

W. E. Watt, President &c.,
Fisher Building,
277 Dearborn St., Chicago, Ill.
My dear Sir:
Please accept my thanks for a copy of the first publication of “Birds.” Please enter my name as a regular subscriber. It is one of the most beautiful and interesting publications yet attempted in this direction. It has other attractions in addition to its beauty, and it must win its way to popular favor.
Wishing the handsome little magazine abundant prosperity, I remain
Yours very respectfully,


Please mention “BIRDS” when you write to Advertisers.

Please mention “BIRDS” when you write to Advertisers.

Please mention “BIRDS” when you write to Advertisers.

Please mention “BIRDS” when you write to Advertisers.

Nature Study Publishing Company
OFFICE: FISHER BUILDING
 american blue jay.
american blue jay.
THE BLUE JAY.

URING about three-fourths of the year the American Jay is an extremely tame, noisy and even obstrusive bird in its habits. As the breeding season approaches he suddenly becomes silent, preparing the nest in the most secluded parts of his native forests, and exercising all his cunning to keep it concealed. He is omniverous but is especially fond of eggs and young birds. The Jay may be regarded as eminently injurious though in spring he consumes a number of insects to atone for his sins of stealing fruit and berries in autumn. He is a professional nest robber, and other birds are as watchful of him as is a mother of her babe. He glides through the foliage of the trees so swiftly and noiselessly that his presence is scarcely suspected until he has committed some depredation. The Robin is his most wary foe, and when the Jay is found near his nest will pursue him and drive him from the neighborhood. He is as brave as he is active, however, and dashes boldly in pursuit of his more plainly attired neighbors who venture to intrude upon his domain.
The Jay has a curious antipathy toward the owl, perching on trees above it and keeping up a continual screeching. Some years ago an Ohio gentleman was presented with a magnificent specimen of the horned owl, which he kept for a time in a large tin cage. In favorable weather the cage was set out of doors, when it would soon be surrounded by Jays, much in the manner described of the Toucan, and an incessant screeching followed, to which the owl appeared indifferent. They would venture near enough to steal a portion of his food, the bars of his cage being sufficiently wide apart to admit them. On one occasion, however, he caught the tail of a Jay in his claws and left the tormentor without his proud appendage.
The Jay remains with us throughout the year. He is one of the wildest of our birds, the shyest of man, although seeing him most. He makes no regular migrations at certain seasons, but, unless disturbed, will live out his life close to his favorite haunts. His wings show him to be unfitted for extended flight.
Jays are most easily discovered in the morning about sunrise on the tops of young live oaks. Their notes are varied. Later in the day it is more difficult to find them, as they are more silent, and not so much on the tree tops as among the bushes.
The Jays breed in woods, forests, orchards, preferring old and very shady trees, placing their nests in the center against the body, or at the bifurcation of large limbs. The nest is formed of twigs and roots; the eggs are from four to six.
THE BLUE JAY.
Something glorious, something gay,
Flits and flashes this-a-way!
’Thwart the hemlock’s dusky shade,
Rich in color full displayed,
Swiftly vivid as a flame—
Blue as heaven and white as snow—
Doth this lovely creature go.
What may be his dainty name?
“Only this”—the people say—
“Saucy, chattering, scolding Jay!”
THE SWALLOW-TAILED INDIAN ROLLER.

WALLOW-TAILED Indian Rollers are natives of Northeastern Africa and Senegambia, and also the interior of the Niger district. The bird is so called from its way of occasionally rolling or turning over in its flight, somewhat after the fashion of a tumbler pigeon. A traveller in describing the habits of the Roller family, says:
“On the 12th of April I reached Jericho alone, and remained there in solitude for several days, during which time I had many opportunities of observing the grotesque habits of the Roller. For several successive evenings, great flocks of Rollers mustered shortly before sunset on some dona trees near the fountain, with all the noise but without the decorum of Rooks. After a volley of discordant screams, from the sound of which it derives its Arabic name of “schurkrak,” a few birds would start from their perches and commence overhead a series of somersaults. In a moment or two they would be followed by the whole flock, and these gambols would be repeated for a dozen times or more.
“Everywhere it takes its perch on some conspicuous branch or on the top of a rock, where it can see and be seen. The bare tops of the fig trees, before they put forth their leaves, are in the cultivated terraces, a particularly favorite resort. In the barren Ghor I have often watched it perched unconcernedly on a knot of gravel or marl in the plain, watching apparently for the emergence of beetles from the sand. Elsewhere I have not seen it settle on the ground.
“Like Europeans in the East, it can make itself happy without chairs and tables in the desert, but prefers a comfortable easy chair when it is to be found. Its nest I have seen in ruins, in holes in rocks, in burrows, in steep sand cliffs, but far more generally in hollow trees. The colony in the Wady Kelt used burrows excavated by themselves, and many a hole did they relinquish, owing to the difficulty of working it. So cunningly were the nests placed under a crumbling, treacherous ledge, overhanging a chasm of perhaps one or two hundred feet, that we were completely foiled in our siege. We obtained a nest of six eggs, quite fresh, in a hollow tree in Bashan, near Gadara, on the 6th of May.
“The total length of the Roller is about twelve inches. The Swallow-tailed Indian Roller, of which we present a specimen, differs from the Europeon Roller only in having the outer tail feathers elongated to an extent of several inches.”
 swallow-tailed indian roller.
swallow-tailed indian roller.
THE RED HEADED WOODPECKER.

ERHAPS no bird in North America is more universally known than the Red Headed Woodpecker. He is found in all parts of the United States and is sometimes called, for short, by the significant name of Red Head. His tri-colored plumage, red, white and black, glossed with steel blue, is so striking and characteristic, and his predatory habits in the orchards and cornfields, and fondness for hovering along the fences, so very notorious, that almost every child is acquainted with the Red Headed Woodpecker. In the immediate neighborhood of large cities, where the old timber is chiefly cut down, he is not so frequently found. Wherever there is a deadening, however, you will find him, and in the dead tops and limbs of high trees he makes his home. Towards the mountains, particularly in the vicinity of creeks and rivers, these birds are extremely numerous, especially in the latter end of summer. It is interesting to hear them rattling on the dead leaves of trees or see them on the roadside fences, where they flit from stake to stake. We remember a tremendous and quite alarming and afterwards ludicrous rattling by one of them on some loose tin roofing on a neighbor’s house. This occurred so often that the owner, to secure peace, had the roof repaired.
They love the wild cherries, the earliest and sweetest apples, for, as is said of him, “he is so excellent a connoisseur in fruit, that whenever an apple or pear is found broached by him, it is sure to be among the ripest and best flavored. When alarmed he seizes a capital one by striking his open bill into it, and bears it off to the woods.” He eats the rich, succulent, milky young corn with voracity. He is of a gay and frolicsome disposition, and half a dozen of the fraternity are frequently seen diving and vociferating around the high dead limbs of some large trees, pursuing and playing with each other, and amusing the passerby with their gambols. He is a comical fellow, too, prying around at you from the bole of a tree or from his nesting hole therein.
Though a lover of fruit, he does more good than injury. Insects are his natural food, and form at least two thirds of his subsistence. He devours the destructive insects that penetrate the bark and body of a tree to deposit their eggs and larvae.
About the middle of May, he begins to construct his nest, which is formed in the body of large limbs of trees, taking in no material but smoothing it within to the proper shape and size. The female lays six eggs, of a pure white. The young appear about the first of June. About the middle of September the Red Heads begin to migrate to warmer climates, travelling at night time in an irregular way like a disbanded army and stopping for rest and food through the day.
The black snake is the deadly foe of the Red Head, frequently entering his nest, feeding upon the young, and remaining for days in possession.
“The eager school-boy, after hazarding his neck to reach the Woodpecker’s hole, at the triumphant moment when he thinks the nestlings his own, strips his arm, launches it down into the cavity, and grasping what he conceives to be the callow young, starts with horror at the sight of a hideous snake, almost drops from his giddy pinnacle, and retreats down the tree with terror and precipitation.”
THE WOODPECKER.
The Drummer Bird.
My dear girls and boys:
The man who told me to keep still and look pleasant while he took my picture said I might write you a letter to send with it. You say I always keep on the other side of the tree from you. That is because someone has told you that I spoil trees, and I am afraid that you will want to punish me for it. I do not spoil trees. The trees like to have me come to visit them, for I eat the insects that are killing them. Shall I tell you how I do this?
I cling to the tree with my strong claws so sharply hooked. The pointed feathers of my tail are stiff enough to help hold me against the bark. Then my breast bone is quite flat, so that I may press close to the tree. When I am all ready you hear my r-r-rap—just like a rattle. My head goes as quickly as if it were moved by a spring. Such a strong, sharp bill makes the chips fly! The tiny tunnel I dig just reaches the insect.
Then I thrust out my long tongue. It has a sharp, horny tip, and has barbs on it too. Very tiny insects stick to a liquid like glue that covers my tongue. I suppose I must tell you that I like a taste of the ripest fruit and grain. Don’t you think I earn a little when I work so hard keeping the trees healthy?
I must tell you about the deep tunnel my mate and I cut out of a tree. It is just wide enough for us to slip into. It is not straight down, but bent, so that the rain cannot get to the bottom. There we make a nest of little chips for our five white eggs.
I should like to tell you one of the stories that some boys and girls tell about my red head. You will find it on another page of the book. Now I must fly away to peck for more bugs.
Your loving friend,
Woodpecker.
 red headed woodpecker.
red headed woodpecker.
MEXICAN MOT MOT.
OT MOTS are peculiar to the new world, being found from Mexico throughout the whole of Central America and the South American continent. The general plumage is green, and the majority of the species have a large racket at the end of the center tail feathers, formed by the bird itself.
The Houton, (so called from his note,) according to Waterson, ranks high in beauty among the birds of Demerara. This beautiful creature seems to suppose that its beauty can be increased by trimming its tail, which undergoes the same operation as one’s hair in a barber shop, using its own beak, which is serrated, in lieu of a pair of scissors. As soon as its tail is fully grown, he begins about an inch from the extremity of the two longest feathers in it and cuts away the web on both sides of the shaft, making a gap about an inch long. Both male and female wear their tails in this manner, which gives them a remarkable appearance among all other birds.
To observe this bird in his native haunts, one must be in the forest at dawn. He shuns the society of man. The thick and gloomy forests are preferred by the Houton. In those far extending wilds, about day-break, you hear him call in distinct and melancholy tone, “Houton, Houton!” An observer says, “Move cautiously to the place from which the sound proceeds, and you will see him sitting in the underwood, about a couple of yards from the ground, his tail moving up and down every time he articulates “Houton!”.”
The Mot Mot lives on insects and berries found among the underwood, and very rarely is seen in the lofty trees. He makes no nest, but rears his young in a hole in the sand, generally on the side of a hill.
Mr. Osbert Salvin tells this curious anecdote: “Some years ago the Zoological Society possessed a specimen which lived in one of the large cages of the parrot house by itself. I have a very distinct recollection of the bird, for I used every time I saw it to cheer it up a bit by whistling such of its notes as I had picked up in the forests of America. The bird always seemed to appreciate this attention, for although it never replied, it became at once animated, hopped about the cage, and swung its tail from side to side like the pendulum of a clock. For a long time its tail had perfect spatules, but toward the end of its life I noticed that the median feathers were no longer trimmed with such precision, and on looking at its beak I noticed that from some cause or other it did not close properly, gaped slightly at the tip, and had thus become unfitted for removing the vanes of the feathers.”
KING PARROT OR KING LORY.
ORY is the name of certain birds, mostly from the Moluccas and New Guinea, which are remarkable for their bright scarlet or crimson coloring, though also applied to some others in which the plumage is chiefly green. Much interest has been excited by the discovery of Dr. A. B. Meyer that the birds of this genus having a red plumage are the females of those wearing green feathers. For a time there was much difference of opinion on this subject, but the assertion is now generally admitted.
They are called “brush-tongued” Parrots. The color of the first plumage of the young is still unsettled. This bird is a favorite among bird fanciers, is readily tamed, and is of an affectionate nature. It can be taught to speak very creditably, and is very fond of attracting the attention of strangers and receiving the caresses of those whom it likes.
There are few things a parrot prefers to nuts and the stones of various fruits. Wood says he once succeeded in obtaining the affections of a Parisian Parrot, solely through the medium of peach stones which he always saved for the bird and for which it regularly began to gabble as soon as it saw him coming. “When taken freshly from the peach,” he says, “the stones are very acceptable to the parrot, who turns them over, chuckling all the while to show his satisfaction, and picking all the soft parts from the deep indentations in the stone.” He used to crack the stone before giving it to the bird, when his delight knew no bounds. They are fond of hot condiments, cayenne pepper or the capsicum pod. If a bird be ailing, a capsicum will often set it right again.
The parrot is one of the hardiest of birds when well cared for and will live to a great age. Some of these birds have been known to attain an age of seventy years, and one seen by Vaillant had reached the patriarchal age of ninety three. At sixty its memory began to fail, at sixty-five the moult became very irregular and the tail changed to yellow. At ninety it was a very decrepit creature, almost blind and quite silent, having forgotten its former abundant stock of words.
A gentleman once had for many years a parrot of seemingly rare intelligence. It was his custom during the summer to hang the parrot’s cage in front of his shop in a country village, where the bird would talk and laugh and cry, and condole with itself. Dogs were his special aversion and on occasions when he had food to spare, he would drop it out of the cage and whistle long and loud for them. When the dogs had assembled to his satisfaction he would suddenly scream in the fiercest accents, “Get out, dogs!” and when they had scattered in alarm his enjoyment of it was demonstrative. This parrot’s vocabulary, however, was not the most refined, his master having equipped him with certain piratical idioms.
According to authority, the parrot owner will find the health of his pet improved and its happiness promoted by giving it, every now and then, a small log or branch on which the mosses and lichens are still growing. Meat, fish, and other similar articles of diet are given with evil effects.
It is impossible for anyone who has only seen these birds in a cage or small inclosure to conceive what must be the gorgeous appearance of a flock, either in full flight, and performing their various evolutions, under a vertical sun, or sporting among the superb foliage of a tropical forest which, without these, and other brilliant tenants, would present only a solitude of luxuriant vegetation.
 king parrot.
king parrot.
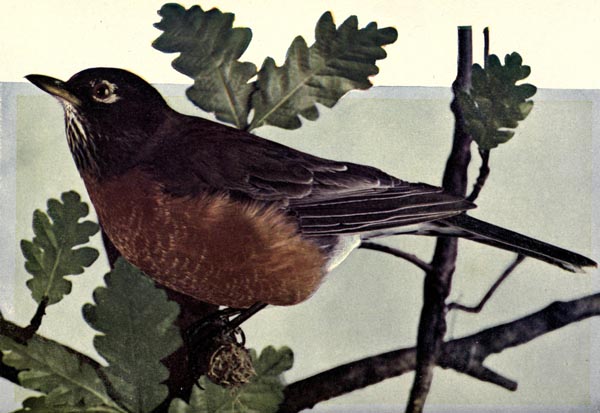
THE AMERICAN ROBIN.
The Bird of the Morning.
Yes, my dear readers, I am the bird of the morning. Very few of you rise early enough to hear my first song. By the time you are awake our little ones have had their breakfast, Mrs. Robin and I have had our morning bath and we are all ready to greet you with our morning song.
I wonder if any of you have seen our nest and can tell the color of the eggs that Mrs. Robin lays. Some time I will let you peep into the nest and see them, but of course you will not touch them.
I wonder, too, if you know any of my cousins—the Mocking bird, the Cat-bird or the Brown Thrush—I think I shall ask them to have their pictures taken soon and talk to you about our gay times.
Did you ever see one of my cousins on the ground? I don’t believe you can tell how I move about. Some of you may say I run, and some of you may say I hop, and others of you may say I do both. Well, I’ll tell you how to find out. Just watch me and see. My little friends up north won’t be able to see me though until next month, as I do not dare leave the warm south until Jack Frost leaves the ground so I can find worms to eat.
I shall be about the first bird
to visit you next month and I
want you to watch for me.
When I do come it will be to
stay a long time, for I shall be
the last to leave you. Just
think, the first to come and last
to leave. Don’t you think we
ought to be great friends? Let
us get better acquainted when
next we meet. Your friend,
Robin.
How do the robins build their nest?
Robin Red Breast told me,
First a wisp of yellow hay
In a pretty round they lay;
Then some shreds of downy floss,
Feathers too, and bits of moss,
Woven with a sweet, sweet song,
This way, that way, and across:
That’s what Robin told me.
Where do the robins hide their nest?
Robin Red Breast told me,
Up among the leaves so deep,
Where the sunbeams rarely creep,
Long before the winds are cold,
Long before the leaves are gold
Bright-eyed stars will peep and see
Baby Robins—one, two, three:
That’s what Robin told me.
THE AMERICAN ROBIN.
“Come, sweetest of the feathered throng.”

UR American Robin must not be confounded with the English Robin Redbreast, although both bear the same name. It is the latter bird in whose praise so much has been written in fable and song. The American Robin belongs to the Thrush family; the Mocking bird, Cat-bird and Brown Thrush, or Thrasher, being other familiar children. In this family, bird organization reaches its highest development. This bird is larger than his English cousin the Redbreast and many think has a finer note than any other of the Thrush family.
The Robin courts the society of man, following close upon the plow and the spade and often becoming quite tame and domestic. It feeds for a month or two on strawberries and cherries, but generally on worms and insects picked out of the ground. It destroys the larvae of many insects in the soil and is a positive blessing to man, designed by the Creator for ornament and pleasure, and use in protecting vegetation. John Burroughs, the bird lover, says it is the most native and democratic of our birds.
It is widely diffused over the country, migrating to milder climates in the Winter. We have heard him in the early dawn on Nantucket Island welcoming the coming day, in the valleys of the Great and the little Miami, in the parks of Chicago, and on the plains of Kansas, his song ever cheering and friendly. It is one of the earliest heralds of Spring, coming as early as March or April, and is one of the latest birds to leave us in Autumn. Its song is a welcome prelude to the general concert of Summer.
“When Robin Redbreast sings,
We think on budding Springs.”
The Robin is not one of our most charming songsters, yet its carol is sweet, hearty and melodious. Its principal song is in the morning before sunrise, when it mounts the top of some tall tree, and with its wonderful power of song, announces the coming of day. When educated, it imitates the sounds of various birds, and even sings tunes. It must be amusing to hear it pipe out so solemn a strain as Old Hundred.
It has no remarkable habits. It shows considerable courage and anxiety for its young, and is a pattern of propriety when keeping house and concerned with the care of its offspring. Two broods are often reared out of the same nest. In the Fall these birds become restless and wandering, often congregating in large flocks, when, being quite fat, they are much esteemed as food.
The Robin’s nest is sometimes built in a corner of the porch, but oftener it is saddled on the horizontal limb of an orchard tree. It is so large and poorly concealed that any boy can find it, yet it is seldom molested. The Robin is not a skillful architect. The masonry of its nest is rough and the material coarse, being composed largely of leaves or old grass, cemented with mud. The eggs number four to six and are greenish blue in color.
An observer tells the following story of this domestic favorite:
“For the last three years a Robin has nested on a projecting pillar that supports the front piazza. In the Spring of the first year she built her nest on the top of the pillar—a rude affair—it was probably her first effort. The same season she made her second nest in the forks of an Oak, which took her only a few hours to complete.
[Continued page 59]
 american robin.
american robin.
 mexican mot mot.
mexican mot mot.
THE AMERICAN ROBIN.
[continued]
“She reared three broods that season; for the third family she returned to the piazza, and repaired the first nest. The following Spring she came again to the piazza, but selected another pillar for the site of her domicile, the construction of which was a decided improvement upon the first. For the next nest she returned to the Oak and raised a second story on the old one of the previous year, but making it much more symmetrical than the one beneath. The present season her first dwelling was as before, erected on a pillar of the piazza—as fine a structure as I ever saw this species build. When this brood was fledged she again repaired to the Oak, and reared a third story on the old domicile, using the moss before mentioned, making a very elaborate affair, and finally finishing up by festooning it with long sprays of moss. This bird and her mate were quite tame. I fed them with whortleberries, which they seemed to relish, and they would come almost to my feet to get them.”
The amount of food which the young robin is capable of absorbing is enormous. A couple of vigorous, half-grown birds have been fed, and in twelve hours devoured ravenously, sixty-eight earth worms, weighing thirty-four pennyweight, or forty-one per cent more than their own weight. A man at this rate should eat about seventy pounds of flesh per day, and drink five or six gallons of water.
The following poem by the good Quaker poet Whittier is sweet because he wrote it, interesting because it recites an old legend which incidentally explains the color of the robin’s breast, and unique because it is one of the few poems about our American bird.
THE ROBIN.
My old Welsh neighbor over the way
Crept slowly out in the sun of spring,
Pushed from her ears the locks of gray,
And listened to hear the robin sing.
Her grandson, playing at marbles, stopped,
And—cruel in sport, as boys will be—
Tossed a stone at the bird, who hopped
From bough to bough in the apple tree.
“Nay!” said the grandmother; “have you not heard,
My poor, bad boy! of the fiery pit,
And how, drop by drop, this merciful bird
Carries the water that quenches it?
“He brings cool dew in his little bill,
And lets it fall on the souls of sin:
You can see the mark on his red breast still
Of fires that scorch as he drops it in.
“My poor Bron rhuddyn! my breast-burned bird,
Singing so sweetly from limb to limb,
Very dear to the heart of Our Lord
Is he who pities the lost like Him.”
“Amen!” I said to the beautiful myth;
“Sing, bird of God, in my heart as well:
Each good thought is a drop wherewith
To cool and lessen the fires of hell.
“Prayers of love like rain-drops fall,
Tears of pity are cooling dew,
And dear to the heart of Our Lord are all
Who suffer like Him in the good they do.”
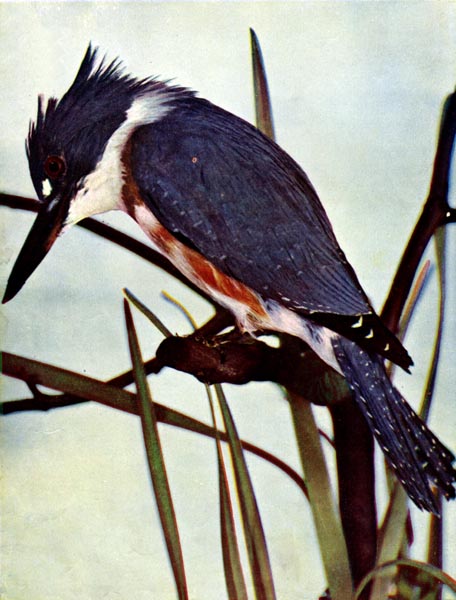
THE KINGFISHER.
Dear Children:
I shall soon arrive from the south. I hear that all the birds are going to tell stories to the boys and girls.
I have never talked much with children myself for I never really cared for people. They used to say that the dead body of a Kingfisher kept them safe in war and they said also that it protected them in lightning.
Even now in some places in France they call us the moth birds, for they believe that our bodies will keep away moths from woolen cloth.
I wish that people would not believe such things about us. Perhaps you cannot understand me when I talk. You may think that you hear only a child’s rattle.
Listen again! It is I, the Kingfisher. That sound is my way of talking. I live in the deep woods. I own a beautiful stream and a clear, cool lake. Oh, the little fish in that lake are good enough for a king to eat! I know, for I am a king.
You may see me or some of my mates near the lake any pleasant day. People used to say that we always brought pleasant weather. That is a joke. It is the pleasant weather that always brings us from our homes. When it storms or rains we cannot see the fish in the lake. Then we may as well stay in our nests.
My home once belonged to a water rat. He dug the fine hall in the gravel bank in my stream. It is nearly six feet long. The end of it is just the kind of a place for a nest. It is warm, dry and dark. In June my wife and I will settle down in it. By that time we shall have the nest well lined with fish bones. We shall put in some dried grass too. The fish bones make a fine lining for a nest. You know we swallow the fish whole, but we save all the bones for our nest.
I shall help my wife hatch her five white eggs and shall try in every way to make my family safe.
Please tell the people not to
believe those strange things
about me and you will greatly
oblige,
A neighbor,
The Kingfisher.
 kingfisher.
kingfisher.Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
THE KINGFISHER.
The Lone Fisherman.

HE American species belongs to the true group of Kingfishers. It occupies the whole continent of North America and although migrating in the north, he is a constant resident of our southern states. The belted Kingfisher is the only variety found along the inland streams of the United States. Audubon declares that “belted” should apply only to the female, however.
Like most birds of brilliant plumage, the Kingfisher prefers a quiet and secluded haunt. It loves the little trout streams, with wooded and precipitous banks, the still ponds and small lakes, ornamental waters in parks, where it is not molested, and the sides of sluggish rivers, drains and mill-ponds.
Here in such a haunt the bird often flits past like an indistinct gleam of bluish light. Fortune may sometimes favor the observer and the bird may alight on some twig over the stream, its weight causing it to sway gently to and fro. It eagerly scans the shoal of young trout sporting in the pool below, when suddenly it drops down into the water, and, almost before the observer is aware of the fact, is back again to its perch with a struggling fish in its beak. A few blows on the branch and its prey is ready for the dexterous movement of the bill, which places it in a position for swallowing. Sometimes the captured fish is adroitly jerked into the air and caught as it falls.
Fish is the principal food of the Kingfisher; but it also eats various kinds of insects, shrimps, and even small crabs. It rears its young in a hole, which is made in the banks of the stream it frequents. It is a slatternly bird, fouls its own nest and its peerless eggs. The nesting hole is bored rather slowly, and takes from one to two weeks to complete. Six or eight white glossy eggs are laid, sometimes on the bare soil, but often on the fish bones which, being indigestible, are thrown up by the bird in pellets.
The Kingfisher has a crest of feathers on the top of his head, which he raises and lowers, especially when trying to drive intruders away from his nest.
The plumage is compact and oily, making it almost impervious to water. The flesh is fishy and disagreeable to the taste, but the eggs are said to be good eating. The wings are long and pointed and the bill longer than the head. The voice is harsh and monotonous.
It is said that few birds are connected with more fables than the Kingfisher. The superstition that a dead Kingfisher when suspended by the throat, would turn its beak to that particular point of the compass from which the wind blew, is now dead. It was also supposed to possess many astonishing virtues, as that its dried body would avert thunderbolts, and if kept in a wardrobe would preserve from moths the woolen stuffs and the like contained in it.
Under the name of “halcyon,” it was fabled by the ancients to build its nest on the surface of the sea, and to have the power of calming the troubled waves during its period of incubation; hence the phrase “halcyon days.”
A pair of Kingfishers have had their residence in a bank at the south end of Washington Park, Chicago, for at least three seasons past. We have watched the Kingfisher from secluded spots on Long Island ponds and tidal streams, where his peculiar laughing note is the same as that which greets the ear of the fisherman on far inland streams on still summer days.
THE BLACKBIRD.
“I could not think so plain a bird
Could sing so fine a song.”
One on another against the wall
Pile up the books—I am done with them all;
I shall be wise, if I ever am wise,
Out of my own ears, and of my own eyes.
One day of the woods and their balmy light—
One hour on the top of a breezy hill,
There in the sassafras all out of sight
The Blackbird is splitting his slender bill
For the ease of his heart:
Do you think if he said
“I will sing like this bird with the mud colored back
And the two little spots of gold over his eyes,
Or like to this shy little creature that flies
So low to the ground, with the amethyst rings
About her small throat—all alive when she sings
With a glitter of shivering green—for the rest,
Gray shading to gray, with the sheen of her breast
Half rose and half fawn—
Or like this one so proud,
That flutters so restless, and cries out so loud,
With stiff horny beak and a top-knotted head,
And a lining of scarlet laid under his wings—”
Do you think, if he said, “I’m ashamed to be black!”
That he could have shaken the sassafras-tree
As he does with the song he was born to? not he!
—Alice Cary.
“Do you ne’er think what wondrous beings these?
Do you ne’er think who made them—who taught
The dialect they speak, where melodies
Alone are the interpreters of thought?
Whose household words are songs in many keys,
Sweeter than instrument of man ere caught!
Whose habitation in the tree-tops even
Are half-way houses on the road to heaven!
* * * * * * *
“You call them thieves or pillagers; but know,
They are the winged wardens of your farms,
Who from the cornfields drive the insidious foe,
And from your harvest keep a hundred harms;
Even the blackest of them all, the crow,
Renders good service as your man-at-arms,
Crushing the beetle in his coat of mail,
And crying havoc on the slug and snail.”
—From “The Birds of Killingworth.”
 blue mountain lory.
blue mountain lory.
BLUE MOUNTAIN LORY.

HIS bird inhabits the vast plains of the interior of New South Wales. It is one of the handsomest, not only of the Australian Parrots, but takes foremost place among the most gorgeously dressed members of the Parrot family that are to be met with in any part of the world. It is about eleven or twelve inches in length. The female cannot with certainty be distinguished from her mate, but is usually a very little smaller. The Lory seldom descends to the ground, but passes the greater part of its life among the gum trees upon the pollen and nectar on which it mainly subsists. In times of scarcity, however, it will also eat grass seeds, as well as insects, for want of which it is said, it often dies prematurely when in captivity.
Dr. Russ mentions that a pair obtained from a London dealer in 1870 for fifty dollars were the first of these birds imported, but the London Zoological Society had secured some of them two years before.
Despite his beauty, the Blue Mountain Lory is not a desirable bird to keep, as he requires great care. A female which survived six years in an aviary, laying several eggs, though kept singly, was fed on canary seed, maize, a little sugar, raw beef and carrots. W. Gedney seems to have been peculiarly happy in his specimens, remarking, “But for the terribly sudden death which so often overtakes these birds, they would be the most charming feathered pets that a lady could possess, having neither the power nor inclination to bite savagely.” The same writer’s recommendation to feed this Lory exclusively upon soft food, in which honey forms a great part, probably accounts for his advice to those “whose susceptible natures would be shocked” by the sudden death of their favorite, not to become the owner of a Blue Mountain Lory.
Like all the parrot family these Lories breed in hollow boughs, where the female deposits from three to four white eggs, upon which she sits for twenty-one days. The young from the first resemble their parents closely, but are a trifle less brilliantly colored.
They are very active and graceful, but have an abominable shriek. The noise is said to be nearly as disagreeable as the plumage is beautiful. They are very quarrelsome and have to be kept apart from the other parrots, which they will kill. Other species of birds however, are not disturbed by them. It is a sort of family animosity. They have been bred in captivity.
The feathers of the head and neck are long and very narrow and lie closely together; the claws are strong and hooked, indicating their tree climbing habits. Their incessant activity and amusing ways make these birds always interesting to watch.
THE RED WING BLACK BIRD.
The Bird of Society.
The blackbirds make the maples ring
With social cheer and jubilee;
The redwing flutes his o-ka-lee.—Emerson.

HE much abused and persecuted Red Wing Black Bird is found throughout North America, from the Atlantic to the Pacific; and it breeds more or less abundantly wherever found. In New England it is generally migratory, though instances are on record where a few have been known to remain throughout the winter in Massachusetts. Passing, in January, through the lower counties of Virginia, one frequently witnesses the aerial evolutions of great numbers of these birds. Sometimes they appear as if driven about like an enormous black cloud carried before the wind, varying every moment in shape. Sometimes they rise suddenly from the fields with a noise like thunder, while the glittering of innumerable wings of the brightest vermillion, amid the black cloud, occasion a very striking effect. At times the whole congregated multitude will suddenly alight in some detached grove and commence one general concert, that can plainly be distinguished at the distance of more than two miles. With the Redwings the whole winter season seems one continued carnival. They find abundant food in the old fields of rice, buckwheat and grain, and much of their time is spent in aerial movements, or in grand vocal performances.
The Redwings, for their nest, always select either the borders of streams or low marshy situations, amongst thick bunches of reeds. One nest was found built on a slender sapling at the distance of fourteen feet from the ground. The nest was pensile, like that of the Baltimore Oriole.
They have from one to three or more broods in a season, according to locality.
In the grain growing states they gather in immense swarms and commit havoc, and although they are shot in great numbers, and though their ranks are thinned by the attacks of hawks, it seems to have but little effect upon the survivors.
On the other hand, these Black Birds more than compensate the farmer for their mischief by the benefit they confer in the destruction of grub worms, caterpillars, and various kinds of larvae, the secret and deadly enemies of vegetation. It has been estimated the number of insects destroyed by these birds in a single season, in the United States, to be twelve thousand millions.
The eggs average about an inch in length. They are oval in shape, have a light bluish ground, and are marbled, lined and blotched with markings of light and dark purple and black.
BLACKBIRD.
’Tis a woodland enchanted!
By no sadder spirit
Than blackbirds and thrushes,
That whistle to cheer it
All day in the bushes,
This woodland is haunted;
And in a small clearing,
Beyond sight or hearing
Of human annoyance,
The little fount gushes.—Lowell.
 red-wing black bird.
red-wing black bird.
THE BIRD OF SOCIETY.
The blackbird loves to be one of a great flock. He talks, sings or scolds from morning until night. He cannot keep still. He will only stay alone with his family a few months in the summer. That is the reason he is called the “Bird of Society.” When he is merry, he gaily sings, “Conk-quer-ree.” When he is angry or frightened he screams, “Chock! Chock!” When he is flying or bathing he gives a sweet note which sounds like ee-u-u. He can chirp—chick, check, chuck, to his little ones as softly as any other bird. But only his best friends ever hear his sweetest tones, for the Blackbirds do not know how to be polite. They all talk at once. That is why most people think they only scream and chatter. Did you ever hear the blackbirds in the cornfields? If the farmers thought about it perhaps they would feel that part of every corn crop belongs to the Blackbirds. When the corn is young, the farmer cannot see the grubs which are eating the young plants. The Blackbirds can. They feed them to their babies—many thousands in a day. That is the way the crops are saved for the farmer. But he never thinks of that. Later when the Blackbirds come for their share of the corn the farmer says, “No, they shall not have my corn. I must stop that quickly.” Perhaps the Blackbirds said the same thing to the grubs in the spring. It is hard to have justice for everyone.
In April the Blackbird and his mate leave the noisy company. They seek a cosy home near the water where they can be quiet until August. They usually choose a swampy place among low shrubs and rushes. Here in the deep nest of coarse grass, moss and mud the mother bird lays her five eggs. They are very pretty—light blue with purple and black markings. Their friends say this is the best time to watch the blackbirds. In the flock they are all so much alike we cannot tell one from another. You would like to hear of some of the wise things Blackbirds do when they are tame.
One friend of the birds turned her home into a great open bird cage. Her chair was the favorite perch of her birds. She never kept them one minute longer than they wanted to stay. Yet her home was always full. This was Olive Thorne Miller. If you care to, you might ask mother to get “Bird Ways” and read you what she says about this “bird of society” and the other birds of this book.
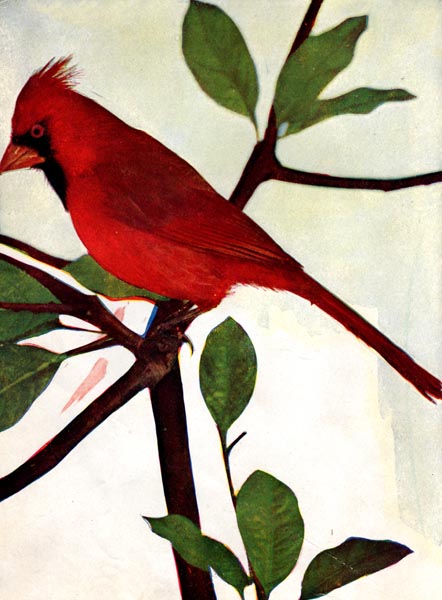
THE AMERICAN RED BIRD.

MERICAN RED BIRDS are among our most common cage birds, and are very generally known in Europe, numbers of them having been carried over both to France and England. Their notes are varied and musical; many of them resembling the high notes of a fife, and are nearly as loud. They are in song from March to September, beginning at the first appearance of dawn and repeating successively twenty or thirty times, and with little intermission, a favorite strain.
The sprightly figure and gaudy plumage of the Red Bird, his vivacity, strength of voice, and actual variety of note, and the little expense with which he is kept, will always make him a favorite.
This species is more numerous to the east of the great range of the Alleghenies, but is found in Pennsylvania and Ohio, and is numerous in the lower parts of the Southern States. In January and February they have been found along the roadsides and fences, hovering together in half dozens, associating with snow birds, and various kinds of sparrows. In the northern states they are migratory, and in the southern part of Pennsylvania they reside during the whole year, frequenting the borders of rivulets, in sheltered hollows, covered with holly, laurel, and other evergreens. They love also to reside in the vicinity of fields of Indian corn, a grain that constitutes their chief and favorite food. The seeds of apples, cherries, and other fruit are also eaten by them, and they are accused of destroying bees.
Early in May the Red Bird begins to prepare his nest, which is very often fixed in a holly, cedar or laurel bush. A pair of Red Birds in Ohio returned for a number of years to build their nest in a honeysuckle vine under a portico. They were never disturbed and never failed to rear a brood of young. The nest was constructed of small twigs, dry weeds, slips of vine bark, and lined with stalks of fine grass. Four eggs of brownish olive were laid, and they usually raised two broods in a season.
In confinement they fade in color, but if well cared for, will live to a considerable age. They are generally known by the names: Red Bird, Virginia Red Bird, Virginia Nightingale, and Crested Red Bird. It is said that the female often sings nearly as well as the male.
THE REDBIRDS.
Two Redbirds came in early May,
Flashing like rubies on the way;
Their joyous notes awoke the day,
And made all nature glad and gay.
Thrice welcome! crested visitants;
Thou doest well to seek our haunts;
The bounteous vine, by thee possessed,
From prying eyes shall keep thy nest.
Sing to us in the early dawn;
’Tis then thy scarlet throats have drawn
Refreshing draughts from drops of dew,
The enchanting concert to renew.
No plaintive notes, we ween, are thine;
They gurgle like a royal wine;
They cheer, rejoice, they quite outshine
Thy neighbor’s voice, tho’ it’s divine.
Free as the circumambient air
Do thou remain, a perfect pair,
To come once more when Proserpine
Shall swell the buds of tree and vine.
—C. C. M.
 cardinal.
cardinal.
THE RED BIRD.
Is it because he wears a red hat,
That we call him the Cardinal Bird?
Or is it because his voice is so rich
That scarcely a finer is heard?
’Tis neither, but this—I’ve guessed it, I’m sure—
His dress is a primary color of Nature.
It blends with the Oriole’s golden display,
And the garment of Blue Bird completes the array.
—C. C. M.
ATTEND THE BEST.
CHICAGO BUSINESS COLLEGE
Wabash Ave. & Randolph St.

Elegant new building. Finer apartments than any other Commercial School in the United States. Thorough courses in BUSINESS, SHORTHAND and ENGLISH. Day and Evening Sessions. Write for catalogue mailed FREE.
Address GONDRING & VIRDEN, Principals.
Please mention “BIRDS” when you write to Advertisers.


What POINTS do You Want in a COPYING Machine?

fast—durable—simple.
SAVES TIME, MATERIAL, MONEY.
SAVES ITS COST EVERY YEAR BY ECONOMY IN COPYING PAPER.
EVERY BUSINESS AND PROFESSIONAL MAN NEEDS IT.
Will allow for your old screw press. SEND FOR TRADE PROPOSITION. Address
ANDERSON AUTOMATIC COPYING MACHINE CO.
910 Monadnock Block, CHICAGO.
Please mention “BIRDS” when you write to Advertisers.

Please mention “BIRDS” when you write to Advertisers.
TESTIMONIALS.
Frankfort. Ky., February 3, 1897.
W. J. Black, Vice-President,
Chicago, Ill.
Dear Sir: I have a copy of your magazine entitled “Birds,” and beg to say that I consider it one of the finest things on the subject that I have ever seen, and shall be pleased to recommend it to county and city superintendents of the state.
Very respectfully,
W. J. Davidson,
State Superintendent Public Instruction.
San Francisco, Cal., January 27, 1897.
W. J. Black, Esq.,
Chicago, Ill.
Dear Sir: I am very much obliged for the copy of “Birds” that has just come to hand. It should be in the hands of every primary and grammar teacher. I send herewith copy of “List of San Francisco Teachers.”
Very respectfully,
M. Babcock.
Lincoln, Neb., February 9, 1897.
W. J. Black,
Chicago, Ill.
Dear Sir: The first number of your magazine, “Birds,” is upon my desk. I am highly pleased with it. It will prove a very serviceable publication—one that strikes out along the right lines. For the purpose intended, it has, in my opinion, no equal. It is clear, concise, and admirably illustrated.
Very respectfully,
W. R. Jackson,
State Superintendent Public Instruction.
North Lima, Ohio, February 1, 1897.
Mr. W. E. Watt,
Dear Sir: Sample copy of “Birds” received. All of the family delighted with it. We wish it unbounded success. It will be an excellent supplement to “In Birdland” in the Ohio Teachers’ Reading Circle, and I venture Ohio will be to the front with a good subscription list. I enclose list of teachers.
Very truly,
C. M. L. Altdoerffer,
Township Superintendent.
Milwaukee, January 30, 1897.
Nature Study Publishing Company,
227 Dearborn Street, Chicago.
Gentlemen: I acknowledge with pleasure the receipt of your publication, “Birds,” with accompanying circulars. I consider it the best on the subject in existence. I have submitted the circulars and publication to my teachers, who have nothing to say but praise in behalf of the monthly.
Julius Torney,
Principal 2nd Dist. Primary School, Milwaukee, Wis.
