sounded on board, Tom replied, imitating them as nearly as possible, and turning “full front” to the frigate, over whose sides were seen sundry heads, peering at the whaler to see what could be the matter. To all this, however, Tom paid no attention, but continued his dignified strut, interspersing his walk with all manner of “calls” on his boatswain’s whistle. The quarter-master of the frigate now leveled his glass at the whaler’s “boatswain,” and took a long squint. Perceiving this, Tom called for his glass, and one of the boys passed him a handspike. Bringing it to bear, he “squinted” in return at the quarter-master; then would take a turn or two fore and aft the deck, give a shrill whistle, and again level his “glass.” By this time most of the officers of the “Susquehanna” were gathered on the quarter-deck of that vessel, staring at us, and probably thinking all hands drunk or crazy. Tom, who knew how far to carry the joke, now came down from his elevated position.
The sails having been loosed to dry during the day, toward evening the watch were sent up to furl them. Every thing in readiness, Tom’s whistle sounded, all hands sprang into the rigging, and mounted aloft. The296 sail was rolled on the yard at the sound of the whistle; the men descended from aloft, and mounted, furled a second, then a third sail, and so on through the whole programme: all was done at the sound of the boatswain’s whistle. This proceeding “astonished the natives;” the officers and crews of the several men-of-war and other vessels gazing at the new “wrinkle,” and systematic style of performing work on board a Yankee sperm whaler!
Notwithstanding the fact that numerous naval vessels belonging to the United States, England, and France are nearly all the time on this station, yet the coast and Canton River swarm with Chinese pirates. The government of China, also, has an armed junk, mounting twelve guns, stationed on the coast, for the ostensible purpose of protecting commerce; but it is pretty strongly believed that this Chinese man-of-war not only winks at the piracies committed, but is not backward about running up the black flag herself on certain occasions. About the time we arrived at Hong Kong, a brig bound to some part of the East Indies was overhauled, before she was clear of the bay, by a number of fishing-junks, as they professed to call themselves, and, after massacring nearly all the crew, and wounding the remainder—leaving them dead, as they supposed—they rifled the brig, taking away every thing they found of any value. The next morning she was found in this disabled condition by the Chinese man-of-war, who took her in tow, and brought her into port. One of the English men-of-war immediately got under weigh, and, after cruising among the various islands a few days, overhauled some of the junks and brought them in. The prisoners were immediately taken ashore and tried; several were hung, and the remainder imprisoned at hard labor for the remainder of their lives.
We had heard much of the Chinese theatre, or Sing 297 Song, as they term it, and concluded we would pay it a visit. The building, which is a temporary erection, is very large, built of bamboo, and capable of containing four or five thousand persons. The gallery is large and commodious, it being built for the accommodation of the “fan-qui-loo” (foreign devils). The Celestials occupy the pit, and, there being no seats, they are compelled to stand. To see such a mass of heads, “all shaven and shorn,” in one compact space, swaying to and fro, and hear the continual buzz of their voices, is really amusing. And then to watch them as a policeman goes through the crowd, semi-occasionally bringing his short club down upon the bare heads of the Chinese, just heavy enough to make them sing out “Hi-yar-r-h! how can do? no proper.” Still, they make room for him, not caring to receive a second whack. After looking at the crowd below us, and wondering where they all came from, until we became somewhat restless, we were fairly startled by a most frightful, horrible din. Gongs, bells, and sundry other equally harmonious instruments were made visible, and the “orchestra” were beating and playing them as if each were paid according to the amount of noise he made, and was determined to win. This horrible music, as they termed it, appeared to increase, until we were obliged to stop our ears with our fingers, to prevent being entirely deafened. However, it ceased as suddenly as it commenced, and the performers made their appearance, dressed in the richest Chinese style. Alter going through a sort of pantomime, which lasted about half an hour, a couple of them, who appeared to be leaders of the different parties, jabbered away at each other in Chinese, and finally commenced a regular fight, which soon became general, all hands “pitching in” in the most scientific Chinese manner. Fire-crackers were burned, gongs sounded, and other warlike demonstrations generally were gone through with, until one of the 298 parties, having killed their opponents, now dragged them from the stage. This was followed by other scenes equally interesting to those who could understand nothing that was said. The performances closed by acrobatic feats, which were equal, if not superior, to any we ever saw. We can only sum up the whole by saying the crowd was immense, the performance nonsensical, and the music horrible.
The Chinese method of erecting stone buildings is very singular; and, although it shows the inferiority of the Celestials to the “outside barbarians,” still it is very ingenious. A perpendicular bamboo wall is first built as a guide, and the stones are then laid inside and against it till the walls are complete. One would naturally think that they could lay the stone wall as perpendicular as they could build the bamboo, yet we were assured they could not. We noticed a fine building in process of erection—a masonic temple. This building was for the use of a lodge working under a charter from England, and composed of English and American residents.
We were rejoiced to learn that a “Bethel” had been established in Hong Kong, and we gladly accepted the opportunity given us of attending it. It is a floating “Bethel,” and seems especially adapted to the wants of seamen, who feel much more “at home” there than inside brick walls. The chaplain appeared to be an excellent, earnest, kind man, devoted to the cause in which he was engaged. We were pleased to notice the quiet deportment and strict attention paid to the remarks by the seamen in attendance.
We had now been in Hong Kong several weeks, and it was time for the “old man” to think of deep water again. Accordingly, on Tuesday, February 28th, we commenced preparations for sea—for our last cruise. Our provisions, water and all, were on board, and all that 299 was wanting was the word, and the anchor would soon be apeak. A little incident transpired, however, which served to detain us a day longer. Several Chinese merchants were on board, showing their goods and doing their best endeavors to effect sales. They knew, from seeing the “Blue Peter” at the fore, that we were to sail on that day, and they were off in great numbers in consequence. Among the rest were several shoemakers, who appeared determined to sell. After a good deal of bargaining and bantering, the chief mate ordered all to leave instanter. In collecting their shoes preparatory to leaving, one of them discovered, or supposed he discovered, a pair missing, for which he had received no pay. This put him in a great rage, and he left muttering vengeance on the “’parme whaler,” as he termed it. He soon returned, however, accompanied by a policeman, who explained what he came for. The Chinaman charged one of the crew with stealing them, whose chest was immediately searched, but no shoes were found. There was now no remedy but the man must go on shore before a magistrate. In company with the chief mate, the man proceeded to the magistrate’s office, where the Chinaman was called upon to make his statement. After having sworn him as to the truth of it, the prisoner was put upon the witness’ stand and sworn. On being asked if he saw the Chinaman on board the ship with shoes for sale, he answered “yes.”
“Did you take any of those shoes unlawfully?” was the next question.
“No, sir,” was the answer.
“Did you see any person take any shoes unlawfully from the plaintiff?”
“No, sir.”
The magistrate now turned to the Celestial, and sternly remarked: “Look here, John Chinaman, if you ever come before me again with such a story, I will send you300 to the ‘lock-up’ for two years,” and then dismissed the case.
The following day, March 1st, we took our anchor from China soil, bade adieu to Hong Kong, and with light hearts made sail for Japan. The pilot remained with us until the day following, when we took leave of him with three hearty cheers, with three more for a “lucky cruise.”
Thursday morning, March 3d, saw us clear of the land, with no wind, and enveloped in a thick fog. At noon the fog commenced rising, and as it continued slowly, exposed to our view a swarm of fishing junks. This did not create a very pleasant feeling in our midst, as we well knew that many of the so-called fishing junks were only pirates in disguise. One of them sent a boat with some fish, which we purchased, and then sent him off, as we did not like his appearance. It was still calm, and all hands were “whistling for a breeze,” which soon came, and before evening we were bowling it off at the rate of nine knots.
We had forgotten to mention that while in port we shipped two men, an officer and a boat-steerer. The officer, Mr. M., was a windy, braggadocio fellow, not over-stocked with common sense, whom all hands learned soon to hate and despise. The other, Davy, the boat-steerer, was a Frenchman, a very quiet, easy fellow, not at all inclined to kill himself with hard work.
302
We had been but a few days from port, and while yet in the China Sea, when the glad cry was heard, “T-h-e-r-e she b-l-o-w-s.” As this was our last cruise, it can be easily imagined how “eager for the fray” we were. Down went the boats, the men following, feeling decidedly fishy. The larboard and starboard boats soon fastened, and killed their whales with but little trouble; but not so with the bow boat. Our new officer must needs “show off” his skill, and, after fastening to his whale, drove the boat completely on to him, when he turned, and commenced very coolly chewing the boat to pieces. This was very unfortunate, as the waist boat, which was nearly up to a fourth whale, was necessarily obliged to go to the relief of the stove boat. The wounded whale fortunately received the harpoon in a vital part, and soon “turned up,” so that we got three whales, which was not a bad commencement for the cruise.
We now experienced very heavy gales of wind—what seamen call the “tail end” of a typhoon. It came upon us at first unawares, and we were near losing all our sails and spars, which would have rendered us a complete wreck. For an hour or two the wind would blow with tremendous force—it appeared that every thing must give way; and then a calm of an hour or two would occur, the sea now rolling and pitching in great fury. This weather lasted for two or three days; and when pleasant weather again broke upon us, never was it more welcome. We now sighted the northern islands of the Bashee group, and it was with difficulty that we kept clear of them.
On Thursday, March 24th, we sighted the southernmost island of the Loo Choo group, belonging to the Japan government. These islands possessed a peculiar interest to us at this time, as Commodore Perry was then on his celebrated expedition to Japan, and it was expected he would visit the Loo Choos about this time.
303
Twice during our voyage had death visited us, and taken from us officers and shipmates. Again he came, and on this occasion visited the forecastle, taking with him one of our Roratongo natives. He died on Monday, April 12th, of consumption. When he left his native island he was troubled with a severe cough, which grew worse rather than better, until his condition was one past all hope. While in Hong Kong he was placed in the hospital, and every thing that medical skill could do to effect a cure was resorted to, but all in vain. The captain endeavored to persuade him to remain there, promising to leave him so situated that he would be as comfortable as possible while he lived; but this he would not consent to. He said he did not wish to remain there and die among strangers, but would rather be with those with whom he had lately lived—those who were his acquaintances, and among his native friends. Every thing that could be done by captain, officers, and crew to make his last days comfortable and happy, was done. But the time drew near when he was to depart. Death already stood at his bedside, awaiting the summons to convey him over the dark river. Calling his Kanaka friends about him, whose tears flowed fast and full, he gave them sundry messages to his parents, brothers, and sisters; told them to say to all he died a Christian, firm in the faith of a redeeming Savior; and that, although his body might be buried in the depths of the dark blue sea, yet his soul would ascend to that glorious home above, which his Savior had “prepared for all those who love him.” He exhorted us all, in as strong a voice as his weak nature would permit, to prepare for death, for death would as surely come to us as to him. Requesting his native friends to sing, in their language, his favorite “missionary hymn,” as he termed it, “Oh! that will be joyful, joyful, joyful,” etc., he quietly dropped asleep in death.
304
What a lesson was here taught us nominal Christians by this poor native! An inhabitant of an island but a few years since barbarous, dying strong in the faith of a blessed immortality beyond the grave. If all the missionaries who have left their homes to labor for the spread of the Gospel among the heathen had accomplished no more, through Christ, than the salvation of this one native, yet were they well repaid. “What shall it profit a man if he gain the whole world and lose his own soul? or what shall a man give in exchange for his soul?”
At four P.M. all sail was taken in, the ensign half-mast, and again were all hands called to “witness burial service.” After the usual ceremonies, which were very affecting, the plank was raised, and the body committed to the deep.
Reader, when you die, it will be, we trust, in the Sabbath calm of your hushed chamber; but the poor sailor dies at sea, between the narrow decks of his rolling home. The last accents that reach your ear will be those of love and affection, such as alone flow from a mother’s heart and a sister dear; the last sounds that reach the dying sailor’s ear are the hoarse murmur of that wave which seems impatient to grasp its victim. You will be buried beneath the green tree, where love and grief may go to strew their flowers and cherish your virtues; but the poor sailor is hearsed in the dark depths of the ocean, there to drift about in its under-currents till the great judgment day. Alas! for the poor sailor, often the child of misfortune, impulse, and error, his brief life fraught with privations, hardship, and peril, his grave, at last, the foaming deep! Though man pity him not, may God, in his great mercy, remember his weaknesses and trials, and save him through his Son!
From this time until about the 15th of April we were very successful, obtaining, in three weeks’ time, about 305 three hundred barrels of oil. This, with the whales we captured in the China Sea, increased our store nearly four hundred barrels since leaving Hong Kong. As a matter of course, all hands, from captain to cook, were in the best possible humor. This was our last cruise, and “every whale counted.” We were now steering for the Bonin Islands, to procure turtle, sweet potatoes, watermelons, etc.
Saturday, April 30th, brought to view a sail on our weather beam, the clipper whaler “Jireh Perry,” of New Bedford, Captain Lawrence. This man was a perfect tyrant on board ship, and no crew had ever sailed with him from home and returned. It was stated, and pretty generally believed, that he had killed no less than three men since he had become master of a ship; yet, because he always was fortunate enough to obtain large quantities of oil, and mean enough to treat his crew so that they would all desert at the last port touched at before leaving for home rather than go home in the ship, thereby leaving all the profits to the owners, he could obtain a ship of whom he liked.
A few days later we spoke the “Alabama,” Captain Coggeshall, who reported that the day before Captain L., of the “Jireh Perry,” had shot his cook for some trifling cause.
On Saturday, May 21st, we “gammed” with our old friends of the “Mohawk.” Probably the reader is unacquainted with the meaning of the term “gam,” which is peculiar to whalemen alone. It is simply visiting from one ship to another. When two ships meet, one captain invites the other to come on board and pass the day. On his arrival with a boat’s crew, the chief mate of the vessel that has given the invitation returns with a boat’s crew from his own ship to the stranger, thus leaving the two captains on one ship, and the two mates on the other, and exchanging boat’s crews. The first 306 salute generally is, “How are you, shipmate? how long are you out? how much oil have you got? what part of the States are you from?” But a short time elapses before all hands are acquainted; the visitors are invited into the forecastle, where some time is spent in spinning yarns. After a short general conversation, the song is called for, and some one, generally the singer of the ship, leads off, singing some love-ditty, pirate, or sailor song, all hands joining in the chorus, and making the welkin ring. The song goes round, and he who can not sing must spin a yarn; all must contribute to the general amusement. The day passes pleasantly away, all labor being suspended except the look-out for whales and sailing the ship. These “gams” are to the sailor moments of recreation, and serve to create general satisfaction among all hands. During these “gams” whales are often raised, and the oil secured on the occasion is equally divided between the two ships, “be the same more or less.”
A queer genius was Captain Hayden, of the “Roscoe.” Meeting him about the 1st of June, Captain Ewer invited him on board. On crossing the “Roscoe’s” stern, we observed that Captain H. had his right arm in a sling. Fears were expressed that he had injured himself in some manner. His head also was bound up in a handkerchief. Coming alongside, the man-rope was swung to him, and he came up the ship’s side with one hand, keeping the other in the sling. After congratulations had been exchanged, Captain E. anxiously inquired what was the matter with his arm, “hoping he had not injured it severely, or broken any bones.” Captain H. replied, his countenance as grave as a judge, that “he had been at work very hard during the day, and his arm being somewhat tired, he was merely resting it!” Captain E. replied that he might have suspected some trick of that kind, and asked him “what was the matter307 with his head; if that had been hard at work also?” He pulled off the handkerchief which bound it, and exposed a completely bald head; making the remark that “he had not seen a whale for two months, and he had shaved his head, and should keep it so, until he took one hundred barrels of oil.” After passing a very pleasant day and evening they departed. We now shaped our course for the Bonin Islands.
It is sometimes the case that disputes arise among the foremast hands, and, instead of settling the matter in an amicable manner, resort is often had to blows. An instance of this kind occurring about this time, and reaching the captain’s ears, the disputants were called aft, and each were furnished with a rope, and ordered to flog one another until he told them to stop. This novel mode of settling the affair they did not relish, yet obey they must, and at it they went. After belaboring each other to their hearts’ content, they were ordered to cease, and went forward rather ashamed of themselves.
We saw the “E. L. B. Jenny,” of Fairhaven, Captain Marsh, on Friday, June 10th. They had taken, a few days previous, a whale which “stowed down” upward of one hundred and thirty barrels. Such whales are very “few and far between.”
On Wednesday, June 15th, we raised a strange sail to leeward. Running down to her, we found it to be the bark “Empress,” a Peruvian merchantman, from Cumsingmoon, China, to Callao, with four hundred Chinese coolies on board, bound to the mines in Peru. This system of deception is equaled only by the African slave-trade. The Chinese (who are generally of the lower classes) are allured, by flattering inducements, to go to California, or some other equally rich country, where, they are told, they will become rich in a few years, and can return to their own country. As soon as they get them on shipboard, a guard is stationed over them, with308 orders to shoot down the first one that shows any signs of resistance. Being kept such close prisoners, and on the coarsest food, they are naturally joyous at the sight of land, and leave the vessel with glad hearts, only to enter the slavery of the Peruvian mines. This species of slave-trade is, like the African slave-trade in our own land, forbidden by the laws of the country, but secretly connived and winked at.
“Ormsby’s Peak,” of which we give a sketch taken on shipboard, we saw on Saturday, June 18th. It rises about two hundred feet above the level of the ocean, and has no shallow shores around it. Soundings can not be obtained close to the rock. It is one of nature’s great curiosities.
On Thursday, June 23d, we first raised the Bonin Islands, consisting of Perry’s Group, Peel’s and Bailey’s Islands. We here caught a green turtle, who was asleep upon the water. We soon had him in our coppers, making turtle-soup for all hands.
The morning of Monday, June 27th, saw us close in to Peel’s Island. This island presents a fine appearance from the sea, the land being moderately high, and thickly covered with verdure. On the west side is a fine harbor with good anchorage, and very convenient for ships wishing to water. About 9 A.M. the wind died away, leaving it a dead, dull calm, and the current slowly drifted us toward the northern point of the island. As we neared the land destruction appeared almost inevitable, and we feared that the voyage of the “Emily Morgan” was about being brought to a sudden termination, leaving her bones to bleach upon the rocks. But an overruling Providence held all in His hands, and, when within a stone’s throw of the shore, we struck a westerly current, which swept us clear of the point.

311
It still continued calm until Wednesday the 29th. During that day a breeze sprang up, and we again made the land. Captain E. and a boat’s crew had been on shore two days, in consequence of our drifting away from the land. They came off on this day, bringing with them some sweet potatoes and two fine large turtle. But very few persons reside on these islands—some twelve or fifteen. Mr. Savory, the oldest inhabitant, came to Peel’s Island in 1812, and has never left it. All living on the island are English or American. Irish and sweet potatoes, corn, melons, onions, and nearly all kinds of vegetables, are raised with the greatest ease. Oranges and pine-apples are of spontaneous growth, and abundant. Green turtle, also, are found here in great numbers, and easily procured.
The expedition to Japan, under Commodore Perry, paid this island a visit, and the commodore was very strongly impressed with the idea of making it a naval and coal dépôt for vessels plying between San Francisco, Australia, and Hong Kong; so much so that he took possession of a portion of it (with the consent and approbation of the inhabitants), and sent on shore three men, with agricultural implements, seeds, live-stock, etc., to experiment, while he proceeded to the Loo Choos, and to await his return.
The reader will doubtless recollect one “John Wilds,” who sailed with us a short time during the first part of the voyage, and who left to go to the gold mines in Australia. What was our surprise to find him living on Peel’s Island. He informed us that, finding it rather hard digging in Australia, he shipped for Hong Kong, where he joined a whaler. Serving a short season in her, he left, and had since resided on Peel’s Island, raising vegetables, and catching turtle for ships. He had thrown aside the profession of sailor, and had become a merchant.
While all hands were busily engaged, from ship to shore, and shore to ship, laying in a stock of vegetables312 and turtle for our last cruise, one of our men became so enamored with Peel’s Island that he concluded to take French leave. Accordingly, while on shore, he took to his heels and made off. The officer in charge of the boat gave chase, but the man was too nimble for him, and he was soon out of sight. Foolish fellow! he was the loser some four hundred dollars by the operation, and in a few months later lost his life, having been capsized in a boat and drowned.
We now come to the last anniversary of our nation’s birthday that we were destined to spend together in our ocean home, and we resolved that it should be a merry one. All unnecessary work was suspended; the doctor was ordered to serve up his best dishes for the occasion, and all hands went in for a merry time—a celebration on our own hook. During the morning a national salute was fired, the glorious stars and stripes floating proudly at our mizzen peak the mean while. At twelve dinner was announced. The bill of fare, as presented by the doctor, was turtle soup, boiled turtle, fried turtle, and turtle in every conceivable way; sweet potatoes; cakes; pies; custards; turtle eggs, fried and boiled; plum duff, etc., etc.—the whole forming a repast that Jack seldom sits down to. All hands did ample justice to the dinner, which the old darkey cook received as a great compliment. “I tought,” said he, “I fix dinner for you dis foufh July just suit you, and I been gone done it.” We now postponed further proceedings until evening. Among other good things, the steward had brewed a barrel of excellent small beer for the occasion from sweet potatoes and hops. And now the watch had been set; none on deck save the man at the wheel and the officer pacing his rounds. Forward were all hands in the forecastle, which was brilliantly illuminated by the real spermaceti—the spoils of our own hard-fought battles—each one seated with his pot of beer before him.313 The song was called for; and “Hail Columbia!” was sung by Yankees, Englishmen, Frenchmen, Spaniards, Portuguese, and Kanakas, as never sung before. Patriotic speeches followed, and the sentiment of devotion to our country was toasted: “three times three,” with a will, was given for the “land of the free and the home of the brave.” The Kanakas and Portuguese, although not understanding the “merits of the case,” entered into the sport with a hearty good-will, drinking their small-beer, occasionally exclaiming, “Hurra Fourth July! very good; I like s’pose he come every day.” And thus our last Fourth of July in a whaler passed. Although not making as much of a “splurge” as did many patriots on that day, yet our hearts beat as true, and expressed as much devotion to our country.
From this time our good fortune, that had followed us during the cruise so far, appeared to gain. During the next thirty days we captured nearly three hundred barrels of oil, which was in itself a good season’s work. Fortune had at last crowned our efforts with success, and each day, as it passed, would hear some one exclaim, “One day less on board the old hooker!”
Nothing of peculiar interest transpired further during the cruise except an occasional meeting with a brother whaleman. We were all the time working our way to the eastward, preparatory to leaving the ground in September. On Tuesday, August 4th, spoke the “Rambler,” of Nantucket, Captain Potter. Soon after parting company, we lowered our boats and captured two large whales, they yielding us about one hundred and sixty barrels of oil. On the 25th of the same month we gammed with the “Hope,” of New Bedford, Captain Gifford. We found him quite ill, and hardly able to walk the deck; yet in this same feeble condition, a few days previous, when whales were raised, he had been placed in his boat, bolstered up with pillows, and actually 314 captured a large whale. Nothing, he said, but his anxiety to get a good voyage induced him to do so.
The following day we again gammed with our old friends of the “Roscoe.” It will be remembered that we had with us a Kanaka from Simpson’s Island, whom we called “Dick Simpson.” As he did not wish to go to America, the captain told him that he might go into the first ship that we met that would take him to his island. An opportunity now presented itself in the “Roscoe,” and Dick availed himself of it. The captain gave him his discharge, and paid him in tobacco, pipes, calico, trinkets, etc.—the currency of “his land”—and Dick prepared to leave us. Nearly every one of the crew made him some present as a token of affection, for we all loved good-natured, obliging Dick Simpson. What if his skin was of a dingy hue, he had a brave, good heart, as we all could testify, and we could see that heart was heavy as he bade us each an adieu. The “pumps” of more than one warm-hearted sailor were “set going” on that occasion, but none were ashamed of them. Neither was he soon forgotten, but long remembered by us all.
We now, for a few days, turned our attention to fishing on a somewhat different scale than we had been. It is a peculiarity of the Japan sperm-whale fishing-ground that ships are surrounded nearly the whole season by albicore and bonita. These fish are easily caught in the following manner: the fisherman seats himself upon the weather rail, first provided with a line and hook, the bait consisting of a small piece of white rag. This is fastened to the back of the hook in a peculiar manner, so as to resemble a pair of wings as much as possible. Then skimming the hook thus baited along the surface of the water as the ship goes through it, the foolish albicore or bonita sees it, and, thinking to make a meal off some unlucky flying-fish, makes a leap for it, and finds315 himself immediately landed upon deck. Often have we sat thus, and hauled them in as fast as we could drop the line and disengage the hook. As we before remarked, all hands, for two or three days, turned our attention to this kind of fishing, and we soon had about fifty barrels of them cleaned and salted for “liberty money” in the Sandwich Islands: they there command the highest price.

As there must be a “first time for every thing,” so, we suppose, there must be a “last time” also. We had had our “first lowering,” and the time had now arrived when, we hoped, we were to have our “last.” The captain had informed us that, “just as soon as we got one hundred and fifty barrels more, we could sing ‘Homeward Bound.’” No one was dull now at masthead; all eyes were open; and the mastheads were double manned with volunteers every day. Not long was it to be before our wishes were gratified. On the morning of Friday, September 2, at about 8 o’clock, the old cry—never before so welcome—“T-h-e-r-e s-h-e b-l-o-w-s!” broke forth. The excitement that ensued beggars description. The day was beautiful; the whales were to leeward; and a nice breeze was sending us slowly through the water. Every circumstance was in our favor. The men knew the conditions of our being able to soon316 point our ship’s head homeward. We were now nearly four years from home. Many of us had heard no word—not even a word—from the dear friends we left behind. Every man looked “whale” as he stepped into the boat, and our young fourth mate—a boy in years, but a man in soul—said to his crew as he left the ship, “Boys, you need not expect to put foot upon the Emily’s decks again till we have drawn the claret from one of those fellows.” And they did not. In less than two hours after lowering, two more of the leviathans of the deep had ceased to live. They were brought alongside and secured. The captain now called all hands aft, and complimented them upon the day’s success, proposed three cheers, which were given, and which made the old ship ring again: “And now,” said he, “let us have their jackets in on deck as soon as possible.”
The following Wednesday we stowed down the oil, and found we had one hundred and sixty barrels, ten more than we asked for, but which was “good for leeway.” The ship’s head was now pointed toward the Sandwich Islands, with all sail, every stitch we could carry, crowded upon her. Joy now reigned throughout the ship.
On Monday, October 10th, we sighted the islands of Maui and Molokai. The weather was thick and squally, and we stood off and on the land that night, and the following day steered down the passage between the two islands. At noon we came in sight of the anchorage and shipping, but, the wind dying away to a calm, we were not able to come to an anchor until 4 P.M. of the next day, Wednesday. It was hard to bear, lying in a calm, in sight of the anchorage, for twenty-four hours; but we had to submit. But we finally dropped our anchor, for the last time on foreign soil, in the harbor of Lahaina, island of Maui.
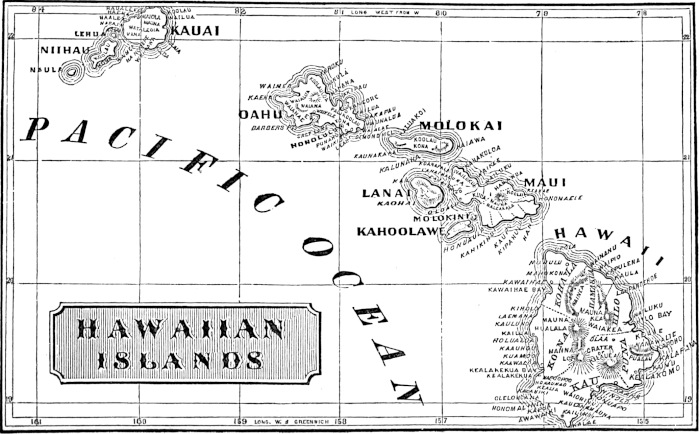

321
Strictly speaking, there is no harbor at this island. The anchorage is merely a roadstead, which is on the south side of it, and protects the shipping from the northerly gales, which are the most prevalent. In case of a sou’easter, however, ships must put to sea or be driven on the reef. We found about seventy sail at anchor, about sixty-five of them American whalemen.
As soon as the anchor was down we were visited by the harbor-master, accompanied by the seamen’s chaplain, Rev. Mr. Bishop. After the former had transacted his business, the latter addressed to us some very excellent remarks, distributed several copies of the “Seamen’s Friend,” and concluded by cordially inviting all to come and see him; also to attend Bethel on the Sabbath. The “Seamen’s Friend” is a sheet published at Honolulu, Wauhoo, by Father Damon, as he is familiarly called, and is devoted to the spiritual and temporal good of the sailor.
The town of Lahaina (pronounced Lahena) is beautifully situated on the level land skirting the sea, and extends along the shore a distance of two miles. Back from the shore it reaches to the foot of the mountains, thus lying hemmed in, as it were, by the sea in front and the mountains in the rear. The streets are lined with beautiful shade-trees on either side, which, in the hot weather, afford a cool and delicious retreat. The reef extends the whole length of the town, about forty rods from shore, and, but for a small opening or break in it, boats would be unable to land. In times of a southerly gale the breakers extend across this passage, and then it is extremely difficult and dangerous to go through. Many seamen have lost their lives in attempting to go through the passage at such times.
Immediately in front of the landing is a large fort, built of coral rock, yet not very formidable in its appearance. The black guns which peer over the dingy walls are of small calibre, and not capable of doing much execution.322 The site is a most excellent one, as the whole shipping lies within its range. It is guarded by a portion of the Hawaiian army, who look malicious enough, though not much like militia. They have very little of the air and appearance of soldiers.
The main or principal street runs nearly east and west, and on it are situated the public stores, and most of the residences of the foreign population. We found, also, a large and commodious hotel on the north side of this street, the front commanding a view of the shipping, and the sides and back surrounded by a beautiful grove, altogether one of the most beautiful and lovely spots imaginable. This hotel is frequented by captains and officers of the various ships in port.
On the first street in the rear of the one above mentioned stands a native church. It is under the direction of American missionaries. Rambling about in search of something new, we accidentally came to a “Seamen’s Reading-room,” in the basement of the Bethel Church. Here we found late papers from all parts of the Union, and were soon lost to every thing but them. As evening drew nigh, it warned us that we must depart, but with more of a home feeling than we had experienced for years. This reading-room is supported by voluntary contributions from seamen visiting Lahaina, and is under the direction and charge of Rev. Mr. Bishop, its founder. It is open from 8 A.M. to 5 P.M., and is situated in a delightfully cool and shady spot. It forms an excellent retreat from the scorching rays of the sun, and too much praise can not be awarded to Mr. B. for his kindness and liberality in establishing so useful and pleasant a place of resort for the sailor to pass his hours in instructive reading.
The form of government of the Sandwich Islands is too well known to need even a passing notice here. The king resides at Honolulu, which is the capital of the323 kingdom, but he has a palace in the eastern portion of this village, which is his residence while on this island, attending to matters of government. It is a large stone building, two stories, with a piazza at either end. It resembled a prison, we thought, more than a palace.
It is well known that the missionaries of the cross have been the humble instruments in the hands of God of doing much good at these islands. We were informed that nearly all the natives of influence throughout the kingdom had united with the Church of Christ, and were earnest in their efforts to promote the happiness and prosperity of the whole population. Yet many of them (the lower classes) cling to the superstitions of their ancestors, and, so long as they do, they must remain rude and ignorant. The climate appears to agree with foreign residents remarkably well. Although situated within the tropics, the northeast trade-winds, which almost constantly blow here, cool the atmosphere, and make it exceedingly genial and pleasant. Being situated nearly in the centre of the North Pacific, the temperature of the atmosphere is very regular, seldom varying more than five degrees for months; and we were informed by an old resident that he had not known the thermometer to vary ten degrees in years. It generally is about eighty in the shade.
Back from the village, upon a fine eminence, is a missionary settlement, called Lahainaluna, with schools for the education of the young. It is a beautiful location. In front may be seen the village of Lahaina and the shipping, with the island of Molokai in the distance; to the right, Wauhoo and Ranai present themselves to the eye of the beholder; on the left, Tahoorowa; and on a clear day the volcanic heights of Mount Roa, on the island of Owyhee, loom up in the far-off sky like a huge bank of black clouds threatening a tempest. Fresh breezes sweep down the gulleys of the mountains, laden with324 the perfumes of the orange, the banana, pine-apple, and mountain apple trees; the beautiful grounds laid out with taste: all these combined render Lahainaluna what its native name indicates—the Lovely Mountain Home.
The principal authority on the island of Maui (pronounced Mowee) is vested in a governor. He is assisted, however, by petty chiefs, or captains, who hold their office by his appointment. Subordinate to these are the kikos, or Kanaka policemen, who patrol the streets day and night. They are hated and despised by natives and foreigners, and frequently take advantage of Jack Tar by allowing him to do as he pleases for a time, and then, for some trifling breach of the laws, arresting him, and taking him to the calaboose or lock-up.
Seamen are obliged to be clear of the beach at drum-beat—eight o’clock in the evening. No person is allowed to remain on shore over night, unless furnished with a proper pass by the captain of the port; and any one found on the beach, or in the town, with no pass, after the proper time, is marched to the calaboose, where he is kept in confinement till morning, and then mulcted in a pretty round sum for breaking the laws. This is generally paid by the captain, and afterward, with pretty good interest, deducted from Jack’s pay.
Saturday is a holiday with all hands in Lahaina. Every body and their wives procure horses on that day, great numbers of which are found here, and pass the whole day in horseback riding. Go where you will, in whatever street you like, you will see a gay cavalcade of equestrians approaching, male and female. The latter dress in the gayest of gay calico, the “yaller” being the predominant color, and, seating themselves astride a horse in the same manner as the men, with six or eight feet of the calico swinging on each side, galloping through the streets, they present a rather novel appearance.
The Hawaiians appear to have queer ideas of justice. 325 What is crime when committed by a foreigner, can be done with impunity by a native. For instance: a native is allowed to gallop through the streets at the highest rate of speed to which he can urge his horse, while a foreigner must content himself with riding on a slow walk, except in the outskirts of town. We were witness to an occurrence of this kind one day. An officer belonging to one of the ships in port was mounted upon a fractious horse, and, while passing near the grand square, the animal became frightened, and commenced his antics, endeavoring to run. It was with difficulty that the rider was enabled to retain his seat; and several kikos, perceiving what was the matter, ran and caught the horse by the bridle, and ordered the officer to dismount, telling him he had broken the laws against fast riding, and must go to jail or calaboose. This he refused to do, but offered to give bail for his appearance before the police magistrate the next morning to answer to the charge. This was accordingly done; and on the trial the following morning, he was fined. Not a day passed while we were on shore that we did not see natives riding at a high rate of speed through the principal streets of Lahaina.
On Sunday morning, October 16th, the packet, with the mail from Honolulu, arrived. We hastened on shore, and were met by the captain, who reached forth a letter—the first in four years—which was immediately recognized by the superscription. It is useless to attempt describing our feelings. They who have been “in like circumstances” can understand them—no others can. As the boat was passing from shore to ship, thousands of thoughts rushed through our mind, coming one upon another like a hurricane. Break the seal there and then we durst not. No; we would wait till we got in some quiet corner on board, and there, undisturbed by any thing, first learn the good or bad news. We felt that326 during the long interval of four years many changes must necessarily have taken place; perhaps some of those we most loved had been taken away, and we would never more behold their face this side heaven. But we remembered that all things were in the hands of a good and wise God, and in Him we could trust. Arriving on board, we hastened to a quiet nook, and there, with trembling hand, broke the seal. What was our happiness to read “all are well,” and that the rover was not forgotten, but that prayers daily ascended to a Throne of Grace that he might be returned in safety to his home. We read and reread the precious words, and our heart went out in thanksgiving to that Almighty Power who had thus far brought us on our dangerous voyage. In the afternoon we attended Bethel, but fear that the sermon did not profit us much, as our thoughts would wander, in spite of us, to that home “far over the deep blue sea.”
The productions of these islands are similar to those of most tropical climes. Grapes are raised in great abundance and of a superior flavor. The wine made from them is said to be excellent, especially for medicinal purposes, in comparison with other wines. Melons of all descriptions are raised here in great abundance, and are not equaled, we think, by any raised on Yankee soil. The attention of the more enterprising natives and half-breeds has of late been turned to the cultivation of sugar and cotton, and we predict the time to be not far distant when they will be the staple productions of the islands.
While at Lahaina we formed the acquaintance of Captain M‘Culloch, then master of the clipper whaler “Niagara,” of Fairhaven. He related to us an incident in which he figured somewhat conspicuously, and we take the liberty of giving it here for the benefit of the reader. It will serve to show that the whaleman has dangers 327 with which to contend aside from those connected with killing the monster of the deep.
While the “Sharon,” of New Bedford, Captain Morris, was cruising near the King Mill Group, whales were raised, and the boats sent in pursuit. Captain M., two Kanakas, and a boy remained on board. For some time after the boats left the captain remained at masthead, watching the boats and whales. The boy then went to masthead, leaving the two natives on deck, and soon after the captain came down. He was immediately attacked by the natives, murdered, and his body cut in small pieces, and thrown to the hogs. On seeing this, the boy immediately went to work and cut all the running rigging, thereby disabling the ship, and preventing her from being run ashore, as the natives wished to do, being near to land. Those in the boats, seeing the condition of things, and rightly judging something to be wrong, immediately gave up the chase and returned. When within hailing distance, the natives cried out to them that, if they came on board, they were dead men, at the same time holding up to their view portions of the captain’s dead body. The boats retired a short distance to consult as to the best manner of retaking the ship. Mr. M‘C., at that time third officer of the vessel, offered to board her if six men would volunteer to accompany him; but, among twenty-four, none appeared willing to make the attempt. In justice to them, however, it is proper to state that it was more a want of presence of mind than of bravery that deterred them. He persuaded, advised, coaxed, and threatened, but all to no purpose. He then offered to go if one could be found willing to accompany him, but a panic appeared to have seized hold upon them, and not one would venture. Knowing that something must be done, and that speedily, he said, “It was as well to die on board the ship, fighting in her defense, as to fall into the hands of the328 natives on shore, and be butchered by them.” Divesting himself of his clothing, he took a large boat-knife, and, as it was nearly dark, plunged overboard, and cautiously swam for the stern of the vessel. This he reached undiscovered. Fortunately, a rope was towing over the stern, which he seized, and by almost superhuman efforts, succeeded in swinging himself into the cabin windows. Groping about, he found a pair of heavy horse-pistols, and, while examining one of them, accidentally dropped it. The natives heard the noise, and rushed into the cabin. Mr. M‘C. knocked the foremost one down with the remaining pistol; the other being armed with a cutlass, a fierce and savage fight ensued in the dark. It ended in the Kanaka being slain, Mr. M‘C. receiving a severe wound in the thigh. After having securely bound the one stunned by the blow from the pistol, he went on deck, and made signals for the boats to come alongside. It was some time, however, before they ventured to do so, as they thought that Mr. M‘C. was murdered, and the natives were endeavoring to allure them to a similar fate; but on hearing his well-known voice they immediately came on board. All sail was now made upon the ship, and she was soon clear of the land. The prisoner was handed over to the authorities of the next port they visited, tried, and executed for piracy on the high seas.
We accidentally learned that a fellow-townsman was lying sick at the hospital, and hastened to visit him. On arriving, we inquired for him, and were led to his bedside. It proved to be a Mr. Stoddard, who had, like ourself, been trying life in a whaler. He went one season in the “Arctic,” and, on his return to Lahaina, finding his health completely shattered, procured his discharge, and was placed in the hospital, there to die, away from home and friends. We found his case to be one demanding great sympathy. For one year had he been329 there with that deceitful disease, consumption. During this time he had heard no word from the loved ones at home, nor met with any one from that locality. How eagerly did he grasp our hands, and, although we had never been acquainted with each other at home, yet we felt like brothers. He said this meeting was to him the brightest spot of his life; that never before had he so longed to see any one from home as while he had been in the hospital. He was very pale and thin, and fast wasting away, yet very patient and resigned. Trusting in the blessed Jesus for a home beyond the grave, where shall be “no more sorrow, sickness, or death,” he cheerfully submitted to his sufferings, believing they would “work out for him a far more exceeding weight of glory.” He spoke of his physician, Dr. Dow, in terms of the highest praise; also of the Rev. Mr. Bishop—of the words of comfort and consolation he had poured into his wretched and distracted heart—of the feeling and beautiful manner in which he had pointed him to the “Lamb of God, which taketh away the sin of the world”—of his daily visits, always bringing consolation. Handing us a Bible, well worn, he said, “Take this book, and give it to my parents. Tell them that, although I shall never more see them on earth, yet I trust and pray that I may meet them in heaven. Tell them I die firm in the Christian faith; that I have gone to Jesus with my sins, and he has taken them all from me, and blessed me; that my whole trust is in Him; that my peace is made with God, and I long to be released from this world of sin and death to dwell with Jesus evermore.” His voice appeared to fail him; and, as we extended to him our hand, with tearful eyes, we felt that we were clasping his for the last time. As we turned to depart, our ears caught these words issuing from his lips:
330
We bade him farewell, and returned to the ship with a sad and heavy heart. We felt to thank God that we were yet in health and strength, and to ask Him to return us to our friends at home safely. On reaching the hospital the following morning, we found that Stoddard had peacefully departed during the preceding night. He “fell sweetly asleep in Jesus.”
Much has been written and said about the shark, and, to speak plainly, many falsehoods told. It has become a common idea that all sharks will devour a man as soon as look at him, if they get a chance; but a more delusive one was never entertained. Of the many different varieties of sharks, there are but two that will attack a man in the water. These are the blue shark, and the ground, or shovel-nosed shark. No more danger need be apprehended from the common brown shark than from a porpoise. We have often seen a Kanaka jump overboard in a perfectly calm day, and swim after them with a sheath-knife, endeavoring to stab them, but Johnny Shark would keep out of his reach. And whenever we had a whale alongside, the sharks would be around in great numbers, and yet never touch the boat-steerer, who was overboard on the whale. But of the blue and ground sharks, the farther one keeps from them the better for his safety. On the night of Sunday, October 23d, one of the officers of the “South Boston,” while walking the deck, made a misstep and fell overboard. Hearing the splash, some of the crew jumped into the boat alongside, and hauled under the stern, where the man had fallen; but no sign or trace was to be seen of him. He was an excellent swimmer, but, in all probability, was seized by one of the numerous ground-sharks that prowl round the shipping in port. The water in Lahaina is very clear, the bottom being distinctly visible at the depth of twenty fathoms, or one hundred and twenty feet; and, although every search was made the331 next morning at daylight, the body could nowhere be found. No doubt now remained but he had fallen a victim to the rapacity of the voracious ground-shark.
On the afternoon of this Sabbath we attended service in the Kanaka church. It was filled with natives of both sexes, intermingled with whites, of whom here and there might be seen one. The interior of the church is fashioned similar to our American ones—very tasty and neat, without being gaudy. In the morning the sermon is delivered in the native tongue; in the afternoon, in English.
The natives of these islands, like all others who have been visited by Europeans, have suffered from the dreadful ravages of diseases brought by the latter. During our stay at Lahaina, the small-pox raged with great violence there and at Honolulu. Hundreds of the natives were swept off, and, what appeared very singular, scarcely a white man was attacked, and none died from it, although hundreds of seamen were daily exposed.
In the following chapter we give a “legend,” as related to us by an old native whose acquaintance we formed, probably the “oldest inhabitant;” and then, with the reader, we will be “homeward bound.”
A heavy gloom was upon the minds of the people of Wauhoo in consequence of the recent death of their king, Hoapili. Melancholy filled their hearts; wailings and lamentations of various kinds were heard over all parts of the island. Every grade mourned for the regal victim of death; and men, women, and children were seen tearing their hair, wounding themselves with sharp-pointed weapons, tearing their flesh with sharks’ teeth, and breaking their own front teeth with stones, to convince each other of the acuteness of their sorrows; and, above all, they prepared, as was their usual custom on such events, to offer up to the Great Spirit five human beings as a sacrifice. Many a loving maiden, when she heard of the king’s death, felt a pang rush through her heart and a whirling through her brain as she thought of the youth who had won her affections.
On such occasions, it was customary for the eric, or chief of each district, to select a young man from that part of the country over which he had control, and to send him to the proper place as one of the victims to be immolated at the shrine of the deceased king. Thus there was a dreadful uncertainty in the minds of the whole people until the unfortunates were chosen; and there was no appeal from the will of the eric; so that, when the summons was made, there remained no hope for the unhappy chosen one.
In the village of Waikukii, of which Nahi was the eric, or chieftain, lived Tuanoa, a young man, and Kinau, his betrothed bride. They had resided near each333 other from their infancy, and, even in the early dawning of the mind and the affections, they were observed constantly together; and no doubt, at that time, there was interwoven with their young heartstrings the tender passion of love, that “grew with their growth and strengthened with their strength.” Tuanoa was a fine young man, much beloved by his neighbors. He was active and brave in the extreme, and he had performed many acts of prowess, which gave him a standing-place within the circle of the conquerors at a feast, or “hoola hoola;” and he was, withal, of a most kind and affectionate disposition, of which his friends and neighbors were well aware. Kinau, his beloved maiden, was the most beautiful girl in the village, and of good family and estate; besides which, she was the most esteemed tappa-maker in the whole island. None of her competitors could approach her genius, which was so frequently displayed in designing figures and ornaments to adorn her productions, so that her tappas (native cloths) exceeded in beauty and strength those of all others, and they were worn by the king and queen. Her disposition was of that rare and delightful description which finds pleasure in searching after the sorrows of others in order to relieve them, and blessing itself that it had the power to do so. With such a person, disposition, and possessions, we can not wonder that Kinau was much beloved, and that Tuanoa was so much envied by the spirited young men of the village. But they enjoyed no hope of gaining the object of their admiration, for she took every opportunity of expressing her undying love for Tuanoa, and he to her.
Notwithstanding all this, there had been an eye fixed long and ardently upon Kinau, and she was well aware of the fact, much to her sorrow; and many a burning tear, as it rolled over her beautiful cheek, awakened in Tuanoa’s breast a powerful feeling of regret, mingled334 with surprise at the unhappy change which had come over the mind of his beloved. How often did he entreat, in tenderest words, for the avowal of the cause, which never was fully given. Kinau full well knew that if Tuanoa were to be made aware of the fact, he would commit some rash act that would most probably hurl them both to destruction; and she left the whole to chance, hoping that soon a day would come when the dark cloud of anticipated misfortune would be dispelled, and the sunshine of her love again break forth strong and clear.
It was the eye of the powerful eric Nahi which had fallen on Kinau, and he had even sought a private interview with her, and declared his love; but she resolutely refused to listen to his advances a moment. “What!” said the haughty eric, “do you refuse to listen to the voice of Nahi, your chief? Daughter of my neighbor, tremble! Let tears as salt as the waters of the ocean fall quick and fast from thy earth-bound eye! Refuse to listen to the voice of Nahi, and the volcano of Waikukii shall consume the blood of Tuanoa, as the shark of the ocean devours the newly-hatched turtle.”
“Oh great Nahi,” answered Kinau, “suffer your neighbor’s daughter to return the love of Tuanoa, whose love, like mine, burns as the fire of the volcano, which the waters of the ocean can not quench.”
“Tremble!” exclaimed the eric, “daughter of Kuakini, and the beloved of Tuanoa. Go from the presence of Nahi, and let there be no more said.”
Kinau went from his presence with trembling limbs and a palpitating heart. She knew the disposition of Nahi; cruel and vindictive in the extreme, he spared nothing to obtain the object of his wishes. He had committed many crimes, for which he had often been reproved by the late king and his fellow erics. The people, also, were disgusted with his tyrannical conduct, and335 these things combined caused him to be more careful than he had been in the earlier part of his government. Kinau was well aware of this, and she therefore trusted that he would cease his importunities; but she dreaded his revenge, as she well knew that if an opportunity should ever present itself whereby he might injure her or Tuanoa, and escape the observation of the people from the apparent injustice of the act, he would seize upon it with avidity; and this was the cause of her dejection.
The king, Hoapili, had been dangerously ill for some days, and the active mind of Kinau saw the dreadful chasm which might be opened to receive her in the event of the king’s death. She knew that Nahi had the power of choosing one of the victims for the sacrifice, and the thought almost bereft her of her senses. She well knew that Tuanoa, the brave and beloved Tuanoa, would be sacrificed to the revenge of the cruel eric; and, under these trying circumstances, the constitution of Kinau evidently began to decline, much to the grief of her lover, who perceived his beautiful companion, like a lovely flower beset by the canker-worm, silently robbed of her beauty. He saw the devastation it committed, but could not discover its retreat. Kinau still kept the secret within her own breast.
One evening, as, to their minds, the sun was once more going to rest in the deep bosom of the ocean, the lovers reclined on the shelving and moss-covered rocks which were near to the habitation of Kinau, in the beautiful valley of Menoa. The broad-leaved banana waved around them, and fanned their cheeks with the sweet-scented evening air, when, just as the Pelé of Nuanu cast its deep shadow across the valley of her fathers, a distant cry of sorrow fell upon the ears of the unhappy pair. To Kinau’s mind the cause was revealed in an instant. “The king is gone!” shrieked the unhappy maid. “Oh, Tuanoa, 336 let us fly; let us bury ourselves in the depths of the ocean, for death is for us also!” The extreme agitation of her mind robbed her of her senses; and as she lay, apparently without life, in the arms of her beloved and thunder-stricken Tuanoa, a number of their friends quickly approached the scene to render assistance, and to inquire the cause of the outcry.
“Neighbors,” exclaimed the bewildered Tuanoa, “my peace is broken; my beloved is no longer herself; the spirit of darkness has been here and stolen the light of her soul!” While they were using means to restore Kinau to her senses and to comfort Tuanoa, a band of persons approached, and proclaimed, amid loud wailings, that Hoapili the Good had given his last breath to the winds; and from out this mass of phrensied human beings rushed three men, with disordered dress and disheveled hair, with red streams of blood gushing from self-inflicted wounds, and approached Tuanoa. They immediately produced from under their torn tappas the fatal summons from the eric Nahi, which consisted merely of three dark-colored poisonous nuts, delineated with certain inscriptions and figures. Too well the brave Tuanoa knew their import, but he was helpless before them. They presented them to him with certain forms and ceremonies, and then, as if impatient for his heart’s best blood, leaped upon and bound him securely. Astonishment filled the minds of all his neighbors, who stood around Kinau, their hearts ready to burst with grief. They knew not the revengeful feelings which had actuated the hated eric to the choice of the best person in the village instead of the worst, as was the usual custom; for there was even a by-word among them, which was addressed to persons of bad repute, “Ah! you will serve for the fire—you will serve for the fire,” meaning that they would serve for the purpose for which Tuanoa had been taken. When the sounds of the phrensied multitude337 had passed away, and had left the valley of Menoa again to its solemn quietude, and there was only heard at intervals from out the group which still surrounded the bereft and senseless maiden the low murmur or the sorrowful exclamation for the departed king and the sorrows of the divided lovers, Kinau opened her discolored eyes, and shot them around the group, but saw not Tuanoa.
“Ah!” she exclaimed, “half of my soul has expired. Friends and neighbors, go; stay not with Kinau; the sun no longer shines upon her tarro-patches;[6] the water of the mountain has also turned from their roots, and has fallen into the hands of Nahi.”
Her kind neighbors did all in their power to comfort her in her great affliction, and then left her to the care of her aged parents. Nature soon overcame the infirm pair with sleep, and Kinau left her home, never more to return except with her beloved Tuanoa.
The past few months had altered the lovely Kinau very much. Her features were shrunken and distorted; her hair torn and loose; her dark eyes, rolling and flashing, betokened the storm within; her heaving bosom gave proof of the agitated heart; but her step was firm, and she stood erect, as if, with the last effort of a shattered frame, she had determined to devote all her remaining strength to one great purpose. She was convinced that there remained no hope from human means for the restoration of her beloved Tuanoa, and she therefore determined to visit the enchanter Kelkuewa, a thing seldom or scarcely ever attempted before, even by the bravest of the erics. But Kinau, feeling strong in her virtuous cause, feared not, and dared destruction in its wildest forms. Kelkuewa, the enchanter, resided in a glen at the bottom of the Pelé of Nuanu, and near the 338 entrance of which the enchanted waterfall of two thousand feet in descent finished its perpendicular career. Here was the supposed habitation of a lizard as large as a man, which the tradition of the islanders claims as having resided there since the Flood.
Kinau, with firm determination, commenced her task. Passing alone, away from her friends and neighbors, over the dark plains in the valley of Menoa, she soon began to ascend the steep and rugged mountain of Nuanu, and, after excessive exertion, reached its summit. She cast her wild eyes around, and saw the dark ocean which encompasses Wauhoo; she could hear its distant roar as it broke with violence on the weather side of the island; the chilly and unruly blast of the night-wind almost forced her slender figure from the pointed rock on which she, for a moment, rested; her loose hair lashed her burning forehead with its violence. Behind her was the valley of Menoa, in which she had met the last look of her beloved Tuanoa; before her was the valley of Nuanu, four thousand feet in depth. Midway dashing its white foam, she could just observe the enchanted stream gushing out of a small division in the rocks, and falling two thousand feet into the valley below, at the bottom of which the enchanter resided. Still determined to visit him or die in the attempt, she began the fearful descent of the Pelé of Nuanu, and after great difficulties—now clinging to the branches of some friendly tree, and now sliding in various positions—she succeeded in reaching the source of the waterfall. Almost overcome with fatigue and contending emotions, she here rested. A torrent of tears relieved her aching heart, and she again commenced the arduous task of descending, by the side of the foaming stream, over slippery rocks and sharp craggy points, her feet torn and bleeding, her heart almost broken, and her weary frame nearly exhausted. Her disordered imagination, blinded by339 her tears, saw visions of darkness and despair hanging from every rock; and the murmuring of the trees, as they were moved by the wind, appeared like the voices of her foes imploring for her destruction. But still Kinau wended her way—yes, the tender yet powerful passion of love supported her—the passion of love in woman, invincible love, which has caused the “change of empires and the loss of worlds,” has “inspired heroism and subdued avarice.” She succeeded in reaching the glen, where she bathed her bleeding feet for a moment in the waters of the cascade. The moon, which had before been hidden behind dark clouds, now peeped through an opening in them, as if anxious to look upon the devoted girl and admire her fortitude. The large gray owl, which inhabits the valleys, flapped his broad wings over her head as he moused among the rocks; and the quick-flying bat darted in and out of his caves, as if disturbed by the intruder. Lifting up her eyes, Kinau beheld a tall old man descending the Pelé. Quickly he took advantage of each jutting point of rock to secure his footsteps, and he descended with apparent ease to the spot where Kinau rested. Long gray hair fell over his shoulders, and he thus addressed the maiden:
“Daughter of Kuakini, and the beloved of Tuanoa, I am he whom you seek. I have followed you from the valley of Menoa; I have watched and feel astonished at your strength, fortitude, and love. I know the spirit of darkness has come over you when the gladness of your heart was taken from you. Your love for the brave Tuanoa is like the mountain of Nuanu, fixed forever, and can not change; it is clear and bright as the water that falls from the Pelé; it is like the fire of the volcano of Waikukii, which is unquenchable. Daughter of Kuakini, arise! go to the valley of thy fathers, and rest in the bosom of thy neighbors; for I have seen a Great Spirit, who, before to-morrow’s sun reacheth the valley340 of Nuanu, shall come and save thy Tuanoa from the blood-consuming fire.”
“Oh great Kelkuewa,” said Kinau, “your words are like water to the parched tarro; they are like the waters of the ocean to the expiring fish, which the fisherman returns to its element. I feel my heart lightened; the cold hand of the spirit of darkness has moved from my heart. Oh Kelkuewa,” continued the enraptured girl, “they say you have no daughter. I will be your daughter; I will make your tappas; I will water your tarro-patches, though I bring the water from the other side of the mountain of Nuanu.” The enchanter seized the hand of Kinau, assisted her over the Pelé, and saw her descend to the valley of her fathers.
The morn of the day on which the tragedy was to be ended appeared. Before the sun had risen, thousands of the islanders were moving toward the plains of Whyteetee, on which the immolation of the victims was to take place. Lamentations were heard over the whole island. The plains of Whyteetee were soon covered with countless multitudes, and five immense fires were lighted. As the sun rose, the odor from the burning sandal-wood perfumed the whole of Wauhoo. In an inclosure about one hundred feet long and fifty from front to back, the front wall of which was about six feet high, and the back about twelve, formed of loose stones or masses of lava piled upon each other, and situated upon a rise of ground at the end of the plain, facing the sea, the five victims were placed.
On a mass of rocks about one hundred feet high, which rise abruptly out of the plains, and command a view for a considerable distance around, sat the princes and chiefs, with all the great men of the island. Among them Nahi was observed in a conspicuous situation, watching the proceedings with great earnestness, for he had heard that Kinau had visited the enchanted glen, and he had heard 341 also of the prophecy of Kelkuewa. Indeed, it was upon the lips of every one, and many hoped that the prophecy would be fulfilled. The more noble of the erics and people began to look upon these cruel exhibitions with disgust, and to long for a pretext for abolishing them. They saw the abuse, if we may so call it, to which it was liable, from the base conduct of Nahi, and yet, being a national custom, it was hard to abolish.
The proceedings of the assembly soon commenced. The first victim, who happened to be an abandoned wretch, was led out of the inclosure by the priests, and thrust among the multitude. There were plenty of the wild and infuriated to commence the attack, by hurling stones and beating the unfortunate victim with any weapon with which they might have provided themselves for the occasion, and he was hunted to and fro like a wild beast, until the spark of life was nearly extinct; then he was hurled upon the funeral pile, amid the wild exclamations of the savage throng, while “liquid fire curled round his limbs, and to his hissing bones and marrow clung.”
Kinau, surrounded by her kindred, was seen in an agitated state, frequently looking toward the Pelé of Nuanu, and wondering how the Great Spirit would interpose to save her beloved Tuanoa. Sometimes, full of hope, her countenance would brighten, and she appeared to possess new life; then again she would doubt the enchanter’s successful interference, and her spirits would sink. Thus was her gentle bosom torn with a thousand conflicting emotions. Despair for a moment shadowed her invincible spirit with his dark and death-hovering wings, and the beloved Kinau felt that she would willingly sacrifice her own life to save that of her lover. Tuanoa observed his adored girl with those acute feelings which the pencil can not paint nor the pen justly describe. He was bound to the insensate stake, which342 heard not the heart’s flutter or the despairing sigh—which felt not the tremulous shake of the confined but powerful limb that strove in vain to break from its moveless grasp. At last, despairing, he hung from his confinement, apparently a lifeless being.
Another unfortunate but criminal victim was now given to the infuriated multitude and sacrificed; and the next was to be Tuanoa, the beloved and innocent Tuanoa, who was insensible now from the mental anguish he had suffered. To die so young, and such a horrid death—to go and leave his Kinau behind—this was more than he could bear, and he fainted from misery. The brave maiden could no longer bear this uncertainty. She rushed through the crowd of her kindred—scaled the walls of the inclosure—glided between the guards with a supernatural quickness, and encircled with her devoted arms her beloved. But the guards and the priests quickly proceeded to separate them; and now they unbound, and were about to thrust the bewildered Tuanoa among the savage group who thirsted for his blood. The gate of the inclosure was thrown open; already the savage hand was raised to smite with deadly violence; already the maddened and phrensied eyes of fanatic men were gleaming with murderous excitement to grace the royal death; the impatient, loyal crowd, heap upon heap, swayed to and fro in their eagerness to slay one of themselves—one, too, who had been formerly beloved by them, and for whom they would have made great sacrifices, but now hated and condemned; and they impatiently thirsted for his blood.
But the enchanter at this moment appeared among the people. In a loud voice he commanded their attention, and pointed to an object which was seen upon the ocean at a great distance. All eyes were instantly directed, in great wonder, toward it. During the confusion, a stone was hurled by an unseen hand, which struck343 Nahi, and killed him in an instant; but the event scarcely received attention. The object to which the enchanter still pointed approached the island rapidly. It appeared larger every moment, and in a short time its color was distinguishable. Fear and curiosity increased, for never had the people witnessed such a sight before. At times it appeared of an immense breadth, with wide-spreading wings, and in a moment or two would appear quite narrow, but of great height. Occasionally its apparent wings shook; then anon the whole mass appeared to stoop to the surface of the ocean. Swayed by an irresistible impulse, princes, erics, and people went down to the edge of the sea. The liberated victims, surrounded by their kindred, followed. The prophecy was fulfilled. They were liberated by common consent. Never can poet or painter describe or represent the two enraptured lovers, as they appeared walking together on the beach, having but “one soul in a divided body.”
Reader! the “Great Spirit” which so rapidly approached, and was bringing to those islanders light to disperse their darkness, humanity and religion to abolish their cruelties, the arts and sciences to banish their ignorance, was the great spirit of the immortal navigator Cook, who had just discovered those fertile islands, and whose ship had been observed by the enchanter on the previous evening from the heights of the Pelé of Nuanu.
To the reader who has followed us through the wanderings of more than four years, we tender our thanks, and beg his indulgence through our “homeward bound” passage, where we will take leave of him, with the kindest wishes for his prosperity and happiness.
On Monday, October 31st, we commenced our preparations for sea. All were anxiously longing for the time to come when we should see the ship’s head pointed toward home.
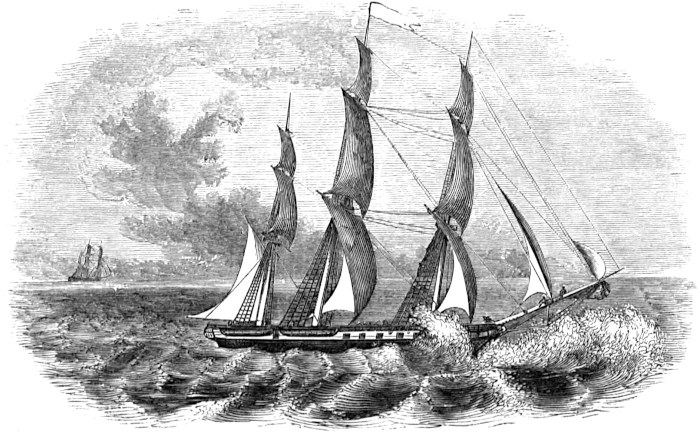
347
We had discharged several men who shipped with us at different times during the voyage “for the last port,” and it became necessary to procure more for “the passage home.” These were now all on board, and we only waited the arrival of the captain and lady to take up our anchor, loose our sails, and be under way. The day came. Tuesday, November 1st, the joyful command was given to “heave away.” The old windlass brakes rattled merrily, and
rang out in full clear chorus from every voice on board, till the hills and mountains of Maui echoed back the sound. We could see the faces of our brother whalemen around us as they looked, no doubt, enviously at our craft, thinking of the long season yet on the “nor’west” to be gone through before they could sing as we did. But we felt that we had a right to be happy. For more than four long and weary years had the ship been our floating home. We had labored, toiled incessantly, in storm and in calm—in the boats and on board ship—beneath the scorching heat of the tropical sun, and the freezing cold of rigid climes—been exposed to all dangers both on sea and land—and now, we hoped, we were going home to enjoy the fruit of our hard-earned savings. Going home! None but they who have been separated from near and dear friends, as we had been, for years, can fully realize the joy which these words produced.
The ponderous anchor was soon raised from its coral bed and snugly stowed away upon the bows; all sail was set, and we gladly left the anchorage of Lahaina with strong northeast trades. We shaped our course west-northwest for the island of Atoowi. The following day we passed to the southward of Wauhoo, which was plainly in sight, and “stood off and on” Atoowi. We procured several boat-loads of sweet potatoes, yams, and other recruits, and then shaped our course for the Society Islands. About an hour after leaving Atoowi a stranger made his appearance on deck. This took the captain rather by surprise, and he inquired of him “who he was and whence he came.” The man replied that “he belonged to the ‘——,’ and did not wish to try another season in the Arctic, and did want to get home; was willing to work his passage, and hoped the captain would allow him to go home in the ship.” After giving him a long lecture upon the evils of desertion, the old man consented that he should remain, and he went forward with a happy heart.
On Friday, November 11th, we spoke the “Uncas,” 348 of New Bedford, Captain James, like ourselves, bound home. We had a very pleasant “gam” with them, talking of the pleasures we were to enjoy, and anticipating with them great happiness. Our captain threw down the gauntlet to Captain J. for a race to New Bedford, which he gallantly accepted, and, we must confess, as gallantly won.
Nothing of great interest to us occurred, except crossing the equator for the last time in the Pacific, until we reached the Societies. We felt, at the time we crossed the line, that another goal was reached and passed—that another “milestone” in our journey was gone by. We sighted the island of Whytootucke, one of the Society Islands, on Friday, December 9th. We passed it, and on the following day raised Roratongo, distant fifty miles. Language is inadequate to describe the feeling of our Kanakas at once more seeing “my land,” as they called it. They were half frantic with joy. But when boat-loads of the natives came off to us the next day (having “beat” up to the island during the night), and they found their own relatives among them, we actually thought they would become crazy. We can not describe the scene. We can only give the reader an idea of their mode of salutation, which is to grasp each other by the right hand, place the other over the back, and rub noses very affectionately! With all our pathetic feeling, we could but laugh at the ludicrous method. But this meeting almost brought tears to our eyes as we thought of those whom we soon hoped to meet.
On Monday, December 12th, the boats went ashore to bring off fruit. Wishing to have one more run on one of “the Pacific Isles,” we jumped into one of the boats, and were soon on shore. On inquiry, we learned that the missionary who was there at our former visit had been recalled, and that Rev. Mr. Buyacott, from England, who had been stationed there many years before,349 was again among them. The natives appeared greatly attached to him; and we must relate a simple incident of this attachment. They had received information of his coming, and when the boat arrived which brought him from the ship to the shore, it was instantly seized by the natives ere he had time to land, and triumphantly borne, with great rejoicings, upon their shoulders to the market-place, where he was received by the authorities and his old friends with a warmth of feeling that bespoke how universally he was beloved, and how rejoiced all were to see him returned to them again.
They had lately erected a fine church edifice under his supervision, which was certainly a credit to him as an architect, and to the islanders. Great preparations were making for its dedication, which was to take place in a few weeks. Under his care and example, the natives appeared cheerful and happy; their little farms well tilled, and themselves well dressed, neat, and contented. All united in saying that Mr. Buyacott was a most excellent man; and the interest he manifested in them, both temporally and spiritually, went far to prove it. Under his supervision we found a printing-office in operation, where tracts, papers, and hymns were printed in the native language, and distributed, not only in Roratongo, but in every island of the group. We found also blacksmiths, carpenters, shoemakers, and nearly all kinds of mechanics, who had received their knowledge from him. His residence was a fine stone house of two stories, situated on a gentle rise of ground, surrounded by a beautiful yard interspersed with shrubbery and flowers. A fine graveled walk led from the gate to the house. We found it a cool, shady retreat, refreshed by the sea-breeze, and shaded by beautiful orange groves.
But it was time for us to leave all this beauty of nature behind, and plow our way homeward. We discharged all our Kanakas save one, who wished to remain350 in the ship and go to America. On asking him what particular reason he had for wishing to see “’Merick,” as he termed it, he replied, “I like see all; and get my sister three fathom (six yards) red ribbon!” We thought him going a long distance for “three fathom red ribbon,” but, as he said “plenty time,” we gave up the argument.
We here shipped three white men who were anxious to go to America, and, having loaded the old ship with tropical fruit for the last time, we bade our Kanaka friends adieu, and were soon on our way home again, steering to the southward for a westerly wind that would send us to the coast.
On Friday, December 16th, we commenced our preparations for doubling the Cape. First, we gave the old ship a new suit of sails throughout, from flying jib to spanker, good and strong ones, that would stand many a heavy storm. Anchors were taken in on deck; also the bow and waist boats, and every thing made snug generally. This was rendered necessary also from the fact that we had commenced leaking so much as to require pumping every four hours; and, these precautions taken, we knew that she would not strain so much in heavy weather.
Sunday, December 25th, was Christmas with us as well as with those at home. And, although we had no visits from Santa Claus, we felt very happy, and knew that when another Christmas-day came round, if living, we should be enjoying it with loved ones at home. The best on board ship was served up for dinner, and all hands enjoyed it with a keen relish, sharpened by the anticipation of the good things yet to come. We were now about eighty degrees to the westward, and twenty to the northward of Cape Horn.
From this time until Tuesday, January 24th, we bowled it along merrily with a southwest wind, every thing351 set that would draw, and every hour lessening the distance between us and the Cape. On that day the gale increased to almost a hurricane, and hauled to the west. We were “scudding” before it, with close-reefed topsails, a heavy sea running, and threatening to ingulf us every moment. The wind increasing and sea still rising, it was deemed prudent to “heave-to.” This was a dangerous proceeding in such a gale, but, with careful management at the helm, it could be done. All hands were called, and placed at their stations. The second and third officers took the helm, the men stationed at the braces, and the ship’s head slowly brought to the wind. She gallantly came up; but a wave—an avalanche of water—struck her on the quarter, dashed in on deck, sweeping every thing before it. “Hold on for your lives!” was the cry from the captain’s lips, and each man grasped the rigging, expecting every moment to be swept overboard. It was a fearful moment. The brave men at the helm were up to their waists in water, but bravely they clung to the wheel, knowing that if they left it death and destruction awaited us all. The body of water on deck was immense, being filled to the rail; and as the noble old ship would roll fearfully from side to side, it would seem as if she never would recover herself. By dint of great exertion, boards were knocked off the bulwarks, and the water began to pour out. This rendered her laboring more easy, and she was soon “luffed-to,” and rode comparatively easy. We all breathed more freely when this was done, and felt that we had had a narrow escape.
As we remained on deck watching the scene, we could not but contemplate its grandeur. As the ship would rise on the top of a gigantic wave, it seemed as if we were placed on the summit of a high mountain, with a yawning gulf at our feet, into which the ship would rapidly plunge as if she would bury herself. A feeling of 352 awe and terror would involuntarily creep over us as she alternately rose to the crest of the mountain waves, and again plunged downward with fearful velocity, as if every plunge would be her last.
As soon as the gale moderated sufficiently sail was again made, and the noble old craft plowed her way onward through the briny wave, bearing her freight of humanity nearer, nearer to that home they so longed to see, and to those friends whose embrace they so longed to clasp. By our reckoning we now found ourselves “off Cape Horn,” and, with a fair wind, hoped soon to leave the Pacific far behind us.
The weather now became very cold, and our Portuguese and Kanaka found some rather tough experiences of it. In fact, they were about froze up. Amo, the Kanaka, would come on deck, and, the cold soon taking hold, exclaim, “What for all the same? Ah! too much bite you no see ’em! What make all the same this?” On asking him if he ever saw cold weather before, he replied, “Golly! no. I no been see all same this my land. Cape Horn, he no good.” He constantly wore three or four coats, and, in fact, all the clothes he could get on. It appeared almost impossible that the cold should penetrate so many thicknesses, yet he complained that it did. Manuel and Amo both came on deck one morning, and found it covered with snow. We never saw two persons more astonished than they. They made all sorts of inquiries, asking where it came from, what it was for, and questions innumerable. Seeing some of the men engaged in snowballing, they thought they would “take a hand,” especially as they occasionally received a quantity in the face. On picking it up, however, and attempting to pack it, they very soon let it fall, exclaiming, “Golly! he hot all the same fire!” and ran off, slapping their hands together, and blowing their fingers.
By our reckoning we found that on Thursday, January353 26th, we had fairly passed Cape Horn, and were once more in the Atlantic. When this fact was announced, a feeling of great joy seemed to pervade the whole ship. We had all dreaded the passage round, and, now that it was passed, all felt a great relief. And we felt that we were so much nearer home. In fact, it appeared as though we were almost home; and as we had before counted the months, and then the weeks that would elapse ere we should tread our native soil, we felt that we could now begin to count the days.
On Saturday, February 3d, we spoke the “Betsey Williams,” of New London, Captain Pendleton. She was, like ourselves, homeward bound, with a full cargo of whale oil. We passed a very pleasant day with them, and at evening wished each other a safe and speedy passage, and parted company.
We had the usual amount of calms and head winds, which brought out the usual quantity of grumbling from all hands, until we sighted the Brazilian coast. We then took a southeast wind, which merrily bowled us onward toward the line, which we were soon to cross for the last time. And cross it we did on Friday, March 10th, but with far different feelings than when we crossed it the first time, nearly five years previous. Then we felt the future to be all uncertainty; now we looked forward to the happy time when we should meet those we so much longed to see. Then we had the prospect of four years’ absence from our native land; now we felt that that time had passed away, and we were soon to reap the fruit of our labor. At evening all hands gathered upon the forecastle, spinning yarns, singing songs, etc., in joyful anticipation, and, with three hearty cheers for “Yankee land,” adjourned.
It was now time for us to begin to paint ship, slick up things generally, and make every thing “shipshape and Bristol fashion.” This must be done in pleasant tropical354 weather, and we soon had a new coat on the old ship, making her look “e’enamost as good as new.” We were on the watch for outward-bound vessels, as we wished to obtain late news from home, and naturally felt anxious to know what was going on, and news of any kind was welcome. On Saturday, March 25th, we spoke the brig “Alpha,” of Halifax, and sent a boat on board to obtain, if possible, some news, and a few vegetables of some kind, as ours had long since, to use a somewhat homely expression, “gi’n out.” The boat soon returned, however, with neither, and we bid our Blue-nose friends good-by, and went on our way.
As we stated in a previous chapter, we obtained our last whales on Japan. It is customary for whalers to man mastheads during the passage home as well as on cruising-grounds, although not as vigilant a watch, we think, is kept. The try-works, also, are kept standing until they arrive near Bermuda. On Saturday, April 1st, the order was given, “Overboard try-works,” and at it we went with a will. Bricks and mortar soon flew into the ocean, and the large try-pots were released from their places and lashed to the deck. “No more whales this voyage,” cried the mate, as the last brick disappeared over the side. Yet we felt a regret at this too, for we would have loved the excitement, just then, of fastening to an eighty barreler, and having a nice run. But it was not to be, and we were not very sorry.
All seamen know the weather which is most common “off the Bermudas.” We had our share of the gales so prevalent there. From this time for a week or more, we experienced all sorts of weather and winds. One day a fair wind, and the next “dead ahead,” as seamen term it, blowing a gale.

357
At last we took a breeze from the southwest, which increased to a heavy gale, but held on until we entered the Gulf Stream. This we knew by the temperature of the water, which is there always blood-warm. On Saturday, April 8th, we ascertained that we were to the northward of the Gulf Stream, and on soundings, the water being a bright green color.
On Monday, April 10th, all hands were ordered to “bend the cables.” It is unnecessary to say that we rejoiced greatly at this order. The chains were dragged from their resting-place in the hold in double-quick time, and every thing got ready for “letting go” the anchor on soil that had not been touched by it for nearly five years. Although not yet in sight of land, we all were anxious, excited, nervous. If the reader asks why, we reply we had been years separated from our native land, and were now returning to it.
The morning of Tuesday, April 11th, broke upon us thick, rainy, cold, and disagreeable. As the fog gradually rose, we discovered around and about us on every side a great number of vessels, probably a majority of them coasters. Bringing the old gun to the gangway, we fired it several times, in hopes it would bring us a pilot. The effort was successful. In a short time, the New Bedford pilot-boat “George Steers” ran alongside, and furnished us with an old gray-headed veteran, a regular old sea-dog, to take charge of the ship, and bring her to an anchor off New Bedford. It is useless to attempt describing the joy, the enthusiasm of all hands, now that the long-looked-for moment had come when “old Hard-a-lee” should put his foot on deck. And when he informed us that he intended to have the ship at anchor in New Bedford harbor at 10 P.M. that night, one simultaneous shout arose, and every man sprang to his post.
We never heard that the adage “There’s many a slip ’twixt the cup and the lip” failed because it is old, and we realized it during that night and the following day. Instead of being in the city of New Bedford, as we anticipated,358 we found ourselves, on the following morning, in the midst of as severe a gale as we had experienced during the voyage. A short time after the sun went down, the wind rose from the northeast, and we were soon stripped to the bare poles. Add to this furious storms of hail and snow pelting us continually, and one can judge of our situation. The gale continued during the whole of Wednesday and Wednesday night, furious as a hurricane, and directly in our teeth. This was tantalizing; but bear it we must, and wait for a fair wind.
The next morning, about eight o’clock, the wind moderated and hauled to the south. It was not many minutes before every stitch of canvas that would draw was set, and we were rapidly approaching the land. Block Island hove in sight, then Montauk Point, and thus one point of land after another rose to view. “That ’Merick?” exclaimed Amo, the Kanaka, as the land loomed up in the distance. “Yes,” we replied, with a feeling of joy and pride, “yes, that is America!”
Bright and beautiful shone the full moon as we sailed up Buzzard’s Bay that evening, steering for Clarke’s Point. Sail was gradually reduced, and furled for the last time. At midnight we dropped anchor off the point, about two miles below the city, and when it struck the bottom, three hearty, enthusiastic cheers were given, that made the welkin ring. The remaining sails were soon furled, and we started for the shore, where we found our friends waiting to receive us with open arms. We breathed a prayer of gratitude to Almighty God, who had spared and shielded us through all the vicissitudes and dangers to which we had been exposed, and permitted us to return in safety to our native land.

361
And what shall we say in conclusion? We thank the reader who has followed us through the wanderings of five years, and, if he has been instructed or amused, we are content. As is remarked in the Preface, we have told our “yarn” in a plain, unvarnished style, laying no claim to literary merit, or wishing to be considered an author, but merely seeking to lay before the public a truthful statement of what we saw. With this conclusion, we wish all our readers long life and happiness, and bid them an affectionate farewell.
His living and truthful picture of events.—Quarterly Review (London), Jan., 1861.
Fertile as the present age has been in historical works of the highest merit, none of them can be ranked above these volumes in the grand qualities of interest, accuracy, and truth.—Edinburgh Quarterly Review, Jan, 1861.
This noble work.—Westminster Review (London).
One of the most fascinating as well as important histories of the century.—Cor. N. Y. Evening Post.
The careful study of these volumes will infallibly afford a feast both rich and rare.—Baltimore Republican.
Already takes a rank among standard works of history.—London Critic.
Mr. Motley’s prose epic.—London Spectator.
Its pages are pregnant with instruction.—London Literary Gazette.
We may profit by almost every page of his narrative. All the topics which agitate us now are more or less vividly presented in the History of the United Netherlands.—New York Times.
Bears on every page marks of the same vigorous mind that produced “The Rise of the Dutch Republic;” but the new work is riper, mellower, and though equally racy of the soil, softer flavored. The inspiring idea which breathes through Mr. Motley’s histories and colors the whole texture of his narrative, is the grandeur of that memorable struggle in the 16th century by which the human mind broke the thraldom of religious intolerance and achieved its independence.—The World, N. Y.
The name of Motley now stands in the very front rank of living historians. His Dutch Republic took the world by surprise; but the favorable verdict then given is now only the more deliberately confirmed on the publication of the continued story under the title of the History of the United Netherlands. All the nerve, and power, and substance of juicy life are there, lending a charm to every page.—Church Journal, N. Y.
Motley, indeed, has produced a prose epic, and his fighting scenes are as real, spirited, and life-like as the combats in the Iliad.—The Press (Phila.).
His history is as interesting as a romance, and as reliable as a proposition of Euclid. Clio never had a more faithful disciple. We advise every reader whose means will permit to become the owner of these fascinating volumes, assuring him that he will never regret the investment.—Christian Intelligencer, N. Y.
![]() Harper & Brothers will send the above Work by
Mail, postage pre-paid (for any distance in the United States under
3000 miles), on receipt of the Money.
Harper & Brothers will send the above Work by
Mail, postage pre-paid (for any distance in the United States under
3000 miles), on receipt of the Money.
The History of England, from the Accession of James II. By Thomas Babington Macaulay. With an Original Portrait of the Author.
Duodecimo Edition, Complete. With Portrait and elaborate Index. Printed on Fine Paper, Muslin, 40 cents a volume; Sheep, 60 cents a volume; Half Calf, $1 25 a volume.
![]() The Fifth Volume contains a Complete Index to the entire Work.
The Fifth Volume contains a Complete Index to the entire Work.
History of England, from the Invasion of Julius Cæsar to the Abdication of James II., 1688. By David Hume. A New Edition, with the Author’s last Corrections and Improvements. To which is prefixed a Short Account of his Life, written by Himself. With a Portrait of the Author. 6 vols. 12mo, Muslin, $2 40; Sheep, $3 60; Half Calf, $7 50.
History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire. By Edward Gibbon. With Notes, by Rev. H. H. Milman and M. Guizot. With Maps and Engravings. A New Cheap Edition. To which is added a Complete Index of the whole Work, and a Portrait of the Author. 6 vols. 12mo, Muslin, $2 40; Sheep extra, $3 60; Half Calf, $7 50.
Octavo Library Edition, Complete. With Portrait and elaborate Index, of indispensable value to a Library Edition. Printed on Superfine Paper, Five Volumes, Muslin, $1 50 a volume; Sheep, $2 00 a volume; Half Calf, $2 50 a volume.
New Edition. With a Portrait of William of Orange. 3 vols. 8vo, Muslin, $6 00; Sheep, $6 75; Half Calf antique, $9 00; Half Calf, extra gilt, $10 50.
We regard this work as the best contribution to modern history that has yet been made by an American.—Methodist Quarterly Review.
The “History of the Dutch Republic” is a great gift to us: but the heart and earnestness that beat through all its pages are greater, for they give us most timely inspiration to vindicate the true ideas of our country, and to compose an able history of our own.—Christian Examiner (Boston).
This work bears on its face the evidences of scholarship and research. The arrangement is clear end effective: the style energetic, lively, and often brilliant. *** Mr. Motley’s instructive volumes will, we trust, have a circulation commensurate with their interest and value.—Protestant Episcopal Quarterly Review.
To the illustration of this most interesting period Mr. Motley has brought the matured powers of a vigorous and brilliant mind, and the abundant fruits of patient and judicious study and deep reflection. The result is, one of the most important contributions to historical literature that have been made in this country.—North American Review.
We would conclude this notice by earnestly recommending our readers to procure for themselves this truly great and admirable work, by the production of which the author has conferred no less honor upon his country than he has won praise and fame for himself, and than which, we can assure them, they can find nothing more attractive or interesting within the compass of modern literature.—Evangelical Review.
It is not often that we have the pleasure of commending to the attention of the lover of books a work of such extraordinary and unexceptionable excellence as this one.—Univeralist Quarterly Review.
There are an elevation and a classic polish in these volumes, and a felicity of grouping and of portraiture, which invest the subject with the attractions of a living and stirring episode in the grand historic drama.—Southern Methodist Quarterly Review.
The author writes with a genial glow and love of his subject.—Presbyterian Quarterly Review.
Mr. Motley is a sturdy Republican and a hearty Protestant. His style is lively and picturesque, and his work is an honor and an important accession to our national literature.—Church Review.
Mr. Motley’s work is an important one, the result of profound research, sincere convictions, sound principles, and manly sentiments; and even those who are most familiar with the history of the period will find in it a fresh and vivid addition to their previous knowledge. It does honor to American literature, and would do honor to the literature of any country in the world.—Edinburgh Review.
A serious chasm in English historical literature has been (by this book) very remarkably filled. *** A history as complete as industry and genius can make it now lies before us, of the first twenty years of the revolt of the United Provinces. *** All the essentials of a great writer Mr. Motley eminently possesses. His mind is broad, his industry unwearied. In power a dramatic description no modern historian, except, perhaps, Mr. Carlyle, surpasses him, and in analysis of character he is elaborate and distinct.— Westminster Review.
It is a work of real historical value, the result of accurate criticism, written in a liberal spirit, and from first to last deeply interesting.—Athenæum.
The style is excellent, clear vivid, eloquent; and the industry with which original sources have been investigated, and through which new light has been shed over perplexed incidents and characters, entitles Mr. Motley to a high rank in the literature of an age peculiarly rich in history.—North British Review.
It abounds in new information, and as a first work, commands a very cordial recognition, not merely of the promise it gives, but of the extent and importance of the labor actually performed on it.— London Examiner.
Mr. Motley’s “History” is a work of which any country might be proud.—Press (London).
Mr. Motley’s History will be a standard book of reference in historical literature.—London Literary Gazette.
Mr. Motley has searched the whole range of historical documents necessary to the composition of his work.—London Leader.
This is really a great work. It belongs to the class of books in which we range our Grotes, Milmans, Merivales, and Macaulays, as the glories of English literature in the department of history. *** Mr. Motley’s gifts as a historical writer are among the highest and rarest.—Nonconformist (London).
Mr. Motley’s volumes will well repay perusal. *** For his learning, his liberal tone, and his generous enthusiasm, we heartily commend him, and bid him good speed for the remainder of his interesting and heroic narrative.—Saturday Review.
The story is a noble one, and is worthily treated. *** Mr. Motley has had the patience to unravel, with unfailing perseverance the thousand intricate plots of the adversaries of the Prince of Orange; but the details and the literal extracts which he has derived from original documents, and transferred to his pages, give a truthful color and a picturesque effect, which are especially charming.— London Daily News.
M. Lothrop Motley dans son magnifique tableau de la formation de notre République.—G. Groen Van Prinsterer.
Our accomplished countryman, Mr. J. Lothrop Motley, who, during the last five years, for the better prosecution of his labors, has established his residence in the neighborhood of the scenes of his narrative. No one acquainted with the fine powers of mind possessed by this scholar, and the earnestness with which he has devoted himself to the task can doubt that he will do full justice to his important but difficult subject.—W. H. Prescott.
The production of such a work as this astonishes, while it gratifies the pride of the American reader.—N. Y. Observer.
The “Rise of the Dutch Republic” at once and by acclamation, takes its place by the “Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire,” as a work which, whether for research, substance or style, will never be superseded.—N. Y. Albion.
A work upon which all who read the English language may congratulate themselves.—New Yorker Handels Zeitung.
Mr. Motley’s place is now (alluding to this book) with Hallam and Lord Mahon, Alison and Macaulay in the Old Country, and with Washington Irving, Prescott, and Bancroft in this.—N. Y. Times.
The authority, in the English tongue, for the history of the period and people to which it refers.—N. Y. Courier and Enquirer.
This work at once places the author on the list of American historians which has been so signally illustrated by the names of Irving, Prescott, Bancroft, and Hildreth.—Boston Times.
The work is a noble one, and a most desirable acquisition to our historical literature.—Mobile Advertiser.
Such a work is an honor to its author, to his country, and to the age in which it was written.—Ohio Farmer.
Harper & Brothers will send the above Work by Mail, postage paid (for any distance in the United States under 3000 miles), on receipt of the Money.
TRUMPS. A Novel. Illustrated by Hoppin. Large 12mo, Muslin, $1 50; Half Calf, $2 35.
THE POTIPHAR PAPERS. Illustrated from Drawings by Hoppin. 12mo, Muslin, $1 00; Half Calf, $1 85.
PRUE AND I. 12mo, Muslin, $1 00; Half Calf, $1 85.
LOTUS-EATING. A Summer-Book. Illustrated from Designs by Kensett. 12mo, Muslin, 75 cents; Half Calf, $1 60.
THE HOWADJI IN SYRIA. 12mo, Muslin, $1 00; Half Calf, $1 85.
NILE NOTES OF A HOWADJI. 12mo, Muslin, $1 00; Half Calf, $1 85.
![]() Harper & Brothers will send either of the
above Works by Mail, postage prepaid (for any distance in the United
States under 3000 miles), on receipt of the Price.
Harper & Brothers will send either of the
above Works by Mail, postage prepaid (for any distance in the United
States under 3000 miles), on receipt of the Price.
History of Friedrich the Second,
called Frederic the Great. 4 vols. 12mo, Muslin, $1 25 each. Vols. I. and II.,
with Portraits and Maps, just ready.
The French Revolution.
A History. Newly Revised by the Author, with
Index, &c. 2 vols. 12mo, Muslin, $2 00; Half Calf; $3 70.
Oliver Cromwell’s Letters and Speeches.
Including the Supplement to the First Edition. With Elucidations and Connecting
Narrative. 2 vols. 12mo, Muslin, $2 00; Half Calf, $3 70.
Past and Present.
Chartism and Sartor Resartus. A New Edition.
Complete in 1 vol. 12mo, Muslin, $1 00; Half Calf, $1 85.
![]() Harper & Brothers will send either of the
above Works by Mail, postage paid (for any distance in the United
States under 3000 miles), on receipt of the Money.
Harper & Brothers will send either of the
above Works by Mail, postage paid (for any distance in the United
States under 3000 miles), on receipt of the Money.
Boat Life in Egypt and Nubia. By William C. Prime, Author of “The Old House by the River,” “Later Years,” &c. Illustrations. 12mo, Muslin, $1 25.
By William C. Prime, Author of “The Old House by the River,” “Later Years,” &c. Illustrations. 12mo, Muslin, $1 25.
By William C. Prime, Author of the “Owl Creek Letters.” 12mo, Muslin, 75 cents.
By William C. Prime, Author of “The Old House by the River.” 12mo, Muslin, $1 00.
Romanism at Home.
Letters to the Hon. Roger B. Taney, Chief-Justice of the United
States. By Kirwan. 12mo, Muslin, 75 cents.
Men and Things
as I saw them in Europe. By Kirwan. 12mo, Muslin, 75 cents.
Parish and other Pencilings.
By Kirwan. 12mo, Muslin, 75 cents.
Letters to Bishop Hughes.
By Kirwan. New and Revised Edition. 12mo.
It is not often that a work of such magnitude is undertaken; more seldom still is such a work so perseveringly carried on, and so soon and yet so worthily accomplished. Mr. Grote has illustrated and invested with an entirely new significance a portion of the past history of humanity, which he, perhaps, thinks the most splendid that has been, and which all allow to have been very splendid. He has made great Greeks live again before us, and has enabled us to realize Greek modes of thinking. He has added a great historical work to the language, taking its place with other great histories, and yet not like any of them in the special combination of merits which it exhibits: scholarship and learning such as we have been accustomed to demand only in Germans; an art of grouping and narration different from that of Hume, different from that of Gibbon, an yet producing the effect of sustained charm and pleasure; a peculiarly keen interest in events of the political order, and a wide knowledge of the business of politics; and, finally, harmonizing all, a spirit or sober philosophical generalization always tending to view facts collectively in their speculative bearing as well as to record them individually. It is at once an ample and detailed narrative of the history of Greece, and a lucid philosophy of Grecian history.—London Athenæum, March 8, 1856.
Mr. Grote will be emphatically the historian of the people of Greece.—Dublin University Magazine.
The acute intelligence, the discipline, faculty of intellect, and the excellent erudition every one would look for from Mr. Grote; but they will here also find the element which harmonises these, and without which, on such a theme, an orderly and solid work could not have been written.—Examiner.
A work second to that of Gibbon alone in English historical literature. Mr. Grote gives the philosophy as well as the facts of history, and it would be difficult to find an author combining in the same degree the accurate learning or the scholar with the experience of a practical statesman. The completion of this great work may well be hailed with some degree of national pride and satisfaction.—Literary Gazette, March 8, 1856.
The better acquainted any one is with Grecian history, and with the manner in which that history has heretofore been written, the higher will be his estimation of this work. Mr. Grote’s familiarity both with the great highways and the obscurest by-paths of Grecian literature and antiquity has seldom been equaled, and not often approached; in unlearned England; while those Germans who have rivaled it have seldom possessed the quality which eminently characterizes Mr. Grote, of keeping historical imagination severely under the restraints of evidence. The great charm of Mr. Grote’s history has been throughout the cordial admiration he feels for the people whose acts and fortunes he has to relate. ** We bid Mr. Grote farewell; heartily congratulating him on the conclusion of a work which is a monument of English learning, of English clear-sightedness, and of English love of freedom and the characters it produces.—Spectator.
Endeavor to become acquainted with Mr. Grote, who is engaged on a Greek History. I expect a great deal from this production.—Niebuhr, the Historian, to Professor Lieber.
The author has now incontestably won for himself the title, not merely of a historian, but of the historian of Greece.—Quarterly Review.
Mr. Grote is, beyond all question, the historian of Greece, unrivaled, so far as we know, in the erudition and genius with which he has revived the picture of a distant past, and brought home every part and feature of its history to our intellects and our hearts.—London Times.
For becoming dignity of style, unforced adaptation of results to principles, careful verification of theory by fact, and impregnation of fact by theory—for extensive and well-weighed learning, employed with intelligence and taste, we have seen no historical work of modern times which we would place above Mr. Grote’s history.—Morning Chronicle.
A New Descriptive Catalogue of Harper & Brothers’ Publications is now ready for distribution, and may be obtained gratuitously on application to the Publishers personally, or by letter inclosing Six Cents in postage stamps. The attention of gentlemen, in town or country, designing to form Libraries or enrich their literary collections, is respectfully invited to this Catalogue, which will be found to comprise a large proportion of the standard and most esteemed works in English Literature—COMPREHENDING MORE THAN TWO THOUSAND VOLUMES—which are offered, in most instances at less than one half the cost of similar productions in England. To Librarians and others connected with Colleges, Schools, &c., who may not have access to a reliable guide in forming the true estimate of literary productions, it is believed this Catalogue will prove especially valuable as a manual of reference. To prevent disappointment, it is suggested that, whenever books can not be obtained through any bookseller or local agent, applications with remittance should be addressed direct to the Publishers, which will meet with prompt attention.
Transcriber’s Notes:
Blank pages have been removed.
Silently corrected a few punctuation errors.
“remainer” corrected to “remainder”, otherwise spelling and hyphenation variations were left as is.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Life and Adventure in the South Pacific, by
John D. Jones
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK LIFE, ADVENTURE IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC ***
***** This file should be named 59684-h.htm or 59684-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/9/6/8/59684/
Produced by Chris Whitehead, Robert Tonsing and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will
be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright
law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works,
so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United
States without permission and without paying copyright
royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part
of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm
concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark,
and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive
specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this
eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook
for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports,
performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given
away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks
not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the
trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
START: FULL LICENSE
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full
Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or
destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your
possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a
Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound
by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the
person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph
1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this
agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the
Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection
of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual
works in the collection are in the public domain in the United
States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the
United States and you are located in the United States, we do not
claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing,
displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as
all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope
that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting
free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm
works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the
Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily
comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the
same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when
you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are
in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States,
check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this
agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing,
distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any
other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no
representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any
country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other
immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear
prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work
on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed,
performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no
restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it
under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this
eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the
United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you
are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is
derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not
contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the
copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in
the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are
redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply
either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or
obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any
additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms
will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works
posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the
beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including
any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access
to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format
other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official
version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site
(www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense
to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means
of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain
Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the
full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
provided that
* You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is owed
to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he has
agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments must be paid
within 60 days following each date on which you prepare (or are
legally required to prepare) your periodic tax returns. Royalty
payments should be clearly marked as such and sent to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the address specified in
Section 4, "Information about donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation."
* You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or destroy all
copies of the works possessed in a physical medium and discontinue
all use of and all access to other copies of Project Gutenberg-tm
works.
* You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of
any money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days of
receipt of the work.
* You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than
are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing
from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The
Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project
Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may
contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate
or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other
intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or
other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or
cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium
with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you
with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in
lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person
or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second
opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If
the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing
without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO
OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of
damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement
violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the
agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or
limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or
unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the
remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in
accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the
production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses,
including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of
the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this
or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or
additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any
Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of
computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It
exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations
from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future
generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see
Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at
www.gutenberg.org
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by
U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the
mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its
volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous
locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt
Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to
date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and
official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND
DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular
state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To
donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project
Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be
freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and
distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of
volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in
the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not
necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper
edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search
facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.